About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 364 results for "Emmanuel Mhike Hove" clear search
Peer reviewed Industrial Symbiosis Network implementation ABM
Igor Nikolic Kasper Pieter Hendrik Lange Gijsbert Korevaar Paulien Herder | Published Tuesday, December 01, 2020 | Last modified Wednesday, June 16, 2021The purpose of the model is to explore the influence of actor behaviour, combined with environment and business model design, on the survival rates of Industrial Symbiosis Networks (ISN), and the cash flows of the agents. We define an ISN to be robust, when it is able to run for 10 years, without falling apart due to leaving agents.
The model simulates the implementation of local waste exchange collaborations for compost production, through the ISN implementation stages of awareness, planning, negotiation, implementation, and evaluation.
One central firm plays the role of waste processor in a local composting initiative. This firm negotiates with other firms to become a supplier of their organic residual streams. The waste suppliers in the model can decide to join the initiative, or to have the waste brought to the external waste incinerator. The focal point of the model are the company-level interactions during the implementation or ending of synergies.
…
Competitive Arousal Agent Based Model
Zoé Chollet | Published Friday, May 13, 2022What is it?
This model demonstrates a very simple bidding market where buyers try to acquire a desired item at the best price in a competitive environment
…
Agent-Based Simulation for International Tax Compliance
Peter Gerbrands | Published Tuesday, July 18, 2023Country-by-Country Reporting and Automatic Exchange of Information have recently been implemented in European Union (EU) countries. These international tax reforms increase tax compliance in the short term. In the long run, however, taxpayers will continue looking abroad to avoid taxation and, countries, looking for additional revenues, will provide opportunities. As a result, tax competition intensifies and the initial increase in compliance could reverse. To avoid international tax reforms being counteracted by tax competition, this paper suggests bilateral responsive regulation to maximize compliance. This implies that countries would use different tax policy instruments toward other countries, including tax and secrecy havens.
To assess the effectiveness of fully or partially enforce tax policies, this agent based model has been ran many times under different enforcement rules, which influence the perceived enforced- and voluntary compliance, as the slippery-slope model prescribes. Based on the dynamics of this perception and the extent to which agents influence each other, the annual amounts of tax evasion, tax avoidance and taxes paid are calculated over longer periods of time.
The agent-based simulation finds that a differentiated policy response could increase tax compliance by 6.54 percent, which translates into an annual increase of €105 billion in EU tax revenues on income, profits, and capital gains. Corporate income tax revenues in France, Spain, and the UK alone would already account for €35 billion.
Construction and Demolition model to track material flows and embodied carbon
Jonathan Edgardo Cohen | Published Monday, September 30, 2024Reusing existing material stocks in developed built environments can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of the construction and demolition sector. However, material reuse in urban areas presents technical, temporal, and geographical challenges. Although a better understanding of spatial and temporal changes in material stocks could improve city resource management, limited scientific contributions have addressed this challenge.
This study details the steps followed in developing a spatially explicit rule-based simulation of materials stock. The simulation provides a proof of concept by incorporating the spatial and temporal dimensions of construction and demolition activities to analyse how various urban parameters determine material flows and embodied carbon in urban areas. The model explores the effects of 1) re-using recycled materials, 2) demolitions, 3) renovations and 4) various building typologies.
To showcase the model’s capabilities, the residential building stock of Gothenburg City is used as a case study, and eight building materials are tracked. Environmental impacts (A1-A3) are calculated with embodied carbon factors. The main parameters are explored in a baseline scenario. Then, a second scenario focuses on a hypothetical policy that promotes improvements in building energy performance.
The simulation can be expanded to include more materials and built environment assets and allows for future explorations on, for example, the role of logistics, the implementation of recycling or reuse stations, and, in general, supporting sustainable and circular strategies from the construction sector.
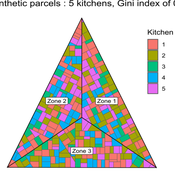
MeReDiem : Fallow Land Simulations to examine the conditions of sustainable village livelihood
Etienne DELAY Paul Chapron Mathieu | Published Monday, January 20, 2025 | Last modified Tuesday, January 21, 2025The MeReDiem model aims to simulate the effect of socio-agricultural practices of farmers and pastors on the food sustainability and soil fertility of a serrer village, in Senegal. The model is a central part of a companion modeling and exploration approach, described in a paper, currently under review)
The village population is composed of families (kitchens). Kitchens cultivate their land parcels to feed their members, aiming for food security at the family level. On a global level , the village tries to preserve the community fallow land as long as possible.
Kitchens sizes vary depending on the kitchens food production, births and migration when food is insufficient.
…
Diffusion dynamics in small-world networks with heterogeneous consumers
Sebastiano Delre | Published Saturday, September 10, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model simulates diffusion curves and it allows to test how social influence, network structure and consumer heterogeneity affect their spreads and their speeds.
Peer reviewed Hohokam Trade Networks Model
Joshua Watts | Published Sunday, October 26, 2014The Hohokam Trade Networks Model focuses on key features of the Hohokam economy to explore how differences in trade network topologies may show up in the archaeological record. The model is set in the Phoenix Basin of central Arizona, AD 200-1450.
Bicycle encounter model
Gudrun Wallentin | Published Saturday, October 29, 2016 | Last modified Friday, March 29, 2019This Bicycle encounter model builds on the Salzburg Bicycle model (Wallentin & Loidl, 2015). It simulates cyclist flows and encounters, which are locations of potential accidents between cyclists.
Peer reviewed FishCensus
Miguel Pais | Published Tuesday, December 06, 2016 | Last modified Thursday, February 09, 2017The FishCensus model simulates underwater visual census methods, where a diver estimates the abundance of fish. A separate model is used to shape species behaviours and save them to a file that can be shared and used by the counting model.
Agent-based model of WiFi tracking system in urban environment
Christopher Thron Khoi Tran | Published Friday, April 21, 2017This code simulates the WiFi user tracking system described in: Thron et al., “Design and Simulation of Sensor Networks for Tracking Wifi Users in Outdoor Urban Environments”. Testbenches used to create the figures in the paper are included.
Displaying 10 of 364 results for "Emmanuel Mhike Hove" clear search