About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 986 results for "J Van Der Beek" clear search
TERRoir level Organic matter Interactions and Recycling model
Myriam Grillot | Published Wednesday, April 19, 2017 | Last modified Wednesday, June 17, 2020The TERROIR agent-based model was built for the multi-level analysis of biomass and nutrient flows within agro-sylvo-pastoral villages in West Africa. It explicitly takes into account both human organization and spatial extension of such flows.
Formation of Lithic Assemblages v. 1
C Michael Barton Julien Riel-Salvatore | Published Thursday, September 04, 2014This model represents technological and ecological behaviors of mobile hunter-gatherers, in a variable environment, as they produce, use, and discard chipped stone artifacts. The results can be analyzed and compared with archaeological sites.
Replication of ECEC model: Environmental Feedback and the Evolution of Cooperation
Pierre Bommel | Published Tuesday, April 05, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The model, presented here, is a re-implementation of the Pepper and Smuts’ model : - Pepper, J.W. and B.B. Smuts. 2000. “The evolution of cooperation in an ecological context: an agent-based model”. Pp. 45-76 in T.A. Kohler and G.J. Gumerman, eds. Dynamics of human and primate societies: agent-based modeling of social and spatial processes. Oxford University Press, Oxford. - Pepper, J.W. and B.B. Smuts. 2002. “Assortment through Environmental Feedback”. American Naturalist, 160: 205-213 […]
The Pampas Model: An agent-based model of agricultural systems in the Argentinean Pampas
Michael North Federico Bert Guillermo P Podestá Santiago L Rovere Charles Macal | Published Tuesday, July 16, 2013 | Last modified Tuesday, February 17, 2015The Pampas Model is an Agent-Based Model intended to explore the dynamics of structural and land use changes in agricultural systems of the Argentine Pampas in response to climatic, technological economic, and political drivers.
Collective Decision Making for Ecological Restoration
Dean Massey Moira Zellner Cristy Watkins Jeremy Brooks Kristen Ross | Published Friday, December 30, 2011 | Last modified Friday, November 21, 2014We present an agent-based model that maps out and simulates the processes by which individuals within ecological restoration organizations communicate and collectively make restoration decisions.
SimDrink: An agent-based NetLogo model of young, heavy drinkers for conducting alcohol policy experiments
Nick Scott James Wilson Michael Livingston Aaron Hart David Moore Paul Dietze | Published Friday, September 25, 2015 | Last modified Thursday, October 15, 2015A proof-of-concept agent-based model ‘SimDrink’, which simulates a population of 18-25 year old heavy alcohol drinkers on a night out in Melbourne to provide a means for conducting policy experiments to inform policy decisions.
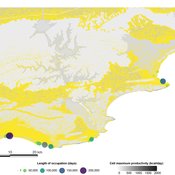
PaleoscapeABM: coastal occupation and shellfish discard
Claudine Gravel-Miguel | Published Tuesday, February 08, 2022This model builds on the Armature distribution within the PaleoscapeABM model, which is itself a variant of the PaleoscapeABM available here written by Wren and Janssen, and.
This model aims to explore where and how much shellfish is discarded at coastal and non-coastal locations by daily coastal foraging. We use this model’s output to test the idea that we can confidently use the archaeological record to evaluate the importance of shellfish in prehistoric people’s diets.
The recognition that aquatic adaptations likely had significant impacts on human evolution triggered an explosion of research on that topic. Recognizing coastal foraging in the past relies on the archaeological signature of that behavior. We use this model to explore why some coastal sites are very intensely occupied and see if it is due to the shellfish productivity of the coast.
An Agent-Based Model of Insurance Customer Behaviour with Word of Mouth Network in C#
Rei England Iqbal Owadally Douglas Wright | Published Friday, March 04, 2022This is an agent-based model with two types of agents: customers and insurers. Insurers are price-takers who choose how much to spend on their service quality, and customers evaluate insurers based on premium, brand preference, and their perceived service quality. Customers are also connected in a small-world network and may share their opinions with their network.
The ABM contains two types of agents: insurers and customers. These act within the environment of a motor insurance market. At each simulation, the model undergoes the following steps:
- Network generation: At the start of the simulation, the model generates a small world network of social links between the customers, and randomly assigns each customer to an initial insurer ...
HMODEL: an exploratory simulation of surface archaeological formation
Benjamin Davies Simon Holdaway Patricia Fanning | Published Thursday, November 30, 2017This model is used to simulate the influence of spatially and temporally variable sedimentary processes on the distribution of dated archaeological features in a surface context.
We construct a new type of agent-based model (ABM) that can simultaneously simulate land-use changes at multiple distant places (namely TeleABM, telecoupled agent-based model). We use soybean trade between Brazil and China as an example, where Brazil is the sending system and China is the receiving system because they are the world’s largest soybean exporter and importer respectively. We select one representative county in each country to calibrate and validate the model with spatio-temporal analysis of historical land-use changes and the empirical analysis of household survey data. The whole model is programmed on RePast Simphony. The most unique features of TeleABM are that it can simulate a telecoupled system and the flows between sending and receiving systems in this telecoupled system.
Displaying 10 of 986 results for "J Van Der Beek" clear search