About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1188 results for "Ian M Hamilton" clear search
Network formation on a two-layer multiplex with shocks
Paul Smaldino | Published Monday, November 27, 2017A dynamic model of social network formation on single-layer and multiplex networks with structural incentives that vary over time.
FeedUS - A global food trade model
Jiaqi Ge | Published Thursday, February 25, 2021 | Last modified Friday, February 26, 2021The purpose of the model is to study the impact of global food trade on food and nutrition security in countries around the world. It will incorporate three main aspects of trade between countries, including a country’s wealth, geographic location, and its trade relationships with other countries (past and ongoing), and can be used to study food and nutrition security across countries in various scenarios, such as climate change, sustainable intensification, waste reduction and dietary change.
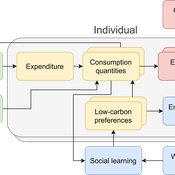
The cultural multiplier of climate policy
Daniel Torren-Peraire | Published Thursday, October 31, 2024For deep decarbonisation, the design of climate policy needs to account for consumption choices being influenced not only by pricing but also by social learning. This involves changes that pertain to the whole spectrum of consumption, possibly involving shifts in lifestyles. In this regard, it is crucial to consider not just short-term social learning processes but also slower, longer-term, cultural change. Against this background, we analyse the interaction between climate policy and cultural change, focusing on carbon taxation. We extend the notion of “social multiplier” of environmental policy derived in an earlier study to the context of multiple consumer needs while allowing for behavioural spillovers between these, giving rise to a “cultural multiplier”. We develop a model to assess how this cultural multiplier contributes to the effectiveness of carbon taxation. Our results show that the cultural multiplier stimulates greater low-carbon consumption compared to fixed preferences. The model results are of particular relevance for policy acceptance due to the cultural multiplier being most effective at low-carbon tax values, relative to a counter-case of short-term social interactions. Notably, at high carbon tax levels, the distinction between social and cultural multiplier effects diminishes, as the strong price signal drives even resistant individuals toward low-carbon consumption. By varying socio-economic conditions, such as substitutability between low- and high-carbon goods, social network structure, proximity of like-minded individuals and the richness of consumption lifestyles, the model provides insight into how cultural change can be leveraged to induce maximum effectiveness of climate policy.
MERCURY extension: population
Tom Brughmans | Published Thursday, May 23, 2019This model is an extended version of the original MERCURY model (https://www.comses.net/codebases/4347/releases/1.1.0/ ) . It allows for experiments to be performed in which empirically informed population sizes of sites are included, that allow for the scaling of the number of tableware traders with the population of settlements, and for hypothesised production centres of four tablewares to be used in experiments.
Experiments performed with this population extension and substantive interpretations derived from them are published in:
Hanson, J.W. & T. Brughmans. In press. Settlement scale and economic networks in the Roman Empire, in T. Brughmans & A.I. Wilson (ed.) Simulating Roman Economies. Theories, Methods and Computational Models. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
…
Zombies
Jennifer Badham | Published Tuesday, June 08, 2021Zombies move toward humans and humans move (faster) away from zombies. They fight if they meet, and humans who lose become zombies.
A Comparative Study on Apprenticeship Systems Using Agent-Based Simulation
Amir Hosein Afshar Sedigh | Published Thursday, October 21, 2021The model is suitable to investigate the effects of different characteristics of apprenticeship programmes both in historical and contemporary societies. The model is built considering five societies, using an agent-based simulation model, we identified six main characteristics which impact the success of an apprenticeship programme in a society, which we measured by considering three parameters, namely the number of skilled agents produced by the apprenticeships, programme completion, and the contribution of programmes in the Gross Domestic Income (GDI) of the society. We investigate different definitions for success of an apprenticeship and some hypothetical societies to test some common beliefs about apprenticeships performance. The model also shows the number of unemployed agents given their work-based skills, wages, and the number of small and large companies who participate in training agents. The model enables exploring the impact of parameters, such as initial wages and the number of training years, along with the stated policies on the system.
Urban-Dynamics-2017
Hideyuki Nagai Setsuya Kurahashi | Published Thursday, October 06, 2016 | Last modified Thursday, October 06, 2016This model is designed for the paper of “Bustle Changes the City - Facility for Stopping off and Modeling Urban Dynamics -“. And all experimental results in the paper were implemented in this model.
The Cardial Spread Model
Sean Bergin | Published Friday, September 29, 2017 | Last modified Monday, February 04, 2019The purpose of this model is to provide a platform to test and compare four conceptual models have been proposed to explain the spread of the Impresso-Cardial Neolithic in the west Mediterranean.
Forest Logging and Ecosystem Degradation
Carla Guerrero | Published Sunday, February 15, 2026This model simulates a forest ecosystem affected by human logging. We explore different kind of approaches and their possible consequences for the ecosystem. Loggers can either be responsible or irresponsible, they will either take care to cut trees or not. In turn their actions will have consequences on the quality of the soil, the atmosphere as well as their profit made from logging. In this model we see that even careful management cannot prevent the degradation of the forest ecosystem.
Displaying 10 of 1188 results for "Ian M Hamilton" clear search