About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1170 results for "Aad Kessler" clear search
Pollution-development Tradeoffs in Nigeria--an Agent-based Model
Christopher Thron | Published Thursday, June 03, 2021Like many developing countries, Nigeria is faced with a number of tradeoffs that pit rapid economic development against environmental preservation. Environmentally sustainable, “green” economic development is slower, more costly, and more difficult than unrestricted, unregulated economic growth. The mathematical model that we develop in this code suggests that widespread public awareness of environmental issues is insufficient to prevent the tendency towards sacrificing the environment for the sake of growth. Even if people have an understanding of negative impacts and always choose to act in their own self-interest, they may still act collectively in such a way as to bring down the quality of life for the entire society. We conclude that additional actions must be taken besides raising public awareness of the environmental problem.
Multi-level model of attitudinal dynamics
Ingo Wolf | Published Wednesday, April 06, 2016 | Last modified Wednesday, May 04, 2016A model of attitudinal dynamics based on the cognitive mechanism of emotional coherence. The code is written in Java. For initialization an additional dataset is required.
Peer reviewed Emergence of Organizations out of Garbage Can Dynamics
Guido Fioretti | Published Monday, April 20, 2020 | Last modified Sunday, April 26, 2020The Garbage Can Model of Organizational Choice (GCM) is a fundamental model of organizational decision-making originally propossed by J.D. Cohen, J.G. March and J.P. Olsen in 1972. In their model, decisions are made out of random meetings of decision-makers, opportunities, solutions and problems within an organization.
With this model, these very same agents are supposed to meet in society at large where they make decisions according to GCM rules. Furthermore, under certain additional conditions decision-makers, opportunities, solutions and problems form stable organizations. In this artificial ecology organizations are born, grow and eventually vanish with time.
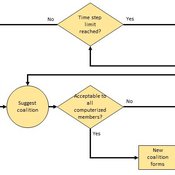
Heuristic Algorithm for Generating Strategic Coalition Structures
Andrew Collins Daniele Vernon-Bido | Published Monday, October 12, 2020The purpose of the model is to generate coalition structures of different glove games, using a specially designed algorithm. The coalition structures can be are later analyzed by comparing them to core partitions of the game used. Core partitions are coalition structures where no subset of players has an incentive to form a new coalition.
The algorithm used in this model is an advancement of the algorithm found in Collins & Frydenlund (2018). It was used used to generate the results in Vernon-Bido & Collins (2021).
Gender differentiation model
Sylvie Huet | Published Monday, April 20, 2020 | Last modified Thursday, April 23, 2020This is a gender differentiation model in terms of reputations, prestige and self-esteem (presented in the paper https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0236840). The model is based on the influence function of the Leviathan model (Deffuant, Carletti, Huet 2013 and Huet and Deffuant 2017) considering two groups.
This agent-based model studies how inequalities can be explained by the difference of open-mindness between two groups of interacting agents. We consider agents having an opinion/esteem about each other and about themselves. During dyadic meetings, agents change their respective opinion about each other and possibly about other agents they gossip about, with a noisy perception of the opinions of their interlocutor. Highly valued agents are more influential in such encounters. We study an heterogeneous population of two different groups: one more open to influence of others, taking less into account their perceived difference of esteem, called L; a second one less prone to it, called S, who designed the credibility they give to others strongly based on how higher or lower valued than themselves they perceive them.
We show that a mixed population always turns in favor to some agents belonging to the group of less open-minded agents S, and harms the other group: (1) the average group self-opinion or reputation of S is always better than the one of L; (2) the higher rank in terms of reputation are more frequently occupied by the S agents while the L agents occupy more the bottom rank; (3) the properties of the dynamics of differentiation between the two groups are similar to the properties of the glass ceiling effect proposed by Cotter et al (2001).
Peer reviewed SIM-VOLATILE: Adoption of emerging circular technologies in the waste-treatment sector
Siavash Farahbakhsh | Published Wednesday, December 14, 2022The SIM-VOLATILE model is a technology adoption model at the population level. The technology, in this model, is called Volatile Fatty Acid Platform (VFAP) and it is in the frame of the circular economy. The technology is considered an emerging technology and it is in the optimization phase. Through the adoption of VFAP, waste-treatment plants will be able to convert organic waste into high-end products rather than focusing on the production of biogas. Moreover, there are three adoption/investment scenarios as the technology enables the production of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), single-cell oils (SCO), and polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA). However, due to differences in the processing related to the products, waste-treatment plants need to choose one adoption scenario.
In this simulation, there are several parameters and variables. Agents are heterogeneous waste-treatment plants that face the problem of circular economy technology adoption. Since the technology is emerging, the adoption decision is associated with high risks. In this regard, first, agents evaluate the economic feasibility of the emerging technology for each product (investment scenarios). Second, they will check on the trend of adoption in their social environment (i.e. local pressure for each scenario). Third, they combine these two economic and social assessments with an environmental assessment which is their environmental decision-value (i.e. their status on green technology). This combination gives the agent an overall adaptability fitness value (detailed for each scenario). If this value is above a certain threshold, agents may decide to adopt the emerging technology, which is ultimately depending on their predominant adoption probabilities and market gaps.
CEDSS is an agent-based model of domestic energy demand at the level of a small community.
An agent-based model generating social practices
Georg Holtz | Published Tuesday, June 04, 2013 | Last modified Thursday, January 30, 2014This model expands approaches from social practice theories and is used to investigate the ability of the underlying conceptual model to explain the emergence of social practices, defined as routine behaviour that is similar amoung peers.
A Simulation of Entrepreneurial Spawning
Mark Bagley | Published Wednesday, June 08, 2016 | Last modified Friday, June 30, 2017Industrial clustering patterns are the result of an entrepreneurial process where spinoffs inherit the ideas and attributes of their parent firms. This computational model maps these patterns using abstract methodologies.
LAMDA - Learning Agents for Mechanism-Design Analysis
Iris Lorscheid Matthias Meyer | Published Monday, August 08, 2016The simulation model LAMDA investigates the influences of varying cognitive abilities of the decision maker on the truth-inducing effect of the Groves mechanism. Bounded rationality concepts are represented by information states and learning models.
Displaying 10 of 1170 results for "Aad Kessler" clear search