About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 190 results for "Kamil C. Klosek" clear search
Food Safety Inspection Model - Random Strategy
Sara Mcphee-Knowles | Published Wednesday, March 05, 2014 | Last modified Monday, April 08, 2019The Inspection Model represents a basic food safety system where inspectors, consumers and stores interact. The purpose of the model is to provide insight into an optimal level of inspectors in a food system by comparing three search strategies.
Food Safety Inspection Model - Stores Signal with Errors
Sara Mcphee-Knowles | Published Wednesday, March 05, 2014 | Last modified Monday, April 08, 2019The Inspection Model represents a basic food safety system where inspectors, consumers and stores interact. The purpose of the model is to provide insight into an optimal level of inspectors in a food system by comparing three search strategies.
Food Safety Inspection Model - Stores Signal
Sara Mcphee-Knowles | Published Wednesday, March 05, 2014 | Last modified Monday, August 26, 2019The Inspection Model represents a basic food safety system where inspectors, consumers and stores interact. The purpose of the model is to provide insight into an optimal level of inspectors in a food system by comparing three search strategies.
Peer reviewed PolicySpace2: modeling markets and endogenous public policies
Bernardo Furtado | Published Thursday, February 25, 2021 | Last modified Friday, January 14, 2022Policymakers decide on alternative policies facing restricted budgets and uncertain future. Designing public policies is further difficult due to the need to decide on priorities and handle effects across policies. Housing policies, specifically, involve heterogeneous characteristics of properties themselves and the intricacy of housing markets and the spatial context of cities. We propose PolicySpace2 (PS2) as an adapted and extended version of the open source PolicySpace agent-based model. PS2 is a computer simulation that relies on empirically detailed spatial data to model real estate, along with labor, credit, and goods and services markets. Interaction among workers, firms, a bank, households and municipalities follow the literature benchmarks to integrate economic, spatial and transport scholarship. PS2 is applied to a comparison among three competing public policies aimed at reducing inequality and alleviating poverty: (a) house acquisition by the government and distribution to lower income households, (b) rental vouchers, and (c) monetary aid. Within the model context, the monetary aid, that is, smaller amounts of help for a larger number of households, makes the economy perform better in terms of production, consumption, reduction of inequality, and maintenance of financial duties. PS2 as such is also a framework that may be further adapted to a number of related research questions.
Enhancing recycling of construction materials; an agent based model with empirically based decision parameters
Igor Nikolic Claudia Binder Christof Knoeri Hans-Joerg Althaus | Published Sunday, October 21, 2012 | Last modified Monday, June 09, 2014This model allows for analyzing the most efficient levers for enhancing the use of recycled construction materials, and the role of empirically based decision parameters.
The Agent-Based Model of the Closed Market( similar to Stock Market) with One Commodity and with careful and risky mechanisms
Mark Voronovitsky | Published Sunday, March 15, 2015 | Last modified Sunday, March 22, 2015The model of market of one commodity , in which there are in each moment of time the same quantity and the same quantity of money was formulated and researched in this text. We also study this system as a game of automata.
The MOBILITY model analyzes how agents’ mobility affects the performance of social-ecological systems in different landscape configurations.
Influence with over-confident agents
Juliette Rouchier Emily Tanimura | Published Wednesday, October 21, 2015Agents can influence each other if they are close enough in knowledge. The probability to convince with good knowledge and number of agents have an impact on the dissemination of knowledge.
PFS - Preference Falsification Simulation (PreFalSim)
Francisco J Miguel Francisco J. León-Medina Jordi Tena-Sanchez | Published Monday, July 01, 2019A model for simulating the evolution of individual’s preferences, incliding adaptive agents “falsifying” -as public opinions- their own preferences. It was builded to describe, explore, experiment and understand how simple heuristics can modulate global opinion dynamics. So far two mechanisms are implemented: a version of Festiguer’s reduction of cognitive disonance, and a version of Goffman’s impression management. In certain social contexts -minority, social rank presure- some models agents can “fake” its public opinion while keeping internally the oposite preference, but after a number of rounds following this falsifying behaviour pattern, a coherence principle can change the real or internal preferences close to that expressed in public.
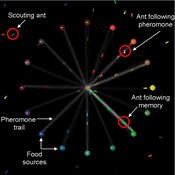
Composite Collective Decision Making - ant colony foraging model
Tomer Czaczkes Benjamin I Czaczkes | Published Thursday, December 17, 2015The model explores how two types of information - social (in the form of pheromone trails) and private (in the form of route memories) affect ant colony level foraging in a variable enviroment.
Displaying 10 of 190 results for "Kamil C. Klosek" clear search