About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1111 results for "Clint A Penick" clear search
The Travel-tour case study
Christophe Sibertin-Blanc Françoise Adreit Joseph El Gemayel | Published Sunday, May 19, 2013 | Last modified Friday, June 14, 2013This model describes and analyses the Travel-Tour Case study.
The MOBILITY model analyzes how agents’ mobility affects the performance of social-ecological systems in different landscape configurations.
FlowLogo: An agent-based platform for simulating complex human-aquifer interactions in managed groundwater systems
Juan Castilla-Rho | Published Sunday, August 30, 2015FlowLogo integrates agent-based and groundwater flow simulation. It aims to simplify the process of developing participatory ABMs in the groundwater space and begin the exploration of novel, bottom-up solutions to conflicts in shared aquifers.
Peer Review Game
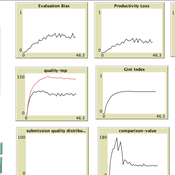
Giangiacomo Bravo Flaminio Squazzoni Francisco Grimaldo Federico Bianchi | Published Monday, April 30, 2018NetLogo software for the Peer Review Game model. It represents a population of scientists endowed with a proportion of a fixed pool of resources. At each step scientists decide how to allocate their resources between submitting manuscripts and reviewing others’ submissions. Quality of submissions and reviews depend on the amount of allocated resources and biased perception of submissions’ quality. Scientists can behave according to different allocation strategies by simply reacting to the outcome of their previous submission process or comparing their outcome with published papers’ quality. Overall bias of selected submissions and quality of published papers are computed at each step.
This program simulates a group of hunter-gatherer (households) moving randomly over an artificial landscapoe pulated with resources randomly distributed (a Gaussian distribution). To survive, agents hunt and gather using their own labor resources and available technology. When labor and technology is not enough to compensate the resource difficulty of access, they need to cooperate. The purpose of the model is to analyze the consequences of cooperation on cultural diversity: the more the agents cooperate, the more their culture (a 10 componenet vector) is updated to imitate the culture of cooperative agents. The less the agent cooperates, the more different its culture becomes.
The PRIF Model
Davide Secchi | Published Friday, November 08, 2019This model takes into consideration Peer Reviewing under the influence of Impact Factor (PRIF) and it has the purpose to explore whether the infamous metric affects assessment of papers under review. The idea is to consider to types of reviewers, those who are agnostic towards IF (IU1) and those that believe that it is a measure of journal (and article) quality (IU2). This perception is somehow reflected in the evaluation, because the perceived scientific value of a paper becomes a function of the journal in which an article has been submitted. Various mechanisms to update reviewer preferences are also implemented.
Citizenship competences and conflict resolution styles
Cecilia Avila Manuel Balaguera Valentina Tabares | Published Monday, February 03, 2020This model represents an agent-based social simulation for citizenship competences. In this model people interact by solving different conflicts and a conflict is solved or not considering two possible escenarios: when individual citizenship competences are considered and when not. In both cases the TKI conflict resolution styles are considered. Each conflict has associated a competence and the information about the conflicts and their competences is retrieved from an ontology which was developed in Protégé. To do so, a NetLogo extension was developed using the Java programming language and the JENA API (to make queries over the ontology).
Peer reviewed Agent-Based Ramsey growth model with Brown and Green capital (ABRam-BG)
Sarah Wolf Aida Sarai Figueroa Alvarez | Published Monday, December 09, 2024The purpose of the ABRam-BG model is to study belief dynamics as a potential driver of green (growth) transitions and illustrate their dynamics in a closed, decentralized economy populated by utility maximizing agents with an environmental attitude. The model is built using the ABRam-T model (for model visit: https://doi.org/10.25937/ep45-k084) and introduces two types of capital – green (low carbon intensity) and brown (high carbon intensity) – with their respective technological progress levels. ABRam-BG simulates a green transition as an emergent phenomenon resulting from well-known opinion dynamics along the economic process.
Transfer of Development Rights (TDR) Simulation for Compact Urban Growth in Dublin: An Agent-Based Model in NetLogo
ajithvyas | Published Wednesday, May 14, 2025This agent-based model simulates the implementation of a Transfer of Development Rights (TDR) mechanism in a stylized urban environment inspired by Dublin. It explores how developer agents interact with land parcels under spatial zoning, conservation protections, and incentive-based policy rules. The model captures emergent outcomes such as compact growth, green and heritage zone preservation, and public cost-efficiency. Built in NetLogo, the model enables experimentation with variable FSI bonuses, developer behavior, and spatial alignment of sending/receiving zones. It is intended as a policy sandbox to test market-aligned planning tools under behavioral and spatial uncertainty.
Peer reviewed Collectivities
Nigel Gilbert | Published Tuesday, April 09, 2019 | Last modified Thursday, August 22, 2019The model that simulates the dynamic creation and maintenance of knowledge-based formations such as communities of scientists, fashion movements, and subcultures. The model’s environment is a spatial one, representing not geographical space, but a “knowledge space” in which each point is a different collection of knowledge elements. Agents moving through this space represent people’s differing and changing knowledge and beliefs. The agents have only very simple behaviors: If they are “lonely,” that is, far from a local concentration of agents, they move toward the crowd; if they are crowded, they move away.
Running the model shows that the initial uniform random distribution of agents separates into “clumps,” in which some agents are central and others are distributed around them. The central agents are crowded, and so move. In doing so, they shift the centroid of the clump slightly and may make other agents either crowded or lonely, and they too will move. Thus, the clump of agents, although remaining together for long durations (as measured in time steps), drifts across the view. Lonely agents move toward the clump, sometimes joining it and sometimes continuing to trail behind it. The clumps never merge.
The model is written in NetLogo (v6). It is used as a demonstration of agent-based modelling in Gilbert, N. (2008) Agent-Based Models (Quantitative Applications in the Social Sciences). Sage Publications, Inc. and described in detail in Gilbert, N. (2007) “A generic model of collectivities,” Cybernetics and Systems. European Meeting on Cybernetic Science and Systems Research, 38(7), pp. 695–706.
Displaying 10 of 1111 results for "Clint A Penick" clear search