About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1113 results for "Bin-Tzong Chi" clear search
FlowLogo: An agent-based platform for simulating complex human-aquifer interactions in managed groundwater systems
Juan Castilla-Rho | Published Sunday, August 30, 2015FlowLogo integrates agent-based and groundwater flow simulation. It aims to simplify the process of developing participatory ABMs in the groundwater space and begin the exploration of novel, bottom-up solutions to conflicts in shared aquifers.
An epidemiological-economic agent-based model of Huanglongbing and Asian citrus psyllid control in California
Jonathan Kaplan | Published Wednesday, June 01, 2022This model simulates economic and epidemiological interaction between citrus production and the disease Huanglongbing (HLB), which is vectored by the Asian citrus psyllid. The model is used to evaluate area-wide coordinated spraying when free-riding is possible given individuals’ beliefs in other grower participation in area-wide spraying and in the information provided by extension on the threat as HLB spread.
Addressing Barriers to Primary Care Access for Latinos in the U.S.: An Agent-Based Model
S.R. Aurora (a.k.a. Mai P. Trinh) Hyunsung Oh | Published Tuesday, August 16, 2022Disparities in access to primary health care have led to health disadvantages among Latinos and other non-White racial groups. To better identify and understand which policies are most likely to improve health care for Latinos, we examined differences in access to primary care between Latinos with proficient English language skills and Latinos with limited English proficiency (LEP) and estimated the extent of access to primary care providers (PCPs) among Latinos in the U.S.
A replication and extension of the Taylor's Simulation Model of Insurance Market Dynamics in C#
Rei England | Published Sunday, September 24, 2023A simple model is constructed using C# in order to to capture key features of market dynamics, while also producing reasonable results for the individual insurers. A replication of Taylor’s model is also constructed in order to compare results with the new premium setting mechanism. To enable the comparison of the two premium mechanisms, the rest of the model set-up is maintained as in the Taylor model. As in the Taylor example, homogeneous customers represented as a total market exposure which is allocated amongst the insurers.
In each time period, the model undergoes the following steps:
1. Insurers set competitive premiums per exposure unit
2. Losses are generated based on each insurer’s share of the market exposure
3. Accounting results are calculated for each insurer
…
Exploring Pesticide use and Inter-row management in European Vineyards and their potential Impacts (EPIEVI)
Nina Schwarz Yang Chen | Published Tuesday, January 24, 2023The purpose of this study is to explore the potential impacts of pesticide use and inter-row management of European winegrowers in response to policy designs and climate change. Pesticides considered in this study include insecticides, pheromone dispensers (as an alternative to insecticides), fungicides (both the synthetic type and copper-sulphur based). Inter-row management concerns the arrangement of vegetation in the inter-rows and the type of vegetation.
Controlling the misinformation diffusion in social media by the effect of different classes of agents
Ali Khodabandeh Yalabadi | Published Thursday, October 05, 2023An agent-based framework to simulate the diffusion process of a piece of misinformation according to the SBFC model in which the fake news and its debunking compete in a social network. Considering new classes of agents, this model is closer to reality and proposed different strategies how to mitigate and control misinformation.
Role of Diversity in Team Performance: the Case of Missing Expertise, an Agent Based Simulations
Tamás Kiss | Published Friday, December 29, 2023This ABM simulates problem solving agents as they work on a set of tasks. Each agent has a trait vector describing their skills. Two agents might form a collaboration if their traits are similar enough. Tasks are defined by a component vector. Agents work on tasks by decreasing tasks’ component vectors towards zero.
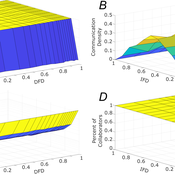
The simulation generates agents with given intrapersonal functional diversity (IFD), and dominant function diversity (DFD), and a set of random tasks and evaluates how agents’ traits influence their level of communication and the performance of a team of agents.
Modeling results highlight the importance of the distributions of agents’ properties forming a team, and suggests that for a thorough description of management teams, not only diversity measures based on individual agents, but an aggregate measure is also required.
…
Retention in Higher Education: An Agent-Based Model of Social Interactions and Motivated Agent Behavior
Andrew Crooks Amira Al-Khulaidy Stine | Published Wednesday, October 23, 2024Educational attainment and student retention in higher education are two of the main focuses of higher education research. Institutions in the U.S. are constantly looking for ways to identify areas of improvement across different aspects of the student experience on university campuses. This paper combines Department of Education data, U.S. Census data, and higher education theory on student retention, to build an agent-based model of student behavior.
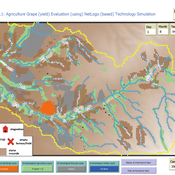
Peer reviewed Agriculture.Grape.yield.Evaluation.using.NetLogo.based.Technology.Simulation (AGENTS): A NetLogo agent-based model developed to assess viticulture efficiency in Byzantine Shivta.
Barak Garty Gil Gambash Guy BarOz Sharona T Levy | Published Friday, December 06, 2024AGENTS model is an agent-based computational framework designed to explore the socio-ecological and economic dynamics of agricultural production in the Byzantine Negev Highlands, with a focus on viticulture. It integrates historical, environmental, and social factors to simulate settlement sustainability, crop yields, and the impacts of varying climate conditions. The model is built in NetLogo and incorporates GIS-based topographical and hydrological data. Key features include the ability to assess climate impacts on crop profitability and settlement strategies, evaluate economic outputs of ancient vineyards, and simulate agent decision-making processes under diverse scenarios.
The AGENTS model is highly flexible, enabling users to simulate agricultural regimes with any two crops: one cash crop (a crop grown for profit, e.g., grapevines) and one staple crop (a crop grown for subsistence, e.g., wheat). While the default setup models viticulture and wheat cultivation in the Byzantine Negev Highlands, users can adapt the model to different environmental and socio-ecological contexts worldwide—both past and present.
Users can load external files to customize precipitation, evaporation, topography, and labor costs (measured as man-days per 0.1ha, converted to kg of wheat per model patch size area), and can also edit key parameters related to yield calculations. This includes modifying crop-specific yield formulas, soil and runoff indices, and any factors influencing crop performance. The model inherently simulates cash crops grown in floodplain regions and staple crops cultivated along riverbanks, providing a powerful tool to investigate societal resilience and responses to climate stressors across diverse environments.
…
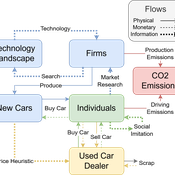
Driving in the wrong direction? A co-evolutionary model of electric vehicle adoption and innovation
Daniel Torren-Peraire | Published Friday, July 11, 2025Car-centric societies face substantial challenges in moving towards sustainable
mobility systems, with internal combustion engine vehicles remaining a major
source of emissions. Electric vehicles play a critical role in addressing this challenge, yet their diffusion depends on the interaction of consumer behaviour, firm
innovation, and policy incentives. This paper develops an agent-based model to
examine these dynamics, calibrated on the data for the state of California over
2001-2023. In the model, heterogeneous car users influenced by their social peers
…
Displaying 10 of 1113 results for "Bin-Tzong Chi" clear search