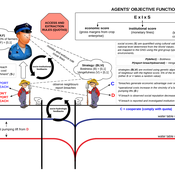
About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 376 results for "Huw Vasey" clear search
The Groundwater Commons Game
Juan Castilla-Rho Rodrigo Rojas | Published Thursday, May 11, 2017 | Last modified Saturday, September 16, 2017The Groundwater Commons Game synthesises and extends existing work on human cooperation and collective action, to elucidate possible determinants and pathways to regulatory compliance in groundwater systems globally.
Collective Decision Making for Ecological Restoration
Dean Massey Moira Zellner Cristy Watkins Jeremy Brooks Kristen Ross | Published Friday, December 30, 2011 | Last modified Friday, November 21, 2014We present an agent-based model that maps out and simulates the processes by which individuals within ecological restoration organizations communicate and collectively make restoration decisions.
Threshold Public Goods Game Models with Punishment
Martin Zoričak Vladimir Gazda Gabriela Koľveková Manuela Raisová | Published Saturday, June 06, 2020This is a set of threshold public goods games models. Set consists of baseline model, endogenous shared punishment model, endogenous shared punishment model with activists and cooperation model. In each round, all agents are granted a budget of size set in GUI. Then they decide on how much they contribute to public goods and how much they keep. Public goods are provided only if the sum of contributions meets or exceeds the threshold defined in the GUI. After each round agents evaluate their strategy and payoff from this strategy.
Cooling in simulated annealing using Metropolis' algorithm (version a & b)
María Pereda José Santos José Manuel Galán Virginia Ahedo | Published Monday, March 15, 2021Netlogo model that shows how the cooling process determines the quality of a solution in simulated annealing using Metropolis algorithm.
RBM - A Relation-based model - a fishery implementation
Nanda Wijermans Maja Schlüter Anja Klein Tilman Hertz | Published Monday, March 17, 2025The Relation-Based Model (RBM) purpose is to operationalise (a form of) process-relational (PR) thinking to serve as a thinking tool for process-relational thinking among social-ecological system (SES) researchers. The development of this model itself has been a ‘Proof of concept’- exercise to see whether we actually represent process-relational thinking in a methodology that is entity-based (ABM).
The target of the agent-based model is to show the emergence, change and disappearance of fishing assemblages (focusing on processes of self-organisation) in a Mexican fishery using a process-relational view. From this view, a fishery is regarded as an assemblage in which fishing can be enabled, fishing can occur, and fish can be bought/sold. These core doings - or sub-assemblages or capacities - maintain the assemblage. Each (sub)assemblage reflects different actualisations of constellations of relations and elements (buyers, fishers, fuel, permits, vessels and wind). The RBM thereby reflects an artificial fishery in which agents (elements) and their links (relations) engage in (enabling) fishing and buying/selling.
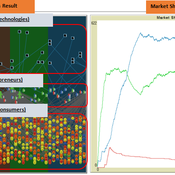
The simulation on the study of the optimal business strategy with the interaction between technologies and consumers.
sej-yoo | Published Monday, June 27, 2022 | Last modified Monday, July 04, 2022HOW IT WORKS
This model consists of three agents, and each agent type operates per business theories as below.
a. New technologies(Tech): It evolves per sustaining or disruptive technology trajectory with the constraint of project management triangle (Scope, Time, Quality, and Cost).
b. Entrepreneurs(Entre): It builds up the solution by combining Tech components per its own strategy (Exploration, Exploitation, or Ambidex).
c. Consumer(Consumer): It selects the solution per its own preference due to Diffusion of innovation theory (Innovators, Early Adopters, Early Majority, Late Majority, Laggards)
…
Peer reviewed ACross (Academic Collaboration, Research, Output, and System Simulation)
Wenhan Feng Bayi Li | Published Saturday, June 28, 2025The primary purpose of this model is to explain the dynamic processes within university-centered collaboration networks, with a particular focus on the complex transformation of academic knowledge into practical projects. Based on investigations of actual research projects and a thorough literature review, the model integrates multiple drivers and influencing factors to explore how these factors affect the formation and evolution of collaboration networks under different parameter scenarios. The model places special emphasis on the impact of disciplinary attributes, knowledge exchange, and interdisciplinary collaboration on the dynamics of collaboration networks, as well as the complex mechanisms of network structure, system efficiency, and interdisciplinary interactions during project formation.
Specifically, the model aims to:
- Simulate how university research departments drive the formation of research projects through knowledge creation.
- Investigate how the dynamics of collaboration networks influence the transformation of innovative hypotheses into matured projects.
- Examine the critical roles of knowledge exchange and interdisciplinary collaboration in knowledge production and project formation.
- Provide both quantitative and qualitative insights into the interactions among academia, industry, and project outputs.
Integrate land use policies into the agent-based model to simulate land use change
Jing Gao | Published Sunday, June 09, 2024This study employs a hierarchical cross-departmental ABM to explore the question: How and to what extent are the land use policies enforced when assessed against the real-world land use pattern? Specifically, two sub-questions are of interest: How can real-world policy interactions be abstracted into the behavior across hierarchical governmental departments in the model? How can the level of enforcement for each land use policy be quantified under these interactions? We build three hierarchical agents—the central level, the local level that incorporates three departments, and the village collective level—with simplified but plausible processes of land use change, with levels of enforcement of different land use policies as key parameters. We calibrate the model using a genetic algorithm to determine those parameters and answer our research question. We further applied the model to simulate potential land use changes and investigate the implications of different policy options. The results are expected to provide insights into the intricate relationships shaping land use processes, contributing to evidence-based decision-making in urban planning and sustainable land use management.
Nudging agents in social networks for collective action
Marco Janssen | Published Sunday, August 14, 2011 | Last modified Sunday, March 17, 2019Agents are linked in a social-network and make decisions on which of 2 types of behavior to adopt. We explore consequences of different information feedback and providing targeted feedback to individuals.
Simulation of Dual Information Exposure Networks: An Agent-Based Model of Panic Buying Behavior in China
dachenga | Published Thursday, April 11, 2024The main function of this simulation model is to simulate the onset of individual panic in the context of a public health event, and in particular to simulate how an individual’s panic develops and dies out in the context of a dual information contact network of online social media information and offline in-person perception information. In this model, eight different scenarios are set up by adjusting key parameters according to the difference in the amount and nature of information circulating in the dual information network, in order to observe how the agent’s panic behavior will change under different information exposure situations.
Displaying 10 of 376 results for "Huw Vasey" clear search