About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 50 results for "Matthias Mueller" clear search
Collective Decision Making for Ecological Restoration version 2.0
Dean Massey Moira Zellner Cristy Watkins Jeremy Brooks Kristen Ross Lynne M Westphal | Published Wednesday, November 19, 2014CoDMER v. 2.0 was parameterized with ethnographic data from organizations dealing with prescribed fire and seeding native plants, to advance theory on how collective decisions emerge in ecological restoration.
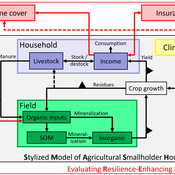
SMASH: Stylized Model of Agricultural Smallholder Households
Tim Williams | Published Tuesday, December 08, 2020The SMASH model is an agent-based model of rural smallholder households. It models households’ evolving income and wealth, which they earn through crop sales. Wealth is carried in the form of livestock, which are grazed on an external rangeland (exogenous) and can be bought/sold as investment/coping mechanisms. The model includes a stylized representation of soil nutrient dynamics, modeling the inflows and outflows of organic and inorganic nitrogen from each household’s field.
The model has been applied to assess the resilience-enhancing effects of two different farm-level adaptation strategies: legume cover cropping and crop insurance. These two strategies interact with the model through different mechanims - legume cover cropping through ecological mechanisms and crop insurance through financial mechanisms. The model can be used to investigate the short- and long-term effects of these strategies, as well as how they may differently benefit different types of household.
Epidemic Simulation with Transportation Simulation
FG Econophysics FG Econophysics | Published Monday, March 01, 2021The Episim framework builds upon the established transportation simulation MATSim and is capable of tracking agents’ movements within a network and thus computing infection chains. Several characteristics of the virus and the environment can be parametred, whilst the infection dynamics is computed based upon a compartment model. The spread of the virus can be mitigated by restricting the agents’ activity in certain places.
Peer reviewed MOOvPOPsurveillance
Matthew Gompper Aniruddha Belsare Joshua J Millspaugh | Published Tuesday, April 04, 2017 | Last modified Tuesday, May 12, 2020MOOvPOPsurveillance was developed as a tool for wildlife agencies to guide collection and analysis of disease surveillance data that relies on non-probabilistic methods like harvest-based sampling.
Livestock drought insurance model
Birgit Müller Felix John Jürgen Groeneveld Karin Frank Russell Toth | Published Tuesday, December 19, 2017 | Last modified Saturday, April 14, 2018The model analyzes the economic and ecological effects of a provision of livestock drought insurance for dryland pastoralists. More precisely, it yields qualitative insights into how long-term herd and pasture dynamics change through insurance.
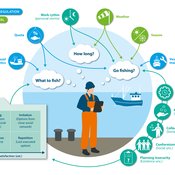
Peer reviewed FISHCODE - FIsheries Simulation with Human COmplex DEcision-making
Birgit Müller Gunnar Dressler Jonas Letschert Christian Möllmann Vanessa Stelzenmüller | Published Monday, August 05, 2024FIsheries Simulation with Human COmplex DEcision-making (FISHCODE) is an agent-based model to depict and analyze current and future spatio-temporal dynamics of three German fishing fleets in the southern North Sea. Every agent (fishing vessel) makes daily decisions about if, what, and how long to fish. Weather, fuel and fish prices, as well as the actions of their colleagues influence agents’ decisions. To combine behavioral theories and enable agents to make dynamic decision, we implemented the Consumat approach, a framework in which agents’ decisions vary in complexity and social engagement depending on their satisfaction and uncertainty. Every agent has three satisfactions and two uncertainties representing different behavioral aspects, i.e. habitual behavior, profit maximization, competition, conformism, and planning insecurity. Availability of extensive information on fishing trips allowed us to parameterize many model parameters directly from data, while others were calibrated using pattern oriented modelling. Model validation showed that spatial and temporal aggregated ABM outputs were in realistic ranges when compared to observed data. Our ABM hence represents a tool to assess the impact of the ever growing challenges to North Sea fisheries and provides insight into fisher behavior beyond profit maximization.
Learning Extension - RAGE RAngeland Grazing Model
Nikita Strelkovskii Cristina I. Apetrei Nikolay Khabarov Valeria Javalera Rincón | Published Saturday, July 22, 2023This is an extension of the original RAGE model (Dressler et al. 2018), where we add learning capabilities to agents, specifically learning-by-doing and social learning (two processes central to adaptive (co-)management).
The extension module is applied to smallholder farmers’ decision-making - here, a pasture (patch) is the private property of the household (agent) placed on it and there is no movement of the households. Households observe the state of the pasture and their neighrbours to make decisions on how many livestock to place on their pasture every year. Three new behavioural types are created (which cannot be combined with the original ones): E-RO (baseline behaviour), E-LBD (learning-by-doing) and E-RO-SL1 (social learning). Similarly to the original model, these three types can be compared regarding long-term social-ecological performance. In addition, a global strategy switching option (corresponding to double-loop learning) allows users to study how behavioural strategies diffuse in a heterogeneous population of learning and non-learning agents.
An important modification of the original model is that extension agents are heterogeneous in how they deal with uncertainty. This is represented by an agent property, called the r-parameter (household-risk-att in the code). The r-parameter is catch-all for various factors that form an agent’s disposition to act in a certain way, such as: uncertainty in the sensing (partial observability of the resource system), noise in the information received, or an inherent characteristic of the agent, for instance, their risk attitude.
Peer reviewed The Viability of the Social-Ecological Agroecosystem (ViSA) Spatial Agent-based Model
Mostafa Shaaban | Published Monday, March 25, 2024ViSA 2.0.0 is an updated version of ViSA 1.0.0 aiming at integrating empirical data of a new use case that is much smaller than in the first version to include field scale analysis. Further, the code of the model is simplified to make the model easier and faster. Some features from the previous version have been removed.
It simulates decision behaviors of different stakeholders showing demands for ecosystem services (ESS) in agricultural landscape. It investigates conditions and scenarios that can increase the supply of ecosystem services while keeping the viability of the social system by suggesting different mixes of initial unit utilities and decision rules.
Peer reviewed Neighbor Influenced Energy Retrofit (NIER) agent-based model
Eric Boria | Published Friday, April 03, 2020The NIER model is intended to add qualitative variables of building owner types and peer group scales to existing energy efficiency retrofit adoption models. The model was developed through a combined methodology with qualitative research, which included interviews with key stakeholders in Cleveland, Ohio and Detroit and Grand Rapids, Michigan. The concepts that the NIER model adds to traditional economic feasibility studies of energy retrofit decision-making are differences in building owner types (reflecting strategies for managing buildings) and peer group scale (neighborhoods of various sizes and large-scale Districts). Insights from the NIER model include: large peer group comparisons can quickly raise the average energy efficiency values of Leader and Conformist building owner types, but leave Stigma-avoider owner types as unmotivated to retrofit; policy interventions such as upgrading buildings to energy-related codes at the point of sale can motivate retrofits among the lowest efficient buildings, which are predominantly represented by the Stigma-avoider type of owner; small neighborhood peer groups can successfully amplify normal retrofit incentives.
The various technologies used inside a Dutch greenhouse interact in combination with an external climate, resulting in an emergent internal climate, which contributes to the final productivity of the greenhouse. This model examines how differing technology development styles affects the overall ability of a community of growers to approach the theoretical maximum yield.
Displaying 10 of 50 results for "Matthias Mueller" clear search