About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 20 results for "Carol El-Hayek" clear search
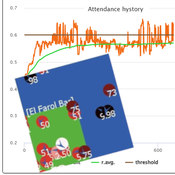
Peer reviewed Flibs’NFarol: Self-Organized Efficiency and Fairness Emergence in an Evolutive Game
Cosimo Leuci | Published Thursday, October 12, 2023According to the philosopher of science K. Popper “All life is problem solving”. Genetic algorithms aim to leverage Darwinian selection, a fundamental mechanism of biological evolution, so as to tackle various engineering challenges.
Flibs’NFarol is an Agent Based Model that embodies a genetic algorithm applied to the inherently ill-defined “El Farol Bar” problem. Within this context, a group of agents operates under bounded rationality conditions, giving rise to processes of self-organization involving, in the first place, efficiency in the exploitation of available resources. Over time, the attention of scholars has shifted to equity in resource distribution, as well. Nowadays, the problem is recognized as paradigmatic within studies of complex evolutionary systems.
Flibs’NFarol provides a platform to explore and evaluate factors influencing self-organized efficiency and fairness. The model represents agents as finite automata, known as “flibs,” and offers flexibility in modifying the number of internal flibs states, which directly affects their behaviour patterns and, ultimately, the diversity within populations and the complexity of the system.
Vacunación-Covid Ecuador
Adrian Lara | Published Tuesday, March 22, 2022El modelo a continuación, fue desarrollado para el DATA CHALLENGE 2022. Es un análisis de la información descargada del Portal de datos abiertos de Ecuador. Dentro del modelo podemos realizar una breve exploración de la información así como una simulación respecto al proceso de vacunación en Ecuador.
Eliminating hepatitis C virus as a public health threat among HIV-positive men who have sex with men
Nick Scott Mark Stoove David P Wilson Olivia Keiser Carol El-Hayek Joseph Doyle Margaret Hellard | Published Wednesday, October 12, 2016 | Last modified Sunday, December 16, 2018We compare three model estimates for the time and treatment requirements to eliminate HCV among HIV-positive MSM in Victoria, Australia: a compartmental model; an ABM parametrized by surveillance data; and an ABM with a more heterogeneous population.
A Pastoral Stoking Strategy Model with Fodder Import and Loan Scenarios
Yanbo Li | Published Tuesday, December 24, 2019This model was built to estimate the impacts of exogenous fodder input and credit loans services on livelihood, rangeland health and profits of pastoral production in a small holder pastoral household in the arid steppe rangeland of Inner Mongolia, China. The model simulated the long-term dynamic of herd size and structure, the forage demand and supply, the cash flow, and the situation of loan debt under three different stocking strategies: (1) No external fodder input, (2) fodders were only imported when natural disaster occurred, and (3) frequent import of external fodder, with different amount of available credit loans. Monte-Carlo method was used to address the influence of climate variability.
Structural Violence and Neurobiological Adaptation: Modeling the Trajectory of Youth Outside of Care
masterpiece33330-prog | Published Thursday, November 27, 2025This study presents a System Dynamics (SD) model that explores the “trajectories of homelessness” among youth outside of the formal care system. Unlike traditional approaches that view runaway behavior as a discrete choice, this model reinterprets it as a neurobiological adaptation to chronic resource deprivation and systemic neglect.
The model incorporates key mechanisms such as ‘Allostatic Load’ accumulation, ‘PFC-Amygdala Switching’, and the ‘Iatrogenic Effects’ of shelter policies. It utilizes Monte Carlo simulations to demonstrate how structural factors create a “probabilistic vulnerability,” trapping youth in cycles of survival crime and isolation regardless of individual resilience.
The uploaded code includes a Python implementation of the model to ensure reproducibility of the stochastic analysis presented in the paper.
Emergency Warning Dissemination in a Multiplex Social Network
Charles Koll | Published Tuesday, January 31, 2023This is an interdisciplinary agent-based model with Monte Carlo simulations to assess the relative effects of broadcast and contagion processes in a multiplex social network. This multiplex approach models multiple channels of informal communication - phone, word-of-mouth, and social media - that vary in their attribute values. Each agent is an individual in a threatened community who, once warned, has a probability of warning others in their social network using one of these channels. The probability of an individual warning others is based on their warning source and the time remaining until disaster impact, among other variables. Default parameter values were chosen from empirical studies of disaster warnings along with the spatial aspects of Coos Bay, OR, USA and Seaside, OR, USA communities.
This model was design to test parameters that affects the number of people shot during mass shooting. This basic formulation places a gunman in a crowd and allows the users to manipulate parameters of the gunman.
On July 20th, James Holmes committed a mass shooting in a midnight showing of The Dark Knight Rises. The Aurora Colorado shooting was used as a test case to validate this framework for modeling mass shootings.
The Travel-tour case study
Christophe Sibertin-Blanc Françoise Adreit Joseph El Gemayel | Published Sunday, May 19, 2013 | Last modified Friday, June 14, 2013This model describes and analyses the Travel-Tour Case study.
The role of argument strength and informational biases in polarization and bipolarization effects
Davide Chiarella Carlo Proietti | Published Thursday, March 30, 2023The model explores the informational causes of polarization and bi-polarization of opinions in groups. To this end it expands the model of the Argument Communication Theory of Bi-polarization. The latter is an argument-based multi-agent model of opinion dynamics inspired by Persuasive Argument Theory. The original model can account for polarization as an outcome of pure informational influence, and reproduces bi-polarization effects by postulating an additional mechanism of homophilous selection of communication partners. The expanded model adds two dimensions: argument strength and more sophisticated protocols of informational influence (argument communication and opinion update).
Displaying 10 of 20 results for "Carol El-Hayek" clear search