About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 41 results supply clear search
Food supply chain innovations under public pressure
Tim Verwaart Wil Hennen Jan Buurma | Published Friday, April 15, 2016 | Last modified Tuesday, November 27, 2018Aroused public opinion has led to public debates on social responsibility issues in food supply chains. This model based op opinion dynamics and the linkages between involved actors simulates the public debate leading to the transitions.
Private forest owner management behavior using social interactions, information flow, and peer-to-peer n
Jessica Leahy Emily Silver Huff Aaron R Weiskittel Caroline L Noblet David Hiebeler | Published Tuesday, October 13, 2015This theoretical model includes forested polygons and three types of agents: forest landowners, foresters, and peer leaders. Agent rules and characteristics were parameterized from existing literature and an empirical survey of forest landowners.
MERCURY: an ABM of tableware trade in the Roman East
Tom Brughmans Jeroen Poblome | Published Thursday, September 25, 2014 | Last modified Friday, May 01, 2015MERCURY aims to represent and explore two descriptive models of the functioning of the Roman trade system that aim to explain the observed strong differences in the wideness of distributions of Roman tableware.
The purpose of the AdaptPumpa model is to analyze the robustness of the Pumpa irrigation system in Nepal to climate change.
Endogenous Dynamics of Housing Market Cycles
Onur Özgün Birnur Özbaş Yaman Barlas | Published Monday, September 09, 2013 | Last modified Wednesday, January 08, 2014The purpose of this model is to analyze the dynamics of endogenously created oscillations in housing prices using a system dynamics simulation model, built from the perspective of construction companies.
The various technologies used inside a Dutch greenhouse interact in combination with an external climate, resulting in an emergent internal climate, which contributes to the final productivity of the greenhouse. This model examines how differing technology development styles affects the overall ability of a community of growers to approach the theoretical maximum yield.
Peer reviewed Pumpa irrigation model
Marco Janssen Irene Perez Ibarra | Published Wednesday, January 09, 2013 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is a replication of the Pumpa model that simulates the Pumpa Irrigation System in Nepal (Cifdaloz et al., 2010).
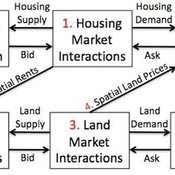
Coupled Housing and Land Markets (CHALMS)
Nicholas Magliocca Virginia Mcconnell Margaret Walls | Published Friday, November 02, 2012 | Last modified Monday, October 27, 2014CHALMS simulates housing and land market interactions between housing consumers, developers, and farmers in a growing ex-urban area.
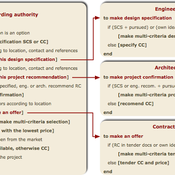
Enhancing recycling of construction materials; an agent based model with empirically based decision parameters
Igor Nikolic Claudia Binder Christof Knoeri Hans-Joerg Althaus | Published Sunday, October 21, 2012 | Last modified Monday, June 09, 2014This model allows for analyzing the most efficient levers for enhancing the use of recycled construction materials, and the role of empirically based decision parameters.
9 Maturity levels in Empirical Validation - An innovation diffusion example
Martin Rixin | Published Wednesday, October 19, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Several taxonomies for empirical validation have been published. Our model integrates different methods to calibrate an innovation diffusion model, ranging from simple randomized input validation to complex calibration with the use of microdata.
Displaying 10 of 41 results supply clear search