About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 957 results for "Gert Jan Kramer" clear search
Role of Diversity in Team Performance: the Case of Missing Expertise, an Agent Based Simulations
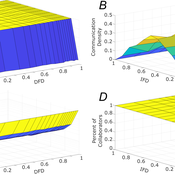
Tamás Kiss | Published Friday, December 29, 2023This ABM simulates problem solving agents as they work on a set of tasks. Each agent has a trait vector describing their skills. Two agents might form a collaboration if their traits are similar enough. Tasks are defined by a component vector. Agents work on tasks by decreasing tasks’ component vectors towards zero.
The simulation generates agents with given intrapersonal functional diversity (IFD), and dominant function diversity (DFD), and a set of random tasks and evaluates how agents’ traits influence their level of communication and the performance of a team of agents.
Modeling results highlight the importance of the distributions of agents’ properties forming a team, and suggests that for a thorough description of management teams, not only diversity measures based on individual agents, but an aggregate measure is also required.
…
Retention in Higher Education: An Agent-Based Model of Social Interactions and Motivated Agent Behavior
Andrew Crooks Amira Al-Khulaidy Stine | Published Wednesday, October 23, 2024Educational attainment and student retention in higher education are two of the main focuses of higher education research. Institutions in the U.S. are constantly looking for ways to identify areas of improvement across different aspects of the student experience on university campuses. This paper combines Department of Education data, U.S. Census data, and higher education theory on student retention, to build an agent-based model of student behavior.
Using a simple ABM to help undergraduates understand impacts of an invasive species: fish, lionfish, and zooplankton
Samantha Farquhar | Published Friday, February 24, 2023This model is an implementation of a predator-prey simulation using NetLogo programming language. It simulates the interaction between fish, lionfish, and zooplankton. Fish and lionfish are both represented as turtles, and they have their own energy level. In this simulation, lionfish eat fish, and fish eat zooplankton. Zooplankton are represented as green patches on the NetLogo world. Lionfish and fish can reproduce and gain energy by eating other turtles or zooplankton.
This model was created to help undergraduate students understand how simulation models might be helpful in addressing complex environmental problems. In this case, students were asked to use this model to make predictions about how the introduction of lionfish (considered an invasive species in some places) might alter the ecosystem.
Reflexivity in a diffusion of innovations model
César García-Díaz Carlos Cordoba | Published Thursday, May 07, 2020In this agent-based model, agents decide to adopt a new product according to a utility function that depends on two kinds of social influences. First, there is a local influence exerted on an agent by her closest neighbors that have already adopted, and also by herself if she feels the product suits her personal needs. Second, there is a global influence which leads agents to adopt when they become aware of emerging trends happening in the system. For this, we endow agents with a reflexive capacity that allows them to recognize a trend, even if they can not perceive a significant change in their neighborhood.
Results reveal the appearance of slowdown periods along the adoption rate curve, in contrast with the classic stylized bell-shaped behavior. Results also show that network structure plays an important role in the effect of reflexivity: while some structures (e.g., scale-free networks) may amplify it, others (e.g., small-world structure) weaken such an effect.
Peer reviewed Are Countertrade credits as flexible and efficient as cash? A novel approach to reducing income inequality using countertrade methodology.
Peter Malliaros | Published Monday, May 03, 2021 | Last modified Tuesday, May 11, 2021The impacts of income inequality can be seen everywhere, regardless of the country or the level of economic development. According to the literature review, income inequality has negative impacts in economic, social, and political variables. Notwithstanding of how well or not countries have done in reducing income inequality, none have been able to reduce it to a Gini Coefficient level of 0.2 or less.
This is the promise that a novel approach called Counterbalance Economics (CBE) provides without the need of increased taxes.
Based on the simulation, introducing the CBE into the Australian, UK, US, Swiss or German economies would result in an overall GDP increase of under 1% however, the level of inequality would be reduced from an average of 0.33 down to an average of 0.08. A detailed explanation of how to use the model, software, and data dependencies along with all other requirements have been included as part of the info tab in the model.
04 TpLab V2.08 – Teleological Pruning Laboratory
Garvin Boyle | Published Saturday, April 15, 2017Our societal belief systems are pruned by evolution, informing our unsustainable economies. This is one of a series of models exploring the dynamics of sustainable economics – PSoup, ModEco, EiLab, OamLab, MppLab, TpLab, CmLab.
Contract farming in the Mekong Delta's rice supply chain
Hung Nguyen | Published Tuesday, February 05, 2019We study three obstacles of the expansion of contract rice farming in the Mekong Delta (MKD) region. The failure of buyers in building trust-based relationship with small-holder farmers, unattractive offered prices from the contract farming scheme, and limited rice processing capacity have constrained contractors from participating in the large-scale paddy field program. We present an agent-based model to examine the viability of contract farming in the region from the contractor perspective.
The model focuses on financial incentives and trust, which affect the decision of relevant parties on whether to participate and honor a contract. The model is also designed in the context of the MKD’s rice supply chain with two contractors engaging in the contract rice farming scheme alongside an open market, in which both parties can renege on the agreement. We then evaluate the contractors’ performances with different combinations of scenarios related to the three obstacles.
Our results firstly show that a fully-equipped contractor who opportunistically exploits a relatively small proportion (less than 10%) of the contracted farmers in most instances can outperform spot market-based contractors in terms of average profit achieved for each crop. Secondly, a committed contractor who offers lower purchasing prices than the most typical rate can obtain better earnings per ton of rice as well as higher profit per crop. However, those contractors in both cases could not enlarge their contract farming scheme, since either farmers’ trust toward them decreases gradually or their offers are unable to compete with the benefits from a competitor or the spot market. Thirdly, the results are also in agreement with the existing literature that the contract farming scheme is not a cost-effective method for buyers with limited rice processing capacity, which is a common situation among the contractors in the MKD region.
DIAL is a model of group dynamics and opinion dynamics. It features dialogues, in which agents put their reputation at stake. Intra-group radicalisation of opinions appears to be an emergent phenomenon.
FlowLogo for a real case study
Vahid Aghaie | Published Monday, May 18, 2020Juan Castilla-Rho et al. (2015) developed a platform, named FLowLogo, which integrates a 2D, finite-difference solution of the governing equations of groundwater flow with agent-based simulation. We used this model for Rafsanjan Aquifer, which is located in an arid region in Iran. To use FLowLogo for a real case study, one needs to add GIS shapefiles of boundary conditions and modify the code written in NetLogo a little bit. The FlowLogo model used in our research is presented here.
Agent-based Line-of-Sight Simulation for safer Crossings (Short Paper - Netlogo Model)
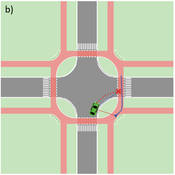
Vincent Franke | Published Thursday, August 05, 2021This software simulates cars and bicycles as traffic participants while crossing different crossroad designs such as roundabouts, protected crossroads and standard crossroads. It is written in Netlogo 6.2 and aims to identify safety characteristics of these layouts using agent-based modeling. Participants track the line of sight to each other and print them as an output alongside with the adjacent destination, used layout, count of collisions/cars/bicycles and time.
Detailed information can be found within the info tab of the program itself.
Displaying 10 of 957 results for "Gert Jan Kramer" clear search