About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1105 results for "Oto Hudec" clear search
Simple models with different types of complexity
Michael Roos | Published Tuesday, September 17, 2024 | Last modified Saturday, March 01, 2025Hierarchical problem-solving model
The model simulates a hierarchical problem-solving process in which a manager delegates parts of a problem to specialists, who attempt to solve specific aspects based on their unique skills. The goal is to examine how effectively the hierarchical structure works in solving the problem, the total cost of the process, and the resulting solution quality.
Problem-solving random network model
The model simulates a network of agents (generalists) who collaboratively solve a fixed problem by iterating over it and using their individual skills to reduce the problem’s complexity. The goal is to study the dynamics of the problem-solving process, including agent interactions, work cycles, total cost, and solution quality.
Pest dispersion (simplified representation)
François Rebaudo | Published Wednesday, October 27, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013Simplified representation of the model used to present the global model to farmers
Ant Colony Optimization for infrastructure routing
Igor Nikolic Emile Chappin P W Heijnen | Published Wednesday, March 05, 2014 | Last modified Saturday, March 24, 2018The mode implements a variant of Ant Colony Optimization to explore routing on infrastructures through a landscape with forbidden zones, connecting multiple sinks to one source.
WeDiG Sim
Reza Shamsaee | Published Monday, May 14, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013WeDiG Sim- Weighted Directed Graph Simulator - is an open source application that serves to simulate complex systems. WeDiG Sim reflects the behaviors of those complex systems that put stress on scale-free, weightedness, and directedness. It has been implemented based on “WeDiG model” that is newly presented in this domain. The WeDiG model can be seen as a generalized version of “Barabási-Albert (BA) model”. WeDiG not only deals with weighed directed systems, but also it can handle the […]
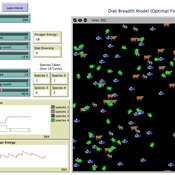
Diet breadth model from Optimal Foraging Theory (Human Behavioral Ecology)
C Michael Barton | Published Wednesday, November 26, 2008 | Last modified Thursday, March 12, 2015Diet breadth is a classic optimal foraging theory (OFT) model from human behavioral ecology (HBE). Different resources, ranked according to their food value and processing costs, are distributed in th
Peer reviewed Pumpa irrigation model
Marco Janssen Irene Perez Ibarra | Published Wednesday, January 09, 2013 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is a replication of the Pumpa model that simulates the Pumpa Irrigation System in Nepal (Cifdaloz et al., 2010).
Peer reviewed The dynamical relationship between individual needs and group performance: A simulation of the self-organising task allocation process
Shaoni Wang | Published Tuesday, October 05, 2021The purpose of the model is to study the dynamical relationship between individual needs and group performance when focusing on self-organizing task allocation. For this, we develop a model that formalizes Deci & Ryan’s self-determination theory (SDT) theory into an ABM creating a framework to study the social dynamics that pertain to the mutual relations between the individual and group level of team performance. Specifically, it aims to answer how the three individual motivations of autonomy, competence, and belonging affect team performance.
MEGADAPT - Socio-hydrological risk model - Theoretical (no data) implementation
Marco Janssen Andres Baeza-Castro Luis Bojorquez Hallie Eakin | Published Wednesday, February 06, 2019The model simulates the decisions of residents and a water authority to respond to socio-hydrological hazards. Residents from neighborhoods are located in a landscape with topographic complexity and two problems: water scarcity in the peripheral neighborhoods at high altitude and high risk of flooding in the lowlands, at the core of the city. The role of the water authority is to decide where investments in infrastructure should be allocated to reduce the risk to water scarcity and flooding events in the city, and these decisions are made via a multi-objective site selection procedure. This procedure accounts for the interdependencies and feedback between the urban landscape and a policy scenario that defines the importance, or priorities, that the authority places on four criteria.
Neighborhoods respond to the water authority decisions by protesting against the lack of investment and the level of exposure to water scarcity and flooding. Protests thus simulate a form of feedback between local-level outcomes (flooding and water scarcity) and higher-level decision-making. Neighborhoods at high altitude are more likely to be exposed to water scarcity and lack infrastructure, whereas neighborhoods in the lowlands tend to suffer from recurrent flooding. The frequency of flooding is also a function of spatially uniform rainfall events. Likewise, neighborhoods at the periphery of the urban landscape lack infrastructure and suffer from chronic risk of water scarcity.
The model simulates the coupling between the decision-making processes of institutional actors, socio-political processes and infrastructure-related hazards. In the documentation, we describe details of the implementation in NetLogo, the description of the procedures, scheduling, and the initial conditions of the landscape and the neighborhoods.
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation under Grant No. 1414052, CNH: The Dynamics of Multi-Scalar Adaptation in Megacities (PI Hallie Eakin).
AnimDens NetLogo
Miguel Pais Christine Ward-Paige | Published Friday, February 10, 2017 | Last modified Sunday, February 23, 2020The model demonstrates how non-instantaneous sampling techniques produce bias by overestimating the number of counted animals, when they move relative to the person counting them.
Learning Extension - RAGE RAngeland Grazing Model
Nikita Strelkovskii Cristina I. Apetrei Nikolay Khabarov Valeria Javalera Rincón | Published Saturday, July 22, 2023This is an extension of the original RAGE model (Dressler et al. 2018), where we add learning capabilities to agents, specifically learning-by-doing and social learning (two processes central to adaptive (co-)management).
The extension module is applied to smallholder farmers’ decision-making - here, a pasture (patch) is the private property of the household (agent) placed on it and there is no movement of the households. Households observe the state of the pasture and their neighrbours to make decisions on how many livestock to place on their pasture every year. Three new behavioural types are created (which cannot be combined with the original ones): E-RO (baseline behaviour), E-LBD (learning-by-doing) and E-RO-SL1 (social learning). Similarly to the original model, these three types can be compared regarding long-term social-ecological performance. In addition, a global strategy switching option (corresponding to double-loop learning) allows users to study how behavioural strategies diffuse in a heterogeneous population of learning and non-learning agents.
An important modification of the original model is that extension agents are heterogeneous in how they deal with uncertainty. This is represented by an agent property, called the r-parameter (household-risk-att in the code). The r-parameter is catch-all for various factors that form an agent’s disposition to act in a certain way, such as: uncertainty in the sensing (partial observability of the resource system), noise in the information received, or an inherent characteristic of the agent, for instance, their risk attitude.
Displaying 10 of 1105 results for "Oto Hudec" clear search