About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 318 results for "Shu-Heng Chen" clear search
Market for Protection
Steven Doubleday | Published Monday, July 01, 2013 | Last modified Monday, August 19, 2013Simulation to replicate and extend an analytical model (Konrad & Skaperdas, 2010) of the provision of security as a collective good. We simulate bandits preying upon peasants in an anarchy condition.
PSMED - Patagonia Simple Model of Ethnic Differentiation
Xavier Vilà Joan A Barceló J A Cuesta Florencia Del Castillo Ricardo Del Olmo José M Galán Laura Mameli Francisco J Miguel David Poza José I Santos | Published Tuesday, December 10, 2013Patagonia PSMED is an agent-based model designed to study a simple case of Evolution of Ethnic Differentiation. It replicates how can hunter-gatherer societies evolve and built cultural identities as a consequence of the way they interacted.
Thermostat II
María Pereda Jesús M Zamarreño | Published Thursday, June 12, 2014 | Last modified Monday, June 16, 2014A thermostat is a device that allows to have the temperature in a room near a desire value.
Segregation and Opinion Polarization
Thomas Feliciani Andreas Flache Jochem Tolsma | Published Wednesday, April 13, 2016This is a tool to explore the effects of groups´ spatial segregation on the emergence of opinion polarization. It embeds two opinion formation models: a model of negative (and positive) social influence and a model of persuasive argument exchange.
The Evolution of Tribalism: A Social-Ecological Model of Cooperation and Inter-group Conflict Under Pastoralism
Nicholas Seltzer | Published Monday, January 21, 2019This study investigates a possible nexus between inter-group competition and intra-group cooperation, which may be called “tribalism.” Building upon previous studies demonstrating a relationship between the environment and social relations, the present research incorporates a social-ecological model as a mediating factor connecting both individuals and communities to the environment. Cyclical and non-cyclical fluctuation in a simple, two-resource ecology drive agents to adopt either “go-it-alone” or group-based survival strategies via evolutionary selection. Novelly, this simulation employs a multilevel selection model allowing group-level dynamics to exert downward selective pressures on individuals’ propensity to cooperate within groups. Results suggest that cooperation and inter-group conflict are co-evolved in a triadic relationship with the environment. Resource scarcity increases inter-group competition, especially when resources are clustered as opposed to widely distributed. Moreover, the tactical advantage of cooperation in the securing of clustered resources enhanced selective pressure on cooperation, even if that implies increased individual mortality for the most altruistic warriors. Troubling, these results suggest that extreme weather, possibly as a result of climate change, could exacerbate conflict in sensitive, weather-dependent social-ecologies—especially places like the Horn of Africa where ecologically sensitive economic modalities overlap with high-levels of diversity and the wide-availability of small arms. As well, global development and foreign aid strategists should consider how plans may increase the value of particular locations where community resources are built or aid is distributed, potentially instigating tribal conflict. In sum, these factors, interacting with pre-existing social dynamics dynamics, may heighten inter-ethnic or tribal conflict in pluralistic but otherwise peaceful communities.
For special issue submission in JASSS.
Peer reviewed NetLogo model of USA mass shootings
Smarzhevskiy Ivan | Published Tuesday, September 24, 2019 | Last modified Tuesday, April 14, 2020Is the mass shooter a maniac or a relatively normal person in a state of great stress? According to the FBI report (Silver, J., Simons, A., & Craun, S. (2018). A Study of the Pre-Attack Behaviors of Active Shooters in the United States Between 2000 – 2013. Federal Bureau of Investigation, U.S. Department of Justice,Washington, D.C. 20535.), only 25% of the active shooters were known to have been diagnosed by a mental health professional with a mental illness of any kind prior to the offense.
The main objects of the model are the humans and the guns. The main factors influencing behavior are the population size, the number of people with mental disabilities (“psycho” in the model terminology) per 100,000 population, the total number of weapons (“guns”) in the population, the availability of guns for humans, the intensity of stressors affecting humans and the threshold level of stress, upon reaching which a person commits an act of mass shooting.
The key difference (in the model) between a normal person and a psycho is that a psycho accumulates stressors and, upon reaching a threshold level, commits an act of mass shooting. A normal person is exposed to stressors, but reaching the threshold level for killing occurs only when the simultaneous effect of stressors on him exceeds this level.
The population dynamics are determined by the following factors: average (normally distributed) life expectancy (“life_span” attribute of humans) and population growth with the percentage of newborns set by the value of the TickReprRatio% slider of the current population volume from 16 to 45 years old.Thus, one step of model time corresponds to a year.
Cellular automata model of social networks
Rubens de Almeida Zimbres | Published Tuesday, August 02, 2022This project was developed during the Santa Fe course Introduction to Agent-Based Modeling 2022. The origin is a Cellular Automata (CA) model to simulate human interactions that happen in the real world, from Rubens and Oliveira (2009). These authors used a market research with real people in two different times: one at time zero and the second at time zero plus 4 months (longitudinal market research). They developed an agent-based model whose initial condition was inherited from the results of the first market research response values and evolve it to simulate human interactions with Agent-Based Modeling that led to the values of the second market research, without explicitly imposing rules. Then, compared results of the model with the second market research. The model reached 73.80% accuracy.
In the same way, this project is an Exploratory ABM project that models individuals in a closed society whose behavior depends upon the result of interaction with two neighbors within a radius of interaction, one on the relative “right” and other one on the relative “left”. According to the states (colors) of neighbors, a given cellular automata rule is applied, according to the value set in Chooser. Five states were used here and are defined as levels of quality perception, where red (states 0 and 1) means unhappy, state 3 is neutral and green (states 3 and 4) means happy.
There is also a message passing algorithm in the social network, to analyze the flow and spread of information among nodes. Both the cellular automaton and the message passing algorithms were developed using the Python extension. The model also uses extensions csv and arduino.
Peer reviewed SequiaBasalto model
Marco Janssen Irene Perez Ibarra Pierre Bommel Diego J. Soler-Navarro Alicia Tenza Peral Francisco Dieguez Cameroni | Published Friday, May 26, 2023This is a replication of the SequiaBasalto model, originally built in Cormas by Dieguez Cameroni et al. (2012, 2014, Bommel et al. 2014 and Morales et al. 2015). The model aimed to test various adaptations of livestock producers to the drought phenomenon provoked by climate change. For that purpose, it simulates the behavior of one livestock farm in the Basaltic Region of Uruguay. The model incorporates the price of livestock, fodder and paddocks, as well as the growth of grass as a function of climate and seasons (environmental submodel), the life cycle of animals feeding on the pasture (livestock submodel), and the different strategies used by farmers to manage their livestock (management submodel). The purpose of the model is to analyze to what degree the common management practices used by farmers (i.e., proactive and reactive) to cope with seasonal and interannual climate variations allow to maintain a sustainable livestock production without depleting the natural resources (i.e., pasture). Here, we replicate the environmental and livestock submodel using NetLogo.
One year is 368 days. Seasons change every 92 days. Each day begins with the growth of grass as a function of climate and season. This is followed by updating the live weight of cows according to the grass height of their patch, and grass consumption, which is determined based on the updated live weight. After consumption, cows grow and reproduce, and a new grass height is calculated. Cows then move to the patch with less cows and with the highest grass height. This updated grass height value will be the initial grass height for the next day.
Seascapes of the Unreal: Using Agent Based Modeling to Examine Traditional Coast Salish Maritime Mobility
Adam Rorabaugh | Published Friday, December 22, 2023Non-traditional tools and mediums can provide unique methodological and interpretive opportunities for archaeologists. In this case, the Unreal Engine (UE), which is typically used for games and media, has provided a powerful tool for non-programmers to engage with 3D visualization and programming as never before. UE has a low cost of entry for researchers as it is free to download and has user-friendly “blueprint” tools that are visual and easily extendable. Traditional maritime mobility in the Salish Sea is examined using an agent-based model developed in blueprints. Focusing on the sea canoe travel of the Straits Salish northwestern Washington State and southwest British Columbia. This simulation integrates GIS data to assess travel time between Coast Salish archaeological village locations and archaeologically represented resource gathering areas. Transportation speeds informed by ethnographic data were used to examine travel times for short forays and longer inter-village journeys. The results found that short forays tended to half day to full day trips when accounting for resource gathering activities. Similarly, many locations in the Salish Sea were accessible in long journeys within two to three days, assuming fair travel conditions. While overall transportation costs to reach sites may be low, models such as these highlight the variability in transport risk and cost. The integration of these types of tools, traditionally used for entertainment, can increase the accessibility of modeling approaches to researchers, be expanded to digital storytelling, including aiding in the teaching of traditional ecological knowledge and placenames, and can have wide applications beyond maritime archaeology.
This is v0.01 of a UE5.2.1 agent based model.
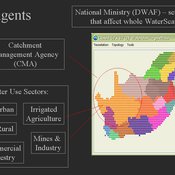
WaterScape
Erin Bohensky | Published Monday, February 06, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The WaterScape is an agent-based model of the South African water sector. This version of the model focuses on potential barriers to learning in water management that arise from interactions between human perceptions and social-ecological system conditions.
Displaying 10 of 318 results for "Shu-Heng Chen" clear search