About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 260 results for "Piergiuseppe Morone" clear search
Extended Flache and Mas (2008)
Hadi Aliahmadi | Published Wednesday, August 16, 2017 | Last modified Monday, February 26, 2018We extend the Flache-Mäs model to incorporate the location and dyadic communication regime of the agents in the opinion formation process. We make spatially proximate agents more likely to interact with each other in a pairwise communication regime.
Benchmark for RepastHPC Agent-based modeling and simulation (ABMS) platform
Andreu Moreno Vendrell Josep Jorba Eduardo César Anna Sikora | Published Friday, November 22, 2024Agent-based modeling and simulation (ABMS) is a class of computational models for simulating the actions and interactions of autonomous agents with the goal of assessing their effects on a system as a whole. Several frameworks for generating parallel ABMS applications have been developed taking advantage of their common characteristics, but there is a lack of a general benchmark for comparing the performance of generated applications. We propose and design a benchmark that takes into consideration the most common characteristics of this type of applications and includes parameters for influencing their relevant performance aspects. We provide an initial implementation of the benchmark for RepastHPC one of the most popular parallel ABMS platforms, and we use it for comparing the applications generated by these platforms.
Benchmark for FLAME Agent-based modeling and simulation (ABMS) platform
Andreu Moreno Vendrell Josep Jorba Eduardo César Anna Sikora | Published Friday, November 22, 2024Agent-based modeling and simulation (ABMS) is a class of computational models for simulating the actions and interactions of autonomous agents with the goal of assessing their effects on a system as a whole. Several frameworks for generating parallel ABMS applications have been developed taking advantage of their common characteristics, but there is a lack of a general benchmark for comparing the performance of generated applications. We propose and design a benchmark that takes into consideration the most common characteristics of this type of applications and includes parameters for influencing their relevant performance aspects. We provide an initial implementation of the benchmark for FLAME one of the most popular parallel ABMS platforms, and we use it for comparing the applications generated by these platforms.
Contact Tracing agent model
Andreu Moreno Vendrell Josep Jorba Eduardo César Anna Sikora | Published Friday, November 22, 2024Contact Tracing Repast HPC agent model
Between Pleasure and Contentment: Evolutionary Dynamics of Some Possible Parameters of Happiness
Yue Gao Shimon Edelman | Published Saturday, March 12, 2016 | Last modified Wednesday, March 16, 2016We build a computational model to investigate, in an evolutionary setting, a series of questions pertaining to happiness.
07 EffLab_V5.07 NL
Garvin Boyle | Published Monday, October 07, 2019EffLab was built to support the study of the efficiency of agents in an evolving complex adaptive system. In particular:
- There is a definition of efficiency used in ecology, and an analogous definition widely used in business. In ecological studies it is called EROEI (energy returned on energy invested), or, more briefly, EROI (pronounced E-Roy). In business it is called ROI (dollars returned on dollars invested).
- In addition, there is the more well-known definition of efficiency first described by Sadi Carnot, and widely used by engineers. It is usually represented by the Greek letter ‘h’ (pronounced as ETA). These two measures of efficiency bear a peculiar relationship to each other: EROI = 1 / ( 1 - ETA )
In EffLab, blind seekers wander through a forest looking for energy-rich food. In this multi-generational world, they live and reproduce, or die, depending on whether they can find food more effectively than their contemporaries. Data is collected to measure their efficiency as they evolve more effective search patterns.
…
The Thin Blue Line Between Protesters and Their Counter-Protesters
Tamsin Lee | Published Monday, March 26, 2018More frequently protests are accompanied by an opposing group performing a counter protest. This phenomenon can increase tension such that police must try to keep the two groups separated. However, what is the best strategy for police? This paper uses a simple agent-based model to determine the best strategy for keeping the two groups separated. The ‘thin blue line’ varies in density (number of police), width and the keenness of police to approach protesters. Three different groups of protesters are modelled to mimic peaceful, average and volatile protests. In most cases, a few police forming a single-file ‘thin blue line’ separating the groups is very effective. However, when the protests are more volatile, it is more effective to have many police occupying a wide ‘thin blue line’, and police being keen to approach protesters. To the authors knowledge, this is the first paper to model protests and counter-protests.
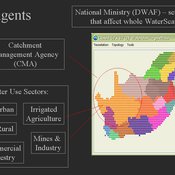
WaterScape
Erin Bohensky | Published Monday, February 06, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The WaterScape is an agent-based model of the South African water sector. This version of the model focuses on potential barriers to learning in water management that arise from interactions between human perceptions and social-ecological system conditions.
Peak-seeking Adder
Julia Kasmire Janne M Korhonen | Published Tuesday, December 02, 2014 | Last modified Friday, February 20, 2015Continuing on from the Adder model, this adaptation explores how rationality, learning and uncertainty influence the exploration of complex landscapes representing technological evolution.
This paper presents an agent-based model to study the dynamics of city-state systems in a constrained environment with limited space and resources. The model comprises three types of agents: city-states, villages, and battalions, where city-states, the primary decision-makers, can build villages for food production and recruit battalions for defense and aggression. In this setting, simulation results, generated through a multi-parameter grid sampling, suggest that risk-seeking strategies are more effective in high-cost scenarios, provided that the production rate is sufficiently high. Also, the model highlights the role of output productivity in defining which strategic preferences are successful in a long-term scenario, with higher outputs supporting more aggressive expansion and military actions, while resource limitations compel more conservative strategies focused on survival and resource conservation. Finally, the results suggest the existence of a non-linear effect of diminishing returns in strategic investments on successful strategies, emphasizing the need for careful resource allocation in a competitive environment.
Displaying 10 of 260 results for "Piergiuseppe Morone" clear search