About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 61 results for "Harry Peter Andreassen" clear search
Neolithic Spread Model Version 1.0
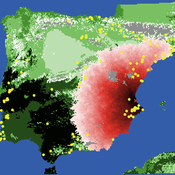
Sean Bergin Salvador Pardo Gordo Joan Bernabeu Auban Michael Barton | Published Thursday, December 11, 2014 | Last modified Monday, December 31, 2018This model simulates different spread hypotheses proposed for the introduction of agriculture on the Iberian peninsula. We include three dispersal types: neighborhood, leapfrog, and ideal despotic distribution (IDD).
Opinion Leaders' Role in Innovation Diffusion
Peter Van Eck | Published Wednesday, March 10, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model is used to investigate the role of opinion leader. More specifically: the influence of ‘innovative behavior’, ‘weigth of normative influence’, ‘better product judgment’, ‘number of opinion
Nudging agents in social networks for collective action
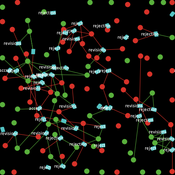
Marco Janssen | Published Sunday, August 14, 2011 | Last modified Sunday, March 17, 2019Agents are linked in a social-network and make decisions on which of 2 types of behavior to adopt. We explore consequences of different information feedback and providing targeted feedback to individuals.
The PRIF Model
Davide Secchi | Published Friday, November 08, 2019This model takes into consideration Peer Reviewing under the influence of Impact Factor (PRIF) and it has the purpose to explore whether the infamous metric affects assessment of papers under review. The idea is to consider to types of reviewers, those who are agnostic towards IF (IU1) and those that believe that it is a measure of journal (and article) quality (IU2). This perception is somehow reflected in the evaluation, because the perceived scientific value of a paper becomes a function of the journal in which an article has been submitted. Various mechanisms to update reviewer preferences are also implemented.
Hybrid Climate Assessment Model (HCAM)
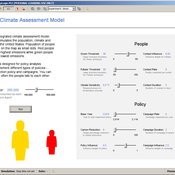
Peer-Olaf Siebers | Published Friday, February 15, 2019Our Hybrid Climate Assessment Model (HCAM) aims to simulate the behaviours of individuals under the influence of climate change and external policy makings. In our proposed solution we use System Dynamics (SD) modelling to represent the physical and economic environments. Agent-Based (AB) modelling is used to represent collections of individuals that can interact with other collections of individuals and the environment. In turn, individual agents are endowed with an internal SD model to track their psychological state used for decision making. In this paper we address the feasibility of such a scalable hybrid approach as a proof-of-concept. This novel approach allows us to reuse existing rigid, but well-established Integrated Assessment Models (IAMs), and adds more flexibility by replacing aggregate stocks with a community of vibrant interacting entities.
Our illustrative example takes the settings of the U.S., a country that contributes to the majority of the global carbon footprints and that is the largest economic power in the world. The model considers the carbon emission dynamics of individual states and its relevant economic impacts on the nation over time.
Please note that the focus of the model is on a methodological advance rather than on applying it for predictive purposes! More details about the HCAM are provided in the forthcoming JASSS paper “An Innovative Approach to Multi-Method Integrated Assessment Modelling of Global Climate Change”, which is available upon request from the authors (contact peer-olaf.siebers@nottingham.ac.uk).
HCAM: A Hybrid Climate Assessment Model
Peer-Olaf Siebers | Published Wednesday, November 06, 2019This model is part of a JASSS article that introduce a conceptual framework for developing hybrid (system dynamics and agent-based) integrated assessment models, which focus on examining the human impacts on climate change. This novel modelling approach allows to reuse existing rigid, but well-established integrated assessment models, and adds more flexibility by replacing aggregate stocks with a community of vibrant interacting entities. The model provides a proof-of-concept of the application of this conceptual framework in form of an illustrative example. taking the settings of the US. It is solely created for the purpose of demonstrating our hybrid modelling approach; we do not claim that it has predictive powers.
Exploring the Potential of Conversational AI Support for Agent-Based Social Simulation Model Design
Peer-Olaf Siebers | Published Sunday, May 12, 2024Our aim is to demonstrate how conversational AI systems, exemplified by ChatGPT, can support the conceptualisation of Agent-Based Social Simulation (ABSS) models, leading to a full ABSS model design document. Through advanced prompt engineering and adherence to the Engineering ABSS framework (Siebers and Klügl 2017), we have constructed a comprehensive script that is easy to use and that supports the design of ABSS models with or even by AI. The performance of the script is demonstrated through an illustrative case study related to the use of adaptive architecture in museums. The repository contains (1) the comprehensive script in a format that allows copying and pasting prompts for use with ChatGPT, (2) the results of the illustrative case study in the form of two conceptual ABSS models, the ground truth and the autogenerated version.
Last Mile Commuter Behavior Model
Dean Massey Moira Zellner Yoram Shiftan Jonathan Levine Maria Arquero | Published Friday, November 07, 2014 | Last modified Friday, November 07, 2014We represent commuters and their preferences for transportation cost, time and safety. Agents assess their options via their preferences, their environment, and the modes available. The model has policy levers to test impact on last-mile problem.
MIXTRUST - crop-livestock interactions at regional level
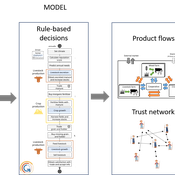
Myriam Grillot Aurélien Peter | Published Tuesday, February 25, 2025 | Last modified Monday, September 01, 2025The basic idea behind developing MIXTRUST was to represent a network of agricultural stakeholders composed of farmers and a cooperative in a mixed landscape to test its performances in response to risks. A mixed landscape here is a landscape where crop and livestock systems interact by the intermediary of material flows of agricultural products. It can be within mixed farms, or between farms, often specialized, (e.g. straw-manure).
Modeling Asian-Papuan Admixture during the Neolithic Expansion across Island Southeast Asia
Murray Cox François Vallée | Published Friday, December 09, 2016This Repast Simphony model simulates genomic admixture during the farming expansion of human groups from mainland Asia into the Papuan dominated islands of Southeast Asia during the Neolithic period.
Displaying 10 of 61 results for "Harry Peter Andreassen" clear search