About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 180 results for "Robin D Fink" clear search
U-TRANS Modelling Urban Transition with Coupled Housing and Labour Markets
Bernardo Furtado Jiaqi Ge | Published Monday, July 31, 2023We develop an agent-based model (U-TRANS) to simulate the transition of an abstract city under an industrial revolution. By coupling the labour and housing markets, we propose a holistic framework that incorporates the key interacting factors and micro processes during the transition. Using U-TRANS, we look at five urban transition scenarios: collapse, weak recovery, transition, enhanced training and global recruit, and find the model is able to generate patterns observed in the real world. For example, We find that poor neighbourhoods benefit the most from growth in the new industry, whereas the rich neighbourhoods do better than the rest when the growth is slow or the situation deteriorates. We also find a (subtle) trade-off between growth and equality. The strategy to recruit a large number of skilled workers globally will lead to higher growth in GDP, population and human capital, but it will also entail higher inequality and market volatility, and potentially create a divide between the local and international workers. The holistic framework developed in this paper will help us better understand urban transition and detect early signals in the process. It can also be used as a test-bed for policy and growth strategies to help a city during a major economic and technological revolution.
Comparing agent-based models on experimental data of irrigation games
Marco Janssen Jacopo A. Baggio | Published Tuesday, July 02, 2013 | Last modified Wednesday, July 03, 2013Comparing 7 alternative models of human behavior and assess their performance on a high resolution dataset based on individual behavior performance in laboratory experiments.
Forager mobility and interaction
L S Premo | Published Thursday, January 10, 2013 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is a relatively simple foraging-radius model, as described first by Robert Kelly, that allows one to quantify the effect of increased logistical mobility (as represented by increased effective foraging radius, r_e) on the likelihood that 2 randomly placed central place foragers will encounter one another within 5000 time steps.
Adoption as a social marker
Paul Smaldino | Published Monday, October 17, 2016A model of innovation diffusion in a structured population with two groups who are averse to adopting a produce popular with the outgroup.
We propose here a computational model of school segregation that is aligned with a corresponding Schelling-type model of residential segregation. To adapt the model for application to school segregation, we move beyond previous work by combining two preference arguments in modeling parents’ school choice, preferences for the ethnic composition of a school and preferences for minimizing the travelling distance to the school.
Peer reviewed BAM: The Bottom-up Adaptive Macroeconomics Model
Alejandro Platas López Alejandro Guerra-Hernández | Published Tuesday, January 14, 2020 | Last modified Sunday, July 26, 2020Overview
Purpose
Modeling an economy with stable macro signals, that works as a benchmark for studying the effects of the agent activities, e.g. extortion, at the service of the elaboration of public policies..
…
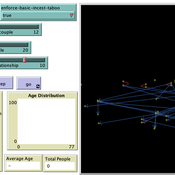
Peer reviewed Monogamous Reproduction in Small Populations and the Enforcement of the Incest Taboo
Ian Stuart | Published Wednesday, January 18, 2023This program was developed to simulate monogamous reproduction in small populations (and the enforcement of the incest taboo).
Every tick is a year. Adults can look for a mate and enter a relationship. Adult females in a Relationship (under the age of 52) have a chance to become pregnant. Everyone becomes not alive at 77 (at which point people are instead displayed as flowers).
User can select a starting-population. The starting population will be adults between the ages of 18 and 42.
…
Simulating the evolution of the human family
Paul Smaldino | Published Wednesday, November 29, 2017The (cultural) evolution of cooperative breeding in harsh environments.
Peer reviewed TRANSOPE: a multi-agent model to simulate outsourcing networks in road freight transport.
Aitor Salas-Peña Blanca Rosa Cases Gutiérrez | Published Friday, October 21, 2022A road freight transport (RFT) operation involves the participation of several types of companies in its execution. The TRANSOPE model simulates the subcontracting process between 3 types of companies: Freight Forwarders (FF), Transport Companies (TC) and self-employed carriers (CA). These companies (agents) form transport outsourcing chains (TOCs) by making decisions based on supplier selection criteria and transaction acceptance criteria. Through their participation in TOCs, companies are able to learn and exchange information, so that knowledge becomes another important factor in new collaborations. The model can replicate multiple subcontracting situations at a local and regional geographic level.
The succession of n operations over d days provides two types of results: 1) Social Complex Networks, and 2) Spatial knowledge accumulation environments. The combination of these results is used to identify the emergence of new logistics clusters. The types of actors involved as well as the variables and parameters used have their justification in a survey of transport experts and in the existing literature on the subject.
As a result of a preferential selection process, the distribution of activity among agents shows to be highly uneven. The cumulative network resulting from the self-organisation of the system suggests a structure similar to scale-free networks (Albert & Barabási, 2001). In this sense, new agents join the network according to the needs of the market. Similarly, the network of preferential relationships persists over time. Here, knowledge transfer plays a key role in the assignment of central connector roles, whose participation in the outsourcing network is even more decisive in situations of scarcity of transport contracts.
Hybrid traffic model
Patrick Taillandier Arnaud Banos Nathalie Corson | Published Thursday, March 16, 2017The model aims at simulating the car traffic. It allows to use either a macro or a micro sub-model for the simulation of the flow on the roads.
Displaying 10 of 180 results for "Robin D Fink" clear search