About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 978 results for "Dave van Wees" clear search
CITMOD A Tax-Benefit Modeling System for the average citizen
Philip Truscott | Published Monday, August 15, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Must tax-benefit policy making be limited to the ‘experts’?
Direct versus Connect
Steven Kimbrough | Published Sunday, January 15, 2023This NetLogo model is an implementation of the mostly verbal (and graphic) model in Jarret Walker’s Human Transit: How Clearer Thinking about Public Transit Can Enrich Our Communities and Our Lives (2011). Walker’s discussion is in the chapter “Connections or Complexity?”. See especially figure 12-2, which is on page 151.
In “Connections or Complexity?”, Walker frames the matter as involving a choice between two conflicting goals. The first goal is to minimize connections, the need to make transfers, in a transit system. People naturally prefer direct routes. The second goal is to minimize complexity. Why? Well, read the chapter, but as a general proposition we want to avoid unnecessary complexity with its attendant operating characteristics (confusing route plans in the case of transit) and management and maintenance challenges. With complexity general comes degraded robustness and resilience.
How do we, how can we, choose between these conflicting goals? The grand suggestion here is that we only choose indirectly, implicitly. In the present example of connections versus complexity we model various alternatives and compare them on measures of performance (MoP) other than complexity or connections per se. The suggestion is that connections and complexity are indicators of, heuristics for, other MoPs that are more fundamental, such as cost, robustness, energy use, etc., and it is these that we at bottom care most about. (Alternatively, and not inconsistently, we can view connections and complexity as two of many MoPs, with the larger issue to be resolve in light of many MoPs, including but not limited to complexity and connections.) We employ modeling to get a handle on these MoPs. Typically, there will be several, taking us thus to a multiple criteria decision making (MCDM) situation. That’s the big picture.
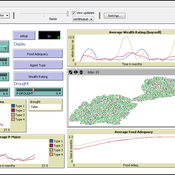
Smallholder Behavioural Decisions During Times of Drought Stress
Samantha Dobbie | Published Sunday, September 15, 2013 | Last modified Saturday, September 27, 2014An empirical ABM of smallholder decisions in times of drought stress.
A simple behavioral model predicts the emergence of complex animal hierarchies
Takao Sasaki Zachary Joseph Shaffer Stephen Pratt Clint A Penick Jürgen Liebig | Published Tuesday, December 22, 2015We used our model to test how different combinations of dominance interactions present in H. saltator could result in linear, despotic, or shared hierarchies.
ThomondSim
Vinicius Marino Carvalho | Published Monday, April 25, 2022 | Last modified Friday, May 12, 2023ThomondSim is a simulation of the political and economic landscape of the medieval kingdom of Thomond, southwestern Ireland, between 1276 and 1318.
Its goal is to analyze how deteriorating environmental and economic conditions caused by the Little Ice Age (LIA), the Great European Famine of 1315-1322, and wars between England and Scotland affected the outcomes of a local war involving Gaelic and English aristocratic lineages.
This ABM attempts to model both the effects of devastation on the human environment and the modus operandi of late-medieval war and diplomacy.
The model is the digital counterpart of the science discovery board game The Triumphs of Turlough. Its procedures closely correspond to the game’s mechanics, to the point that ToT can be considered an interactive, analog version of this ABM.
A language economics perspective on language spread: Simulating Language Dynamics in a Social Network
Marco Civico | Published Saturday, June 07, 2025This model examines language dynamics within a social network using simulation techniques to represent the interplay of language adoption, social influence, economic incentives, and language policies. The agent-based model (ABM) focuses on interactions between agents endowed with specific linguistic attributes, who engage in communication based on predefined rules. A key feature of our model is the incorporation of network analysis, structuring agent relationships as a dynamic network and leveraging network metrics to capture the evolving inter-agent connections over time. This integrative approach provides nuanced insights into emergent behaviors and system dynamics, offering an analytical framework that extends beyond traditional modeling approaches. By combining agent-based modeling with network analysis, the model sheds light on the underlying mechanisms governing complex language systems and can be effectively paired with sociolinguistic observational data.
01b ModEco NLG V1.39 – Model Economies – The PMM
Garvin Boyle | Published Friday, April 14, 2017It is very difficult to model a sustainable intergenerational biophysical/financial economy. ModEco NLG is one of a series of models exploring the dynamics of sustainable economics – PSoup, ModEco, EiLab, OamLab, MppLab, TpLab, CmLab.
07 EffLab_V5.07 NL
Garvin Boyle | Published Monday, October 07, 2019EffLab was built to support the study of the efficiency of agents in an evolving complex adaptive system. In particular:
- There is a definition of efficiency used in ecology, and an analogous definition widely used in business. In ecological studies it is called EROEI (energy returned on energy invested), or, more briefly, EROI (pronounced E-Roy). In business it is called ROI (dollars returned on dollars invested).
- In addition, there is the more well-known definition of efficiency first described by Sadi Carnot, and widely used by engineers. It is usually represented by the Greek letter ‘h’ (pronounced as ETA). These two measures of efficiency bear a peculiar relationship to each other: EROI = 1 / ( 1 - ETA )
In EffLab, blind seekers wander through a forest looking for energy-rich food. In this multi-generational world, they live and reproduce, or die, depending on whether they can find food more effectively than their contemporaries. Data is collected to measure their efficiency as they evolve more effective search patterns.
…
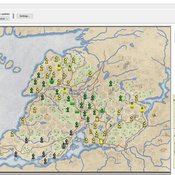
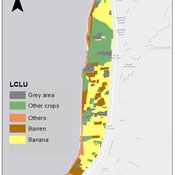
An integrated socio-economic Agent-Based Modeling framework towards assessing farmers’ decision making under water scarcity and varying utility function
Ghinwa Harik | Published Tuesday, September 13, 2022 | Last modified Wednesday, November 23, 2022A spatio-temporal Agent Based Modeling (ABM) framework is developed to probabilistically predict farmers’ decisions in the context of climate-induced water scarcity under varying utility optimization functions. The proposed framework forecasts farmers’ behavior assuming varying utility functions. The framework allows decision makers to forecast the behavior of farmers through a user-friendly platform with clear output visualization. The functionality of the proposed ABM is illustrated in an agriculturally dominated plain along the Eastern Mediterranean coastline.
Study area GIS data available upon request to gxh00@mail.aub.edu
Protein 2.0: An Agent-Based Model for Simulating Norway’s Protein Sector Under Carbon Pricing and the Emergence of Cultivated Proteins
Gary Polhill Nick Roxburgh Rob J.F. Burton Klaus Mittenzwei | Published Thursday, May 08, 2025Protein 2.0 is a systems model of the Norwegian protein sector designed to explore the potential impacts of carbon taxation and the emergence of cultivated meat and dairy technologies. The model simulates production, pricing, and consumption dynamics across conventional and cultivated protein sources, accounting for emissions intensity, technological learning, economies of scale, and agent behaviour. It assesses how carbon pricing could alter the competitiveness of conventional beef, lamb, pork, chicken, milk, and egg production relative to emerging cultivated alternatives, and evaluates the implications for domestic production, emissions, and food system resilience. The model provides a flexible platform for exploring policy scenarios and transition pathways in protein supply. Further details can be found in the associated publication.
Displaying 10 of 978 results for "Dave van Wees" clear search