About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1113 results for "Bin-Tzong Chi" clear search
RiskNetABM
Birgit Müller Jürgen Groeneveld Karin Frank Meike Will Friederike Lenel | Published Monday, July 20, 2020 | Last modified Monday, May 03, 2021The fight against poverty is an urgent global challenge. Microinsurance is promoted as a valuable instrument for buffering income losses due to health or climate-related risks of low-income households in developing countries. However, apart from direct positive effects they can have unintended side effects when insured households lower their contribution to traditional arrangements where risk is shared through private monetary support.
RiskNetABM is an agent-based model that captures dynamics between income losses, insurance payments and informal risk-sharing. The model explicitly includes decisions about informal transfers. It can be used to assess the impact of insurance products and informal risk-sharing arrangements on the resilience of smallholders. Specifically, it allows to analyze whether and how economic needs (i.e. level of living costs) and characteristics of extreme events (i.e. frequency, intensity and type of shock) influence the ability of insurance and informal risk-sharing to buffer income shocks. Two types of behavior with regard to private monetary transfers are explicitly distinguished: (1) all households provide transfers whenever they can afford it and (2) insured households do not show solidarity with their uninsured peers.
The model is stylized and is not used to analyze a particular case study, but represents conditions from several regions with different risk contexts where informal risk-sharing networks between smallholder farmers are prevalent.
…
An Agent-Based Model of Collective Action
Hai-Hua Hu | Published Tuesday, August 20, 2013We provide an agent-based model of collective action, informed by Granovetter (1978) and its replication model by Siegel (2009). We use the model to examine the role of ICTs in collective action under different cultural and political contexts.
The Urban Drought Nexus Tool
Roger Cremades Muhamad Khairulbahri | Published Thursday, December 14, 2023The “Urban Drought Nexus Tool” is a system dynamics model, aiming to facilitate the co-development of climate services for cities under increasing droughts. The tool integrates multiple types of information and still can be applied to other case studies with minimal adjustments on the parameters of land use, water consumption and energy use in the water sector. The tool needs hydrological projections under climate scenarios to evaluate climatic futures, and requires the co-creation of socio-economic future scenarios with local stakeholders. Thus it is possible to provide specific information about droughts taking into account future water availability and future water consumption. Ultimately, such complex system as formed by the water-energy-land nexus can be reduced to single variables of interest, e.g. the number of events with no water available in the future and their length, so that the complexities are reduced and the results can be conveyed to society in an understandable way, including the communication of uncertainties. The tool and an explanatory guide in pdf format are included. Planned further developments include calibrating the system dynamics model with the social dynamics behind each flow with agent-based models.
Peer reviewed FISHCODE - FIsheries Simulation with Human COmplex DEcision-making
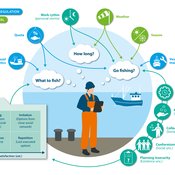
Birgit Müller Gunnar Dressler Jonas Letschert Christian Möllmann Vanessa Stelzenmüller | Published Monday, August 05, 2024FIsheries Simulation with Human COmplex DEcision-making (FISHCODE) is an agent-based model to depict and analyze current and future spatio-temporal dynamics of three German fishing fleets in the southern North Sea. Every agent (fishing vessel) makes daily decisions about if, what, and how long to fish. Weather, fuel and fish prices, as well as the actions of their colleagues influence agents’ decisions. To combine behavioral theories and enable agents to make dynamic decision, we implemented the Consumat approach, a framework in which agents’ decisions vary in complexity and social engagement depending on their satisfaction and uncertainty. Every agent has three satisfactions and two uncertainties representing different behavioral aspects, i.e. habitual behavior, profit maximization, competition, conformism, and planning insecurity. Availability of extensive information on fishing trips allowed us to parameterize many model parameters directly from data, while others were calibrated using pattern oriented modelling. Model validation showed that spatial and temporal aggregated ABM outputs were in realistic ranges when compared to observed data. Our ABM hence represents a tool to assess the impact of the ever growing challenges to North Sea fisheries and provides insight into fisher behavior beyond profit maximization.
Peer reviewed Environmental stochasticity, resource heterogeneity, and the evolution of cooperation
Michaela Starkey Colin Lynch Terry Hunt Carl Lipo | Published Friday, March 14, 2025 | Last modified Wednesday, July 30, 2025The emergence of cooperation in human societies is often linked to environmental constraints, yet the specific conditions that promote cooperative behavior remain an open question. This study examines how resource unpredictability and spatial dispersion influence the evolution of cooperation using an agent-based model (ABM). Our simulations test the effects of rainfall variability and resource distribution on the survival of cooperative and non-cooperative strategies. The results show that cooperation is most likely to emerge when resources are patchy, widely spaced, and rainfall is unpredictable. In these environments, non-cooperators rapidly deplete local resources and face high mortality when forced to migrate between distant patches. In contrast, cooperators—who store and share resources—can better endure extended droughts and irregular resource availability. While rainfall stochasticity alone does not directly select for cooperation, its interaction with resource patchiness and spatial constraints creates conditions where cooperative strategies provide a survival advantage. These findings offer broader insights into how environmental uncertainty shapes social organization in resource-limited settings. By integrating ecological constraints into computational modeling, this study contributes to a deeper understanding of the conditions that drive cooperation across diverse human and animal systems.
Growing Unpopular Norms. A Network-Situated ABM of Norm Choice.
C Merdes | Published Tuesday, November 22, 2016 | Last modified Saturday, March 17, 2018The model’s purpose is to provide a potential explanation for the emergence, sustenance and decline of unpopular norms based on pluralistic ignorance on a social network.
Crowdworking Model
Georg Jäger | Published Wednesday, September 25, 2019The purpose of this agent-based model is to compare different variants of crowdworking in a general way, so that the obtained results are independent of specific details of the crowdworking platform. It features many adjustable parameters that can be used to calibrate the model to empirical data, but also when not calibrated it yields essential results about crowdworking in general.
Agents compete for contracts on a virtual crowdworking platform. Each agent is defined by various properties like qualification and income expectation. Agents that are unable to turn a profit have a chance to quit the crowdworking platform and new crowdworkers can replace them. Thus the model has features of an evolutionary process, filtering out the ill suited agents, and generating a realistic distribution of agents from an initially random one. To simulate a stable system, the amount of contracts issued per day can be set constant, as well as the number of crowdworkers. If one is interested in a dynamically changing platform, the simulation can also be initialized in a way that increases or decreases the number of crowdworkers or number of contracts over time. Thus, a large variety of scenarios can be investigated.
FlipFlop1-ProMEERB: A coupled social-ecological model with a promotional mechanism for emergence of environmentally responsible behavior
Liliana Perez Saeed Harati Roberto Molowny-Horas | Published Friday, December 17, 2021At the heart of a study of Social-Ecological Systems, this model is built by coupling together two independently developed models of social and ecological phenomena. The social component of the model is an abstract model of interactions of a governing agent and several user agents, where the governing agent aims to promote a particular behavior among the user agents. The ecological model is a spatial model of spread of the Mountain Pine Beetle in the forests of British Columbia, Canada. The coupled model allowed us to simulate various hypothetical management scenarios in a context of forest insect infestations. The social and ecological components of this model are developed in two different environments. In order to establish the connection between those components, this model is equipped with a ‘FlipFlop’ - a structure of storage directories and communication protocols which allows each of the models to process its inputs, send an output message to the other, and/or wait for an input message from the other, when necessary. To see the publications associated with the social and ecological components of this coupled model please see the References section.
WealthDistribRes
Romulus-Catalin Damaceanu | Published Friday, May 04, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model WealthDistribRes can be used to study the distribution of wealth in function of using a combination of resources classified in two renewable and nonrenewable.
Agent-based simulation of small group decision-making under no communication
Christopher Poile | Published Thursday, May 26, 2016A computational model of a classic small group study by Alex Bavelas. This computational model was designed to explore the difficulty in translating a seemingly simple real-world experiment into a computational model.
Displaying 10 of 1113 results for "Bin-Tzong Chi" clear search