About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1188 results for "Ian M Hamilton" clear search
Exploring the Effects of Link Recommendations on Social Networks
Andrew Crooks Ciara Sibley | Published Thursday, March 19, 2020The purpose of this model is explore how “friend-of-friend” link recommendations, which are commonly used on social networking sites, impact online social network structure. Specifically, this model generates online social networks, by connecting individuals based upon varying proportions of a) connections from the real world and b) link recommendations. Links formed by recommendation mimic mutual connection, or friend-of-friend algorithms. Generated networks can then be analyzed, by the included scripts, to assess the influence that different proportions of link recommendations have on network properties, specifically: clustering, modularity, path length, eccentricity, diameter, and degree distribution.
NOMAD: Near–Off Mobility under Aspiration Dynamics
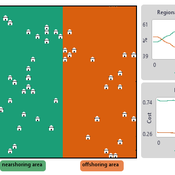
Alejandro Platas López | Published Wednesday, December 17, 2025NOMAD is an agent-based model of firm location choice between two aggregate regions (“near” and “off”) under logistics uncertainty. Firms occupy sites characterised by attractiveness and logistics risk, earn a risk-adjusted payoff that depends on regional costs (wages plus congestion) and an individual risk-tolerance trait, and update location choices using aspiration-based satisficing rules with switching frictions. Logistics risk evolves endogenously on occupied sites through a region-specific absorption mechanism (good/bad events that reduce/increase risk), while congestion feeds back into regional costs via regional shares and local crowding. Runs stop endogenously once the near-region share becomes quasi-stable after burn-in, and the model records time series and quasi-stable outcomes such as near/off composition, switching intensity, costs, average risk, and average risk tolerance.
IUCM - The Integrated Urban Complexity Model
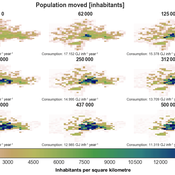
Roger Cremades Philipp S. Sommer | Published Thursday, December 14, 2023We present the Integrated Urban Complexity model (IUCm 1.0) that computes “climate-smart urban forms”, which are able to cut emissions related to energy consumption from urban mobility in half. Furthermore, we show the complex features that go beyond the normal debates about urban sprawl vs. compactness. Our results show how to reinforce fractal hierarchies and population density clusters within climate risk constraints to significantly decrease the energy consumption of urban mobility. The new model that we present aims to produce new advice about how cities can combat climate change. From a technical angle, this model is a geographical automaton, conceptually interfacing between cellular automata and spatial explicit optimisation to achieve normative sustainability goals related to low energy. See a complete user guide at https://iucm.readthedocs.io/en/latest/ .
ThomondSim
Vinicius Marino Carvalho | Published Monday, April 25, 2022 | Last modified Friday, May 12, 2023ThomondSim is a simulation of the political and economic landscape of the medieval kingdom of Thomond, southwestern Ireland, between 1276 and 1318.
Its goal is to analyze how deteriorating environmental and economic conditions caused by the Little Ice Age (LIA), the Great European Famine of 1315-1322, and wars between England and Scotland affected the outcomes of a local war involving Gaelic and English aristocratic lineages.
This ABM attempts to model both the effects of devastation on the human environment and the modus operandi of late-medieval war and diplomacy.
The model is the digital counterpart of the science discovery board game The Triumphs of Turlough. Its procedures closely correspond to the game’s mechanics, to the point that ToT can be considered an interactive, analog version of this ABM.
Evolutionary Model of Subculture Choice
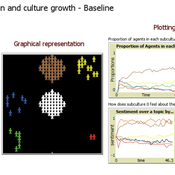
Diogo Alves | Published Monday, December 19, 2022This is an original model of (sub)culture diffusion.
It features a set of agents (dubbed “partygoers”) organized initially in clusters, having properties such as age and a chromosome of opinions about 6 different topics. The partygoers interact with a set of cultures (also having a set of opinions subsuming those of its members), in the sense of refractory or unhappy members of each setting about to find a new culture and trading information encoded in the genetic string (originally encoded as -1, 0, and 1, resp. a negative, neutral, and positive opinion about each of the 6 traits/aspects, e.g. the use of recreational drugs). There are 5 subcultures that both influence (through the aforementioned genetic operations of mutation and recombination of chromosomes simulating exchange of opinions) and are influenced by its members (since a group is a weighted average of the opinions and actions of its constituents). The objective of this feedback loop is to investigate under which conditions certain subculture sizes emerge, but the model is open to many other kinds of explorations as well.
Peer reviewed BAMERS: Macroeconomic effect of extortion
Alejandro Platas López Alejandro Guerra-Hernández | Published Monday, March 23, 2020 | Last modified Sunday, July 26, 2020Inspired by the European project called GLODERS that thoroughly analyzed the dynamics of extortive systems, Bottom-up Adaptive Macroeconomics with Extortion (BAMERS) is a model to study the effect of extortion on macroeconomic aggregates through simulation. This methodology is adequate to cope with the scarce data associated to the hidden nature of extortion, which difficults analytical approaches. As a first approximation, a generic economy with healthy macroeconomics signals is modeled and validated, i.e., moderate inflation, as well as a reasonable unemployment rate are warranteed. Such economy is used to study the effect of extortion in such signals. It is worth mentioning that, as far as is known, there is no work that analyzes the effects of extortion on macroeconomic indicators from an agent-based perspective. Our results show that there is significant effects on some macroeconomics indicators, in particular, propensity to consume has a direct linear relationship with extortion, indicating that people become poorer, which impacts both the Gini Index and inflation. The GDP shows a marked contraction with the slightest presence of extortion in the economic system.
The purpose of the AdaptPumpa model is to analyze the robustness of the Pumpa irrigation system in Nepal to climate change.
WATER REUSE ADOPTION BY FARMERS (WRAF)
Farshid Shoushtarian | Published Tuesday, September 27, 2022Agriculture is the largest water-consuming sector worldwide, responsible for almost 70% of the world’s total freshwater consumption. Agricultural water reuse is one of the most sustainable and reliable methods to alleviate water shortages worldwide. However, the dynamics of agricultural water reuse adoption by farmers and its impacts on local water resources are still unknown to the scientific community, according to the literature. Therefore, the primary purpose of the WRAF model is to investigate the micro-level dynamics of agricultural water reuse adoption by farmers and its impacts on local water resources. The WRAF was developed using agent-based modeling as an exploratory tool for scenario analysis. The model was specifically designed for researchers and water resources decision-makers, especially those interested in natural resources management and water reuse.
WRAF simulates a virtual agricultural area in which several autonomous farms operate. It also simulates these farms’ water consumption dynamics. The developed model includes two types of agents: farmers and wastewater treatment plants. In general, farmer agents are the main water-consuming agents, and wastewater treatment plant agents are recycled water providers in the WRAF model. Dynamic simulation of agricultural water supply and demand in the area allows the user to observe the results of various irrigation water management scenarios, including recycled water. The models also enable the user to apply multiple climate change scenarios, including normal, moderate drought, severe drought, and wet weather conditions.
IDEAL
Arika Ligmann-Zielinska | Published Thursday, August 07, 2014IDEAL: Agent-Based Model of Residential Land Use Change where the choice of new residential development in based on the Ideal-point decision rule.
Critical Sustainability Transitions: Relaunching local agriculture after decline (Model code and description)
Pedro Lopez-Merino | Published Tuesday, April 30, 2024This model simulates the dynamics of agricultural land use change, specifically the transition between agricultural and non-agricultural land use in a spatial context. It explores the influence of various factors such as agricultural profitability, path dependency, and neighborhood effects on land use decisions.
The model operates on a grid of patches representing land parcels. Each patch can be in one of two states: exploited (green, representing agricultural land) or unexploited (brown, representing non-agricultural land). Agents (patches) transition between these states based on probabilistic rules. The main factors affecting these transitions are agricultural profitability, path dependency, and neighborhood effects.
-Agricultural Profitability: This factor is determined by the prob-agri function, which calculates the probability of a non-agricultural patch converting to agricultural based on income differences between agriculture and other sectors. -Path Dependency: Represented by the path-dependency parameter, it influences the likelihood of patches changing their state based on their current state. It’s a measure of inertia or resistance to change. -Neighborhood Effects: The neighborhood function calculates the number of exploited (agricultural) neighbors of a patch. This influences the decision of a patch to convert to agricultural land, representing the influence of surrounding land use on the decision-making process.
Displaying 10 of 1188 results for "Ian M Hamilton" clear search