About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1111 results for "Clint A Penick" clear search
Peer reviewed Price Evolution with Expectations
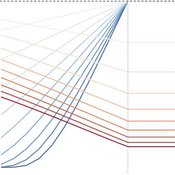
J M Applegate Gesine Steudel Armin Haas Carlo Jaeger | Published Friday, September 10, 2021The Price Evolution with Expectations model provides the opportunity to explore the question of non-equilibrium market dynamics, and how and under which conditions an economic system converges to the classically defined economic equilibrium. To accomplish this, we bring together two points of view of the economy; the classical perspective of general equilibrium theory and an evolutionary perspective, in which the current development of the economic system determines the possibilities for further evolution.
The Price Evolution with Expectations model consists of a representative firm producing no profit but producing a single good, which we call sugar, and a representative household which provides labour to the firm and purchases sugar.The model explores the evolutionary dynamics whereby the firm does not initially know the household demand but eventually this demand and thus the correct price for sugar given the household’s optimal labour.
The model can be run in one of two ways; the first does not include money and the second uses money such that the firm and/or the household have an endowment that can be spent or saved. In either case, the household has preferences for leisure and consumption and a demand function relating sugar and price, and the firm has a production function and learns the household demand over a set number of time steps using either an endogenous or exogenous learning algorithm. The resulting equilibria, or fixed points of the system, may or may not match the classical economic equilibrium.
Peer reviewed General Housing Model
J M Applegate | Published Thursday, May 07, 2020The General Housing Model demonstrates a basic housing market with bank lending, renters, owners and landlords. This model was developed as a base to which students contributed additional functions during Arizona State University’s 2020 Winter School: Agent-Based Modeling of Social-Ecological Systems.
Agent-based model of risk behavior in adolescence
N Schuhmacher P Van Geert L Ballato | Published Monday, June 24, 2013 | Last modified Monday, April 08, 2019The computer model simulates the development of a social network (i.e. formation of friendships and cliques), the (dyadic) interactions between pupils and the development of similarities and differences in their behavioral profiles.
An Agent-Based School Choice Matching Model
Connie Wang Weikai Chen Shu-Heng Chen | Published Sunday, February 01, 2015 | Last modified Wednesday, March 06, 2019This model is to simulate and compare the admission effects of 3 school matching mechanisms, serial dictatorship, Boston mechanism, and Chinese Parallel, under different settings of information released.
COOPER - Flood impacts over Cooperative Winemaking Systems
David Nortes Martinez David Nortes-Martinez | Published Thursday, February 08, 2018 | Last modified Friday, March 22, 2019The model simulates flood damages and its propagation through a cooperative, productive, farming system, characterized as a star-type network, where all elements in the system are connected one to each other through a central element.
Contract farming in the Mekong Delta's rice supply chain
Hung Nguyen | Published Tuesday, February 05, 2019We study three obstacles of the expansion of contract rice farming in the Mekong Delta (MKD) region. The failure of buyers in building trust-based relationship with small-holder farmers, unattractive offered prices from the contract farming scheme, and limited rice processing capacity have constrained contractors from participating in the large-scale paddy field program. We present an agent-based model to examine the viability of contract farming in the region from the contractor perspective.
The model focuses on financial incentives and trust, which affect the decision of relevant parties on whether to participate and honor a contract. The model is also designed in the context of the MKD’s rice supply chain with two contractors engaging in the contract rice farming scheme alongside an open market, in which both parties can renege on the agreement. We then evaluate the contractors’ performances with different combinations of scenarios related to the three obstacles.
Our results firstly show that a fully-equipped contractor who opportunistically exploits a relatively small proportion (less than 10%) of the contracted farmers in most instances can outperform spot market-based contractors in terms of average profit achieved for each crop. Secondly, a committed contractor who offers lower purchasing prices than the most typical rate can obtain better earnings per ton of rice as well as higher profit per crop. However, those contractors in both cases could not enlarge their contract farming scheme, since either farmers’ trust toward them decreases gradually or their offers are unable to compete with the benefits from a competitor or the spot market. Thirdly, the results are also in agreement with the existing literature that the contract farming scheme is not a cost-effective method for buyers with limited rice processing capacity, which is a common situation among the contractors in the MKD region.
Quality uncertainty and market failure
David Poza José Manuel Galán María Pereda José Santos | Published Wednesday, May 14, 2014 | Last modified Wednesday, April 25, 2018Quality uncertainty and market failure: an interactive model to conduct classroom experiments
Agent Based Integrated Assessment Model
Marcin Czupryna | Published Saturday, June 27, 2020Agent based approach to the class of the Integrated Assessment Models. An agent-based model (ABM) that focuses on the energy sector and climate relevant facts in a detailed way while being complemented with consumer goods, labour and capital markets to a minimal necessary extent.
Replication of ECEC model: Environmental Feedback and the Evolution of Cooperation
Pierre Bommel | Published Tuesday, April 05, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The model, presented here, is a re-implementation of the Pepper and Smuts’ model : - Pepper, J.W. and B.B. Smuts. 2000. “The evolution of cooperation in an ecological context: an agent-based model”. Pp. 45-76 in T.A. Kohler and G.J. Gumerman, eds. Dynamics of human and primate societies: agent-based modeling of social and spatial processes. Oxford University Press, Oxford. - Pepper, J.W. and B.B. Smuts. 2002. “Assortment through Environmental Feedback”. American Naturalist, 160: 205-213 […]
NetCommons
Francisco Miguel Quesada | Published Wednesday, May 18, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013NetCommons simulates a social dilemma process in case of step-level public goods. Is possible to generate (or load from DL format) any different networks, to change initial parameters, to replicate a number of experimental situations, and to obtain a event history database in CSV format with information about the context of each agents’ decision, the individual behavior and the aggregate outcomes.
Displaying 10 of 1111 results for "Clint A Penick" clear search