About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 133 results for "Emily S Ihara" clear search
Peer reviewed NetLogo model of USA mass shootings
Smarzhevskiy Ivan | Published Tuesday, September 24, 2019 | Last modified Tuesday, April 14, 2020Is the mass shooter a maniac or a relatively normal person in a state of great stress? According to the FBI report (Silver, J., Simons, A., & Craun, S. (2018). A Study of the Pre-Attack Behaviors of Active Shooters in the United States Between 2000 – 2013. Federal Bureau of Investigation, U.S. Department of Justice,Washington, D.C. 20535.), only 25% of the active shooters were known to have been diagnosed by a mental health professional with a mental illness of any kind prior to the offense.
The main objects of the model are the humans and the guns. The main factors influencing behavior are the population size, the number of people with mental disabilities (“psycho” in the model terminology) per 100,000 population, the total number of weapons (“guns”) in the population, the availability of guns for humans, the intensity of stressors affecting humans and the threshold level of stress, upon reaching which a person commits an act of mass shooting.
The key difference (in the model) between a normal person and a psycho is that a psycho accumulates stressors and, upon reaching a threshold level, commits an act of mass shooting. A normal person is exposed to stressors, but reaching the threshold level for killing occurs only when the simultaneous effect of stressors on him exceeds this level.
The population dynamics are determined by the following factors: average (normally distributed) life expectancy (“life_span” attribute of humans) and population growth with the percentage of newborns set by the value of the TickReprRatio% slider of the current population volume from 16 to 45 years old.Thus, one step of model time corresponds to a year.
CPNorm
Ruth Meyer | Published Sunday, June 04, 2017 | Last modified Tuesday, June 13, 2017CPNorm is a model of a community of harvesters using a common pool resource where adhering to the optimal extraction level has become a social norm. The model can be used to explore the robustness of norm-driven cooperation in the commons.
Tragedy of the Commons with Environmental Feedback: A Model of Human-AI Socio-Environmental Water Dilemma
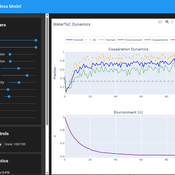
Ivana Malcic Luka Waronig Andrew Crossley | Published Saturday, July 05, 2025 | Last modified Sunday, July 06, 2025This project is an interactive agent-based model simulating consumption of a shared, renewable resource using a game-theoretic framework with environmental feedback. The primary function of this model was to test how resource-use among AI and human agents degrades the environment, and to explore the socio-environmental feedback loops that lead to complex emergent system dynamics. We implemented a classic game theoretic matrix which decides agents´ strategies, and added a feedback loop which switches between strategies in pristine vs degraded environments. This leads to cooperation in bad environments, and defection in good ones.
Despite this use, it can be applicable for a variety of other scenarios including simulating climate disasters, environmental sensitivity to resource consumption, or influence of environmental degradation to agent behaviour.
The ABM was inspired by the Weitz et. al. (2016, https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27830651/) use of environmental feedback in their paper, as well as the Demographic Prisoner’s Dilemma on a Grid model (https://mesa.readthedocs.io/stable/examples/advanced/pd_grid.html#demographic-prisoner-s-dilemma-on-a-grid). The main innovation is the added environmental feedback with local resource replenishment.
Beyond its theoretical insights into coevolutionary dynamics, it serves as a versatile tool with several practical applications. For urban planners and policymakers, the model can function as a ”digital sandbox” for testing the impacts of locating high-consumption industrial agents, such as data centers, in proximity to residential communities. It allows for the exploration of different urban densities, and the evaluation of policy interventions—such as taxes on defection or subsidies for cooperation—by directly modifying the agents’ resource consumptions to observe effects on resource health. Furthermore, the model provides a framework for assessing the resilience of such socio-environmental systems to external shocks.
…
On July 20th, James Holmes committed a mass shooting in a midnight showing of The Dark Knight Rises. The Aurora Colorado shooting was used as a test case to validate this framework for modeling mass shootings.
The Travel-tour case study
Christophe Sibertin-Blanc Françoise Adreit Joseph El Gemayel | Published Sunday, May 19, 2013 | Last modified Friday, June 14, 2013This model describes and analyses the Travel-Tour Case study.
Peer reviewed Yards
srailsback Emily Minor Soraida Garcia Philip Johnson | Published Thursday, November 02, 2023This is a model of plant communities in urban and suburban residential neighborhoods. These plant communities are of interest because they provide many benefits to human residents and also provide habitat for wildlife such as birds and pollinators. The model was designed to explore the social factors that create spatial patterns in biodiversity in yards and gardens. In particular, the model was originally developed to determine whether mimicry behaviors–-or neighbors copying each other’s yard design–-could produce observed spatial patterns in vegetation. Plant nurseries and socio-economic constraints were also added to the model as other potential sources of spatial patterns in plant communities.
The idea for the model was inspired by empirical patterns of spatial autocorrelation that have been observed in yard vegetation in Chicago, Illinois (USA), and other cities, where yards that are closer together are more similar than yards that are farther apart. The idea is further supported by literature that shows that people want their yards to fit into their neighborhood. Currently, the yard attribute of interest is the number of plant species, or species richness. Residents compare the richness of their yards to the richness of their neighbors’ yards. If a resident’s yard is too different from their neighbors, the resident will be unhappy and change their yard to make it more similar.
The model outputs information about the diversity and identity of plant species in each yard. This can be analyzed to look for spatial autocorrelation patterns in yard diversity and to explore relationships between mimicry behaviors, yard diversity, and larger scale diversity.
Ant Colony Optimization for infrastructure routing
Igor Nikolic Emile Chappin P W Heijnen | Published Wednesday, March 05, 2014 | Last modified Saturday, March 24, 2018The mode implements a variant of Ant Colony Optimization to explore routing on infrastructures through a landscape with forbidden zones, connecting multiple sinks to one source.
Exploring homeowners' insulation activity
Georg Holtz Emile Chappin Jonas Friege | Published Monday, June 01, 2015 | Last modified Monday, April 08, 2019We built an agent-based model to foster the understanding of homeowners’ insulation activity.
Individual-based modelling as a tool for elephant poaching mitigation
Ernesto Carrella Richard Bailey Emily Neil Jens Koed Madsen Nicolas Payette | Published Tuesday, June 18, 2019 | Last modified Thursday, August 01, 2019We develop an IBM that predicts how interactions between elephants, poachers, and law enforcement affect poaching levels within a virtual protected area. The model is theoretical at this stage and is not meant to provide a realistic depiction of poaching, but instead to demonstrate how IBMs can expand upon the existing modelling work done in this field, and to provide a framework for future research. The model could be further developed into a useful management support tool to predict the outcomes of various poaching mitigation strategies at real-world locations. The model was implemented in NetLogo version 6.1.0.
We first compared a scenario in which poachers have prescribed, non-adaptive decision-making and move randomly across the landscape, to one in which poachers adaptively respond to their memories of elephant locations and where other poachers have been caught by law enforcement. We then compare a situation in which ranger effort is distributed unevenly across the protected area to one in which rangers patrol by adaptively following elephant matriarchal herds.
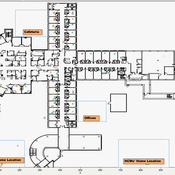
Knowledge Sharing in a Hospital
bpint Emily Molfino Joshua Goldstein Kathryn Schaefer Ziemer Mark Orr Bryan Lewis Jose Jimenez | Published Friday, January 27, 2023Organizations are complex systems comprised of many dynamic and evolving interaction patterns among individuals and groups. Understanding these interactions and how patterns, such as informal structures and knowledge sharing behavior, emerge are crucial to creating effective and efficient organizations. To explore such organizational dynamics, the agent-based model integrates a cognitive model, dynamic social networks, and a physical environment.
Displaying 10 of 133 results for "Emily S Ihara" clear search