About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1188 results for "Ian M Hamilton" clear search
Emergency Warning Dissemination in a Multiplex Social Network
Charles Koll | Published Tuesday, January 31, 2023This is an interdisciplinary agent-based model with Monte Carlo simulations to assess the relative effects of broadcast and contagion processes in a multiplex social network. This multiplex approach models multiple channels of informal communication - phone, word-of-mouth, and social media - that vary in their attribute values. Each agent is an individual in a threatened community who, once warned, has a probability of warning others in their social network using one of these channels. The probability of an individual warning others is based on their warning source and the time remaining until disaster impact, among other variables. Default parameter values were chosen from empirical studies of disaster warnings along with the spatial aspects of Coos Bay, OR, USA and Seaside, OR, USA communities.
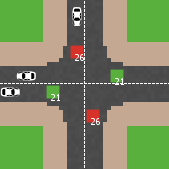
Modelling an intersection with traffic signal countdown timer
Eduard | Published Thursday, May 19, 2022Developed as a part of a project in the University of Augsburg, Institute of Geography, it simulates the traffic in an intersection or junction which uses either regular traffic lights or traffic lights with a countdown timer. The model tracks the average speed of cars before and after traffic lights as well as the throughput.
Artificial Long House Valley-Black Mesa
Lisa Sattenspiel Amy Warren | Published Thursday, March 19, 2020This model is an extension of the Artificial Long House Valley (ALHV) model developed by the authors (Swedlund et al. 2016; Warren and Sattenspiel 2020). The ALHV model simulates the population dynamics of individuals within the Long House Valley of Arizona from AD 800 to 1350. Individuals are aggregated into households that participate in annual agricultural and demographic cycles. The present version of the model incorporates features of the ALHV model including realistic age-specific fertility and mortality and, in addition, it adds the Black Mesa environment and population, as well as additional methods to allow migration between the two regions.
As is the case for previous versions of the ALHV model as well as the Artificial Anasazi (AA) model from which the ALHV model was derived (Axtell et al. 2002; Janssen 2009), this version makes use of detailed archaeological and paleoenvironmental data from the Long House Valley and the adjacent areas in Arizona. It also uses the same methods as the original AA model to estimate annual maize productivity of various agricultural zones within the Long House Valley. A new environment and associated methods have been developed for Black Mesa. Productivity estimates from both regions are used to determine suitable locations for households and farms during each year of the simulation.
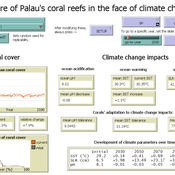
Development of coral reefs under climate change impacts and adaptation options
Nina Preußler | Published Friday, May 30, 2025This NetLogo model simulates how coral reefs around the islands of Palau would develop under different emission scenarios and with selected adaptation strategies. Reef health is indicated by coral cover (%) and is affected by four major climate change impacts: increasing sea surface temperature, sea level rise, ocean acidification, and more intense typhoons. The model differentiates between inner and outer reefs, with the former naturally adapted to warmer, more acidic waters. The simulation includes bleaching events and possible recovery. In addition, the user can choose between different coral transplantation strategies as well as regulate natural thermal adaptation rates.
Peer reviewed The Indus Village's Weather model: procedural generation of daily weather
Andreas Angourakis | Published Tuesday, May 13, 2025Overview
The Weather model is a procedural generation model designed to create realistic daily weather data for socioecological simulations. It generates synthetic weather time series for solar radiation, temperature, and precipitation using algorithms based on sinusoidal and double logistic functions. The model incorporates stochastic variation to mimic unpredictable weather patterns and aims to provide realistic yet flexible weather inputs for exploring diverse climate scenarios.
The Weather model can be used independently or integrated into larger models, providing realistic weather patterns without extensive coding or data collection. It can be customized to meet specific requirements, enabling users to gain a better understanding of the underlying mechanisms and have greater confidence in their applications.
…
Peer reviewed Descriptive Norm and Fraud Dynamics
Alexandra Eckert Matthias Meyer Christian Stindt | Published Tuesday, January 07, 2025The “Descriptive Norm and Fraud Dynamics” model demonstrates how fraudulent behavior can either proliferate or be contained within non-hierarchical organizations, such as peer networks, through social influence taking the form of a descriptive norm. This model expands on the fraud triangle theory, which posits that an individual must concurrently possess a financial motive, perceive an opportunity, and hold a pro-fraud attitude to engage in fraudulent activities (red agent). In the absence of any of these elements, the individual will act honestly (green agent).
The model explores variations in a descriptive norm mechanism, ranging from local distorted knowledge to global perfect knowledge. In the case of local distorted knowledge, agents primarily rely on information from their first-degree colleagues. This knowledge is often distorted because agents are slow to update their empirical expectations, which are only partially revised after one-to-one interactions. On the other end of the spectrum, local perfect knowledge is achieved by incorporating a secondary source of information into the agents’ decision-making process. Here, accurate information provided by an observer is used to update empirical expectations.
The model shows that the same variation of the descriptive norm mechanism could lead to varying aggregate fraud levels across different fraud categories. Two empirically measured norm sensitivity distributions associated with different fraud categories can be selected into the model to see the different aggregate outcomes.
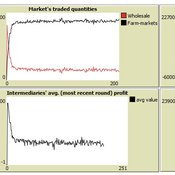
Market-level effects of firm-level adaptation and intermediation in networked markets of fresh foods: a case study in Colombia.
César García-Díaz | Published Sunday, April 12, 2020 | Last modified Sunday, April 12, 2020This a model developed as a part of the paper Mejía, G. & García-Díaz, C. (2018). Market-level effects of firm-level adaptation and intermediation in networked markets of fresh foods: a case study in Colombia. Agricultural Systems 160: 132-142.
It simulates the competition dynamics of the potato market in Bogotá, Colombia. The model explores the economic impact of intermediary actors on the potato supply chain.
Diffusion dynamics in small-world networks with heterogeneous consumers
Sebastiano Delre | Published Saturday, September 10, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model simulates diffusion curves and it allows to test how social influence, network structure and consumer heterogeneity affect their spreads and their speeds.
A modified model of breeding synchrony in colonial birds
James Millington | Published Tuesday, June 26, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This generic individual-based model of a bird colony shows how the influence neighbour’s stress levels synchronize the laying date of neighbours and also of large colonies. The model has been used to demonstrate how this form of simulation model can be recognised as being ‘event-driven’, retaining a history in the patterns produced via simulated events and interactions.
A land-use model to illustrate ambiguity in design
Julia Schindler | Published Monday, October 15, 2012 | Last modified Friday, January 13, 2017This is an agent-based model that allows to test alternative designs for three model components. The model was built using the LUDAS design strategy, while each alternative is in line with the strategy. Using the model, it can be shown that alternative designs, though built on the same strategy, lead to different land-use patterns over time.
Displaying 10 of 1188 results for "Ian M Hamilton" clear search