About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 227 results for "Brian Mac Namee" clear search
Exploring social psychology theory for modelling farmer decision-making
James Millington | Published Tuesday, September 18, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013To investigate the potential of using Social Psychology Theory in ABMs of natural resource use and show proof of concept, we present an exemplary agent-based modelling framework that explicitly represents multiple and hierarchical agent self-concepts
Extended Flache and Mas (2008)
Hadi Aliahmadi | Published Wednesday, August 16, 2017 | Last modified Monday, February 26, 2018We extend the Flache-Mäs model to incorporate the location and dyadic communication regime of the agents in the opinion formation process. We make spatially proximate agents more likely to interact with each other in a pairwise communication regime.
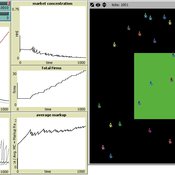
Toward Market Structure as a Complex System: A Web Based Simulation Assignment Implemented in Netlogo
Timothy Kochanski | Published Monday, February 14, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is the model for a paper that is based on a simulation model, programmed in Netlogo, that demonstrates changes in market structure that occur as marginal costs, demand, and barriers to entry change. Students predict and observe market structure changes in terms of number of firms, market concentration, market price and quantity, and average marginal costs, profits, and markups across the market as firms innovate. By adjusting the demand growth and barriers to entry, students can […]
Peer reviewed Casting: A Bio-Inspired Method for Restructuring Machine Learning Ensembles
Colin Lynch Bryan Daniels | Published Thursday, September 18, 2025The wisdom of the crowd refers to the phenomenon in which a group of individuals, each making independent decisions, can collectively arrive at highly accurate solutions—often more accurate than any individual within the group. This principle relies heavily on independence: if individual opinions are unbiased and uncorrelated, their errors tend to cancel out when averaged, reducing overall bias. However, in real-world social networks, individuals are often influenced by their neighbors, introducing correlations between decisions. Such social influence can amplify biases, disrupting the benefits of independent voting. This trade-off between independence and interdependence has striking parallels to ensemble learning methods in machine learning. Bagging (bootstrap aggregating) improves classification performance by combining independently trained weak learners, reducing bias. Boosting, on the other hand, explicitly introduces sequential dependence among learners, where each learner focuses on correcting the errors of its predecessors. This process can reinforce biases present in the data even if it reduces variance. Here, we introduce a new meta-algorithm, casting, which captures this biological and computational trade-off. Casting forms partially connected groups (“castes”) of weak learners that are internally linked through boosting, while the castes themselves remain independent and are aggregated using bagging. This creates a continuum between full independence (i.e., bagging) and full dependence (i.e., boosting). This method allows for the testing of model capabilities across values of the hyperparameter which controls connectedness. We specifically investigate classification tasks, but the method can be used for regression tasks as well. Ultimately, casting can provide insights for how real systems contend with classification problems.
Pedestrian model
Gudrun Wallentin Dana Kaziyeva Martin Loidl Petra Stutz | Published Monday, August 07, 2023The model generates disaggregated traffic flows of pedestrians, simulating their daily mobility behaviour represented as probabilistic rules. Various parameters of physical infrastructure and travel behaviour can be altered and tested. This allows predicting potential shifts in traffic dynamics in a simulated setting. Moreover, assumptions in decision-making processes are general for mid-sized cities and can be applied to similar areas.
Together with the model files, there is the ODD protocol with the detailed description of model’s structure. Check the associated publication for results and evaluation of the model.
Installation
Download GAMA-platform (GAMA1.8.2 with JDK version) from https://gama-platform.github.io/. The platform requires a minimum of 4 GB of RAM.
…
NarrABS
Tilman Schenk | Published Thursday, September 20, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An agent based simulation of a political process based on stakeholder narratives
Peer reviewed JuSt-Social COVID-19
Jennifer Badham | Published Thursday, June 18, 2020 | Last modified Monday, March 29, 2021NetLogo model that allows scenarios concerning general social distancing, shielding of high-risk individuals, and informing contacts when symptomatic. Documentation includes a user manual with some simple scenarios, and technical information including descriptions of key procedures and parameter values.
00 PSoup V1.22 – Primordial Soup
Garvin Boyle | Published Thursday, April 13, 2017PSoup is an educational program in which evolution is demonstrated, on the desk-top, as you watch. Blind bugs evolve sophisticated heuristic search algorithms to be the best at finding food fast.
Agent-Based Model of Transhumant Decision-Making Processes in Senegal
Cheick Amed Diloma Gabriel TRAORE Etienne DELAY Alassane Bah Djibril Diop | Published Wednesday, July 03, 2024Sahelian transhumance is a type of socio-economic and environmental pastoral mobility. It involves the movement of herds from their terroir of origin (i.e., their original pastures) to one or more host terroirs, followed by a return to the terroir of origin. According to certain pastoralists, the mobility of herds is planned to prevent environmental degradation, given the continuous dependence of these herds on their environment. However, these herds emit Greenhouse Gases (GHGs) in the spaces they traverse. Given that GHGs contribute to global warming, our long-term objective is to quantify the GHGs emitted by Sahelian herds. The determination of these herds’ GHG emissions requires: (1) the artificial replication of the transhumance, and (2) precise knowledge of the space used during their transhumance.
This article presents the design of an artificial replication of the transhumance through an agent-based model named MSTRANS. MSTRANS determines the space used by transhumant herds, based on the decision-making process of Sahelian transhumants.
MSTRANS integrates a constrained multi-objective optimization problem and algorithms into an agent-based model. The constrained multi-objective optimization problem encapsulates the rationality and adaptability of pastoral strategies. Interactions between a transhumant and its socio-economic network are modeled using algorithms, diffusion processes, and within the multi-objective optimization problem. The dynamics of pastoral resources are formalized at various spatio-temporal scales using equations that are integrated into the algorithms.
The results of MSTRANS are validated using GPS data collected from transhumant herds in Senegal. MSTRANS results highlight the relevance of integrated models and constrained multi-objective optimization for modeling and monitoring the movements of transhumant herds in the Sahel. Now specialists in calculating greenhouse gas emissions have a reproducible and reusable tool for determining the space occupied by transhumant herds in a Sahelian country. In addition, decision-makers, pastoralists, veterinarians and traders have a reproducible and reusable tool to help them make environmental and socio-economic decisions.
Foundress dilemma model
Marco Janssen Takao Sasaki Zachary Joseph Shaffer Stephen Pratt Brian Haney Jennifer Fewell | Published Thursday, July 28, 2016A haystack-style model of group selection to capture the essential features of colony foundation for queens of the ant based on observation of the ant Pogonomyrmex californicus.
Displaying 10 of 227 results for "Brian Mac Namee" clear search