About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 98 results learning clear search
Managing networked landscapes: conservation in fragmented, regionally connected world
Jacopo A. Baggio Michael Schoon Sechindra Vallury | Published Monday, December 09, 2019Exploring how learning and social-ecological networks influence management choice set and their ability to increase the likelihood of species coexistence (i.e. biodiversity) on a fragmented landscape controlled by different managers.
Cultural Evolution of Sustainable Behaviours: Landscape of Affordances Model
Nikita Strelkovskii Roope Oskari Kaaronen | Published Wednesday, December 04, 2019 | Last modified Wednesday, December 04, 2019This NetLogo model illustrates the cultural evolution of pro-environmental behaviour patterns. It illustrates how collective behaviour patterns evolve from interactions between agents and agents (in a social network) as well as agents and the affordances (action opportunities provided by the environment) within a niche. More specifically, the cultural evolution of behaviour patterns is understood in this model as a product of:
- The landscape of affordances provided by the material environment,
- Individual learning and habituation,
- Social learning and network structure,
- Personal states (such as habits and attitudes), and
…
Co-evolution of mental models among socially learning agents
Garry Sotnik | Published Sunday, October 14, 2018The model simulates seven agents engaging in collective action and inter-network social learning. The objective of the model is to demonstrate how mental models of agents can co-evolve through a complex relationship among factors influencing decision-making, such as access to knowledge and personal- and group-level constraints.
Adaptive model of a consumer advice network
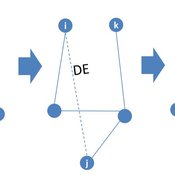
Peng Shao | Published Monday, May 14, 2018In the consumer advice network, users with connections can interact with each other, and the network topology will change during the opinion interaction. When the opinion distance from i to j is greater than the confidence threshold, the two consumers cannot exchange opinions, and the link between them will disconnect with probability DE. Then, a link from node i to node k is established with probability CE and node i learning opinion from node k.
Machine Learning simulates Agent-based Model
Bernardo Furtado | Published Wednesday, March 07, 2018This is an initial exploratory exercise done for the class @ http://thiagomarzagao.com/teaching/ipea/ Text available here: https://arxiv.org/abs/1712.04429v1
The program:
Reads output from an ABM model and its parameters’ configuration
Creates a socioeconomic optimal output based on two ABM results of the modelers choice
Organizes the data as X and Y matrices
Trains some Machine Learning algorithms
…
PercolationPrice
Koen Frenken Luis Izquierdo Paolo Zeppini | Published Thursday, December 21, 2017 | Last modified Thursday, May 03, 2018This model simulate product diffusion on different social network structures.
Dynamic pricing strategies for perishable products in a competitive multi-agent retailer market
Wenchong Chen Hongwei Liu | Published Monday, November 27, 2017 | Last modified Thursday, March 01, 2018This model explores a price Q-learning mechanism for perishable products that considers uncertain demand and customer preferences in a competitive multi-agent retailer market (a model-free environment).
The Informational Dynamics of Regime Change
Dominik Klein Johannes Marx | Published Saturday, October 07, 2017 | Last modified Tuesday, January 14, 2020We model the epistemic dynamics preceding political uprising. Before deciding whether to start protests, agents need to estimate the amount of discontent with the regime. This model simulates the dynamics of group knowledge about general discontent.
Success bias imitation increases the probability of effectively dealing with ecological disturbances
Jacopo A. Baggio Vicken Hillis | Published Thursday, April 13, 2017 | Last modified Thursday, August 02, 2018This model aims to investigate how different type of learning (social system) and disturbance specific attributes (ecological system) influence adoption of treatment strategies to treat the effects of ecological disturbances.
LBD Model: Learning-by-doing for sustainable management of renewable resources
Emilie Lindkvist Örjan Ekeberg Jon Norberg | Published Thursday, March 09, 2017This is a simulation model of an intelligent agent that has the objective to learn sustainable management of a renewable resource, such as a fish stock.
Displaying 10 of 98 results learning clear search