About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1188 results for "Ian M Hamilton" clear search
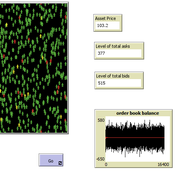
Peer reviewed A financial market with zero intelligence agents
edgarkp | Published Wednesday, March 27, 2024The model’s aim is to represent the price dynamics under very simple market conditions, given the values adopted by the user for the model parameters. We suppose the market of a financial asset contains agents on the hypothesis they have zero-intelligence. In each period, a certain amount of agents are randomly selected to participate to the market. Each of these agents decides, in a equiprobable way, between proposing to make a transaction (talk = 1) or not (talk = 0). Again in an equiprobable way, each participating agent decides to speak on the supply (ask) or the demand side (bid) of the market, and proposes a volume of assets, where this number is drawn randomly from a uniform distribution. The granularity depends on various factors, including market conventions, the type of assets or goods being traded, and regulatory requirements. In some markets, high granularity is essential to capture small price movements accurately, while in others, coarser granularity is sufficient due to the nature of the assets or goods being traded
Individual time preferences and adoption of destructive extraction methods
Marco Janssen Aneeque Javaid Hauke Reuter Achim Schlueter | Published Tuesday, December 06, 2016We model the relationship between natural resource user´s individual time preferences and their use of destructive extraction method in the context of small-scale fisheries.
Effective population size and cultural evolution
Luke Premo | Published Tuesday, May 17, 2016This model illustrates how the effective population size and the rate of change in mean skill level of a cultural trait are affected by the presence of natural selection and/or the cultural transmission mechanism by which it is passed.
Intra-Organizational Bandwagon
Davide Secchi | Published Sunday, October 18, 2015The model simulates the process of widespread diffusion of something due to popularity (i.e., bandwagon) within an organization.
SearchResource
Romulus-Catalin Damaceanu | Published Friday, May 04, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An algorithm implemented in NetLogo that can be used for searching resources.
Political Participation
Didier Ruedin | Published Saturday, April 12, 2014 | Last modified Sunday, September 28, 2025Implementation of Milbrath’s (1965) model of political participation. Individual participation is determined by stimuli from the political environment, interpersonal interaction, as well as individual characteristics.
Modeling Personal Carbon Trading with ABM
Roman Seidl | Published Friday, December 07, 2018 | Last modified Thursday, July 29, 2021A simulated approach for Personal Carbon Trading, for figuring out what effects it might have if it will be implemented in the real world. We use an artificial population with some empirical data from international literature and basic assumptions about heterogeneous energy demand. The model is not to be used as simulating the actual behavior of real populations, but a toy model to test the effects of differences in various factors such as number of agents, energy price, price of allowances, etc. It is important to adapt the model for specific countries as carbon footprint and energy demand determines the relative success of PCT.
Peer reviewed Applying Brantingham’s Neutral Model of Stone Raw Material Procurement to the Pinnacle Point Middle Stone Age Record, Western Cape, South Africa
Marco Janssen Simen Oestmo Haley Cawthra | Published Sunday, March 10, 2019This model is an application of Brantingham’s neutral model to a real landscape with real locations of potential sources. The sources are represented as their sizes during current conditions, and from marine geophysics surveys, and the agent starts at a random location in Mossel Bay Region (MBR) surrounding the Archaeological Pinnacle Point (PP) locality, Western Cape, South Africa. The agent moves at random on the landscape, picks up and discards raw materials based only upon space in toolkit and probability of discard. If the agent happens to encounter the PP locality while moving at random the agent may discard raw materials at it based on the discard probability.
Opinions on contested energy infrastructures
Annalisa Stefanelli | Published Thursday, June 23, 2016This ABM simulates opinions on a topic (originally contested infrastructures) through the interactions between paired agents and based on the sociopsychological assumptions of social judgment theory (SJT; Sherif & Hovland, 1961).
The Opportunistic Acquisition Model of Stone Tool Raw Material Procurement
Marco Janssen Simen Oestmo Haley Cawthra | Published Friday, April 21, 2017 | Last modified Sunday, March 10, 2019The Opportunistic Acquisition Model (OAM) posits that the archaeological lithic raw material frequencies are due to opportunistic encounters with sources while randomly walking in an environment.
Displaying 10 of 1188 results for "Ian M Hamilton" clear search