About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 359 results for "John C Moore" clear search
Concession Forestry Modeling
Andrew Bell Daniel G Brown Rick L Riolo Jacqueline M Doremus Thomas P Lyon John Vandermeer Arun Agrawal | Published Thursday, January 23, 2014A logging agent builds roads based on the location of high-value hotspots, and cuts trees based on road access. A forest monitor sanctions the logger on observed infractions, reshaping the pattern of road development.
Impact of Seasonal Forecast Use on Agricultural Income in a System with Varying Crop Costs and Returns
Thushara Gunda Josh T Bazuin John Nay Kam L Yeung | Published Tuesday, February 07, 2017The objective of the model is to evaluate the impact of seasonal forecasts on a farmer’s net agricultural income when their crop choices have different and variable costs and returns.
Formation of Lithic Assemblages v. 1
C Michael Barton Julien Riel-Salvatore | Published Thursday, September 04, 2014This model represents technological and ecological behaviors of mobile hunter-gatherers, in a variable environment, as they produce, use, and discard chipped stone artifacts. The results can be analyzed and compared with archaeological sites.
The purpose of the AdaptPumpa model is to analyze the robustness of the Pumpa irrigation system in Nepal to climate change.
Resource distribution effects on optimal foraging theory
Marco Janssen Kim Hill | Published Friday, January 27, 2017The original Ache model is used to explore different distributions of resources on the landscape and it’s effect on optimal strategies of the camps on hunting and camp movement.
Peer reviewed Behavioral Dynamics of Epidemic Trajectories and Vaccination Strategies: An Agent-Based Model
Ziyuan Zhang | Published Tuesday, December 10, 2024This agent-based model explores the dynamics between human behavior and vaccination strategies during COVID-19 pandemics. It examines how individual risk perceptions influence behaviors and subsequently affect epidemic outcomes in a simulated metropolitan area resembling New York City from December 2020 to May 2021.
Agents modify their daily activities—deciding whether to travel to densely populated urban centers or stay in less crowded neighborhoods—based on their risk perception. This perception is influenced by factors such as risk perception threshold, risk tolerance personality, mortality rate, disease prevalence, and the average number of contacts per agent in crowded settings. Agent characteristics are carefully calibrated to reflect New York City demographics, including age distribution and variations in infection probability and mortality rates across these groups. The agents can experience six distinct health statuses: susceptible, exposed, infectious, recovered from infection, dead, and vaccinated (SEIRDV). The simulation focuses on the Iota and Alpha variants, the dominant strains in New York City during the period.
We simulate six scenarios divided into three main categories:
1. A baseline model without vaccinations where agents exhibit no risk perception and are indifferent to virus transmission and disease prevalence.
…
06b EiLab_Model_I_V5.00 NL
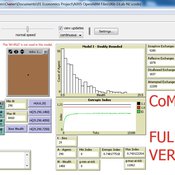
Garvin Boyle | Published Saturday, October 05, 2019EiLab - Model I - is a capital exchange model. That is a type of economic model used to study the dynamics of modern money which, strangely, is very similar to the dynamics of energetic systems. It is a variation on the BDY models first described in the paper by Dragulescu and Yakovenko, published in 2000, entitled “Statistical Mechanics of Money”. This model demonstrates the ability of capital exchange models to produce a distribution of wealth that does not have a preponderance of poor agents and a small number of exceedingly wealthy agents.
This is a re-implementation of a model first built in the C++ application called Entropic Index Laboratory, or EiLab. The first eight models in that application were labeled A through H, and are the BDY models. The BDY models all have a single constraint - a limit on how poor agents can be. That is to say that the wealth distribution is bounded on the left. This ninth model is a variation on the BDY models that has an added constraint that limits how wealthy an agent can be? It is bounded on both the left and right.
EiLab demonstrates the inevitable role of entropy in such capital exchange models, and can be used to examine the connections between changing entropy and changes in wealth distributions at a very minute level.
…
Expectation-Based Bayesian Belief Revision
C Merdes Momme Von Sydow Ulrike Hahn | Published Monday, June 19, 2017 | Last modified Monday, August 06, 2018This model implements a Bayesian belief revision model that contrasts an ideal agent in possesion of true likelihoods, an agent using a fixed estimate of trusting its source of information, and an agent updating its trust estimate.
Hybrid Agent-Based and Equation Based Model for Infectious Disease Spread
Elizabeth Hunter Brian Mac Namee John Kelleher | Published Sunday, April 19, 2020Our model is hybrid agent-based and equation based model for human air-borne infectious diseases measles. It follows an SEIR (susceptible, exposed,infected, and recovered) type compartmental model with the agents moving be-tween the four state relating to infectiousness. However, the disease model canswitch back and forth between agent-based and equation based depending onthe number of infected agents. Our society model is specific using the datato create a realistic synthetic population for a county in Ireland. The modelincludes transportation with agents moving between their current location anddesired destination using predetermined destinations or destinations selectedusing a gravity model.
A model to explore the link between the gender-gap reversal in education and relative divorce risks
Jan Van Bavel Christine Schnor André Grow | Published Thursday, June 30, 2016 | Last modified Wednesday, September 13, 2017This model explores a social mechanism that links the reversal of the gender gap in education with changing patterns in relative divorce risks in 12 European countries.
Displaying 10 of 359 results for "John C Moore" clear search