About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 440 results for "Therese Lindahl" clear search
Agent-based simulation of small group decision-making under no communication
Christopher Poile | Published Thursday, May 26, 2016A computational model of a classic small group study by Alex Bavelas. This computational model was designed to explore the difficulty in translating a seemingly simple real-world experiment into a computational model.
Eliminating hepatitis C virus as a public health threat among HIV-positive men who have sex with men
Nick Scott Mark Stoove David P Wilson Olivia Keiser Carol El-Hayek Joseph Doyle Margaret Hellard | Published Wednesday, October 12, 2016 | Last modified Sunday, December 16, 2018We compare three model estimates for the time and treatment requirements to eliminate HCV among HIV-positive MSM in Victoria, Australia: a compartmental model; an ABM parametrized by surveillance data; and an ABM with a more heterogeneous population.
Livestock drought insurance model
Birgit Müller Felix John Jürgen Groeneveld Karin Frank Russell Toth | Published Tuesday, December 19, 2017 | Last modified Saturday, April 14, 2018The model analyzes the economic and ecological effects of a provision of livestock drought insurance for dryland pastoralists. More precisely, it yields qualitative insights into how long-term herd and pasture dynamics change through insurance.
How does knowledge infrastructure mobilization influence the safe operating space of regulated exploited ecosystems?
Jean-Denis Mathias | Published Tuesday, July 17, 2018Decision-makers often have to act before critical times to avoid the collapse of ecosystems using knowledge \textcolor{red}{that can be incomplete or biased}. Adaptive management may help managers tackle such issues. However, because the knowledge infrastructure required for adaptive management may be mobilized in several ways, we study the quality and the quantity of knowledge provided by this knowledge infrastructure. In order to analyze the influence of mobilized knowledge, we study how the following typology of knowledge and its use may impact the safe operating space of exploited ecosystems: 1) knowledge of the past based on a time series distorted by measurement errors; 2) knowledge of the current systems’ dynamics based on the representativeness of the decision-makers’ mental models of the exploited ecosystem; 3) knowledge of future events based on decision-makers’ likelihood estimates of extreme events based on modeling infrastructure (models and experts to interpret them) they have at their disposal. We consider different adaptive management strategies of a general regulated exploited ecosystem model and we characterize the robustness of these strategies to biased knowledge. Our results show that even with significant mobilized knowledge and optimal strategies, imperfect knowledge may still shrink the safe operating space of the system leading to the collapse of the system. However, and perhaps more interestingly, we also show that in some cases imperfect knowledge may unexpectedly increase the safe operating space by suggesting cautious strategies.
The code enables to calculate the safe operating spaces of different managers in the case of biased and unbiased knowledge.
A Simple Agent Based Modeling Tool for Plastic and Debris Tracking in Oceans
Subu Kandaswamy Koushik Sura Bhaskar Sai Amulya Murukutla Sai Pranay Raju Chinthala Abhishek Bobbillapati | Published Monday, October 04, 2021Plastics and the pollution caused by their waste have always been a menace to both nature and humans. With the continual increase in plastic waste, the contamination due to plastic has stretched to the oceans. Many plastics are being drained into the oceans and rose to accumulate in the oceans. These plastics have seemed to form large patches of debris that keep floating in the oceans over the years. Identification of the plastic debris in the ocean is challenging and it is essential to clean plastic debris from the ocean. We propose a simple tool built using the agent-based modeling framework NetLogo. The tool uses ocean currents data and plastic data both being loaded using GIS (Geographic Information System) to simulate and visualize the movement of floatable plastic and debris in the oceans. The tool can be used to identify the plastic debris that has been piled up in the oceans. The tool can also be used as a teaching aid in classrooms to bring awareness about the impact of plastic pollution. This tool could additionally assist people to realize how a small plastic chunk discarded can end up as large debris drifting in the oceans. The same tool might help us narrow down the search area while looking out for missing cargo and wreckage parts of ships or flights. Though the tool does not pinpoint the location, it might help in reducing the search area and might be a rudimentary alternative for more computationally expensive models.
Peer reviewed Yards
srailsback Emily Minor Soraida Garcia Philip Johnson | Published Thursday, November 02, 2023This is a model of plant communities in urban and suburban residential neighborhoods. These plant communities are of interest because they provide many benefits to human residents and also provide habitat for wildlife such as birds and pollinators. The model was designed to explore the social factors that create spatial patterns in biodiversity in yards and gardens. In particular, the model was originally developed to determine whether mimicry behaviors–-or neighbors copying each other’s yard design–-could produce observed spatial patterns in vegetation. Plant nurseries and socio-economic constraints were also added to the model as other potential sources of spatial patterns in plant communities.
The idea for the model was inspired by empirical patterns of spatial autocorrelation that have been observed in yard vegetation in Chicago, Illinois (USA), and other cities, where yards that are closer together are more similar than yards that are farther apart. The idea is further supported by literature that shows that people want their yards to fit into their neighborhood. Currently, the yard attribute of interest is the number of plant species, or species richness. Residents compare the richness of their yards to the richness of their neighbors’ yards. If a resident’s yard is too different from their neighbors, the resident will be unhappy and change their yard to make it more similar.
The model outputs information about the diversity and identity of plant species in each yard. This can be analyzed to look for spatial autocorrelation patterns in yard diversity and to explore relationships between mimicry behaviors, yard diversity, and larger scale diversity.
A Data-Driven Approach of Layout Evaluation for Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure Using Agent-Based Simulation and GIS
yue zhang | Published Thursday, September 21, 2023The development and popularisation of new energy vehicles have become a global consensus. The shortage and unreasonable layout of electric vehicle charging infrastructure (EVCI) have severely restricted the development of electric vehicles. In the literature, many methods can be used to optimise the layout of charging stations (CSs) for producing good layout designs. However, more realistic evaluation and validation should be used to assess and validate these layout options. This study suggested an agent-based simulation (ABS) model to evaluate the layout designs of EVCI and simulate the driving and charging behaviours of electric taxis (ETs). In the case study of Shenzhen, China, GPS trajectory data were used to extract the temporal and spatial patterns of ETs, which were then used to calibrate and validate the actions of ETs in the simulation. The ABS model was developed in a GIS context of an urban road network with travelling speeds of 24 h to account for the effects of traffic conditions. After the high-resolution simulation, evaluation results of the performance of EVCI and the behaviours of ETs can be provided in detail and in summary. Sensitivity analysis demonstrates the accuracy of simulation implementation and aids in understanding the effect of model parameters on system performance. Maximising the time satisfaction of ET users and reducing the workload variance of EVCI were the two goals of a multiobjective layout optimisation technique based on the Pareto frontier. The location plans for the new CS based on Pareto analysis can significantly enhance both metrics through simulation evaluation.
Shellmound Trade
Henrique de Sena Kozlowski | Published Saturday, June 15, 2024This model simulates different trade dynamics in shellmound (sambaqui) builder communities in coastal Southern Brazil. It features two simulation scenarios, one in which every site is the same and another one testing different rates of cooperation. The purpose of the model is to analyze the networks created by the trade dynamics and explore the different ways in which sambaqui communities were articulated in the past.
How it Works?
There are a few rules operating in this model. In either mode of simulation, each tick the agents will produce an amount of resources based on the suitability of the patches inside their occupation-radius, after that the procedures depend on the trade dynamic selected. For BRN? the agents will then repay their owed resources, update their reputation value and then trade again if they need to. For GRN? the agents will just trade with a connected agent if they need to. After that the agents will then consume a random amount of resources that they own and based on that they will grow (split) into a new site or be removed from the simulation. The simulation runs for 1000 ticks. Each patch correspond to a 300x300m square of land in the southern coast of Santa Catarina State in Brazil. Each agent represents a shellmound (sambaqui) builder community. The data for the world were made from a SRTM raster image (1 arc-second) in ArcMap. The sites can be exported into a shapefile (.shp) vector to display in ArcMap. It uses a UTM Sirgas 2000 22S projection system.
The cultural multiplier of climate policy
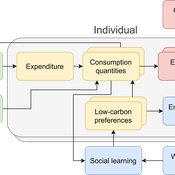
Daniel Torren-Peraire | Published Thursday, October 31, 2024For deep decarbonisation, the design of climate policy needs to account for consumption choices being influenced not only by pricing but also by social learning. This involves changes that pertain to the whole spectrum of consumption, possibly involving shifts in lifestyles. In this regard, it is crucial to consider not just short-term social learning processes but also slower, longer-term, cultural change. Against this background, we analyse the interaction between climate policy and cultural change, focusing on carbon taxation. We extend the notion of “social multiplier” of environmental policy derived in an earlier study to the context of multiple consumer needs while allowing for behavioural spillovers between these, giving rise to a “cultural multiplier”. We develop a model to assess how this cultural multiplier contributes to the effectiveness of carbon taxation. Our results show that the cultural multiplier stimulates greater low-carbon consumption compared to fixed preferences. The model results are of particular relevance for policy acceptance due to the cultural multiplier being most effective at low-carbon tax values, relative to a counter-case of short-term social interactions. Notably, at high carbon tax levels, the distinction between social and cultural multiplier effects diminishes, as the strong price signal drives even resistant individuals toward low-carbon consumption. By varying socio-economic conditions, such as substitutability between low- and high-carbon goods, social network structure, proximity of like-minded individuals and the richness of consumption lifestyles, the model provides insight into how cultural change can be leveraged to induce maximum effectiveness of climate policy.
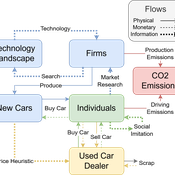
Driving in the wrong direction? A co-evolutionary model of electric vehicle adoption and innovation
Daniel Torren-Peraire | Published Friday, July 11, 2025Car-centric societies face substantial challenges in moving towards sustainable
mobility systems, with internal combustion engine vehicles remaining a major
source of emissions. Electric vehicles play a critical role in addressing this challenge, yet their diffusion depends on the interaction of consumer behaviour, firm
innovation, and policy incentives. This paper develops an agent-based model to
examine these dynamics, calibrated on the data for the state of California over
2001-2023. In the model, heterogeneous car users influenced by their social peers
…
Displaying 10 of 440 results for "Therese Lindahl" clear search