About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 334 results for "Chelsea E Hunter" clear search
ABM Household Decision Making on Solar Energy using Theory of Planned Behaviour
Tatiana Filatova Hannah Muelder | Published Tuesday, May 21, 2019The model aims at estimating household energy consumption and the related greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions reduction based on the behavior of the individual household under different operationalizations of the Theory of Planned Behaviour (TPB).
The original model is developed as a tool to explore households decisions regarding solar panel investments and cumulative consequences of these individual choices (i.e. diffusion of PVs, regional emissions savings, monetary savings). We extend the model to explore a methodological question regarding an interpretation of qualitative concepts from social science theories, specifically Theory of Planned Behaviour in a formal code of quantitative agent-based models (ABMs). We develop 3 versions of the model: one TPB-based ABM designed by the authors and two alternatives inspired by the TPB-ABM of Schwarz and Ernst (2009) and the TPB-ABM of Rai and Robinson (2015). The model is implemented in NetLogo.
Gossip and competitive altruism support cooperation in a Public Good Game
danielevilone | Published Friday, April 16, 2021Here we share the raw results of the social experiments of the paper “Gossip and competitive altruism support cooperation in a Public Good Game” by Giardini, Vilone, Sánchez, Antonioni, under review for Philosophical Transactions B. The experiment is thoroughly described there, in the following we summarize the main features of the experimental setup. The authors are available for further clarifications if requested.
Participants were recruited from the LINEEX subjects pool (University of Valencia Experimental Economics lab). 160 participants mean age = 21.7 years; 89 female) took part in this study in return for a flat payment of 5 EUR and the opportunity to earn an additional payment ranging from 8 to 16 EUR (mean total payment = 17.5 EUR). 80 subjects, divided into 5 groups of 16, took part in the competitive treatment while other 80 subjects participated in the non-competitive treatment. Laboratory experiments were conducted at LINEEX on September 16th and 17th, 2015.
Peer reviewed Are Countertrade credits as flexible and efficient as cash? A novel approach to reducing income inequality using countertrade methodology.
Peter Malliaros | Published Monday, May 03, 2021 | Last modified Tuesday, May 11, 2021The impacts of income inequality can be seen everywhere, regardless of the country or the level of economic development. According to the literature review, income inequality has negative impacts in economic, social, and political variables. Notwithstanding of how well or not countries have done in reducing income inequality, none have been able to reduce it to a Gini Coefficient level of 0.2 or less.
This is the promise that a novel approach called Counterbalance Economics (CBE) provides without the need of increased taxes.
Based on the simulation, introducing the CBE into the Australian, UK, US, Swiss or German economies would result in an overall GDP increase of under 1% however, the level of inequality would be reduced from an average of 0.33 down to an average of 0.08. A detailed explanation of how to use the model, software, and data dependencies along with all other requirements have been included as part of the info tab in the model.
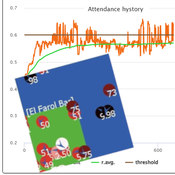
Peer reviewed Flibs’NFarol: Self-Organized Efficiency and Fairness Emergence in an Evolutive Game
Cosimo Leuci | Published Thursday, October 12, 2023According to the philosopher of science K. Popper “All life is problem solving”. Genetic algorithms aim to leverage Darwinian selection, a fundamental mechanism of biological evolution, so as to tackle various engineering challenges.
Flibs’NFarol is an Agent Based Model that embodies a genetic algorithm applied to the inherently ill-defined “El Farol Bar” problem. Within this context, a group of agents operates under bounded rationality conditions, giving rise to processes of self-organization involving, in the first place, efficiency in the exploitation of available resources. Over time, the attention of scholars has shifted to equity in resource distribution, as well. Nowadays, the problem is recognized as paradigmatic within studies of complex evolutionary systems.
Flibs’NFarol provides a platform to explore and evaluate factors influencing self-organized efficiency and fairness. The model represents agents as finite automata, known as “flibs,” and offers flexibility in modifying the number of internal flibs states, which directly affects their behaviour patterns and, ultimately, the diversity within populations and the complexity of the system.
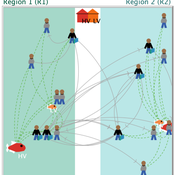
Peer reviewed Small-Trade Model
Emilie Lindkvist Maja Schlüter Blanca Gonzalez-Mon Örjan Bodin | Published Wednesday, July 28, 2021The purpose of this model is to understand the role of trade networks and their interaction with different fish resources, for fish provision. The model is developed based on a multi-methods approach, combining agent-based modeling, network analysis and qualitative data based on a small-scale fisheries study case. The model can be used to investigate both how trade network structures are embedded in a social-ecological context and the trade processes that occur within them, to analyze how they lead to emergent outcomes related to the resilience of fish provision. The model processes are informed by qualitative data analysis, and the social network analysis of an empirical fish trade network. The network analysis can be used to investigate diverse network structures to perform model experiments, and their influence on model outcomes.
The main outcomes we study are 1) the overexploitation of fish resources and 2) the availability and variability of fish provision to satisfy different market demands, and 3) individual traders’ fish supply at the micro-level. The model has two types of trader agents, seller and dealer. The model reveals that the characteristics of the trade networks, linked to different trader types (that have different roles in those networks), can affect the resilience of fish provision.
The Effect of Individual and Collective Characteristics on Team Performance: A Model of Networked Agents Engaged in Collective Problem Solving
Amin Boroomand | Published Tuesday, March 16, 2021 | Last modified Monday, July 26, 2021This code is for an agent-based model of collective problem solving in which agents with different behavior strategies, explore the NK landscape while they communicate with their peers agents. This model is based on the famous work of Lazer, D., & Friedman, A. (2007), The network structure of exploration and exploitation.
Vulnerability of Cooperation Due to Limited Vision
Marco Janssen | Published Thursday, December 02, 2010 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model describes the consequences of limited vision of agents in harvesting a common resource. We show the vulnerability of cooperation due to reduced visibility of the resource and other agents.
Will it spread or not? The effects of social influences and network topology on innovation diffusion
Sebastiano Delre | Published Monday, October 24, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This models simulates innovation diffusion curves and it tests the effects of the degree and the direction of social influences. This model replicates, extends and departs from classical percolation models.
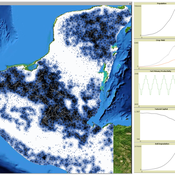
MayaSim: An agent-based model of the ancient Maya social-ecological system
Scott Heckbert | Published Wednesday, July 11, 2012 | Last modified Tuesday, July 02, 2013MayaSim is an agent-based, cellular automata and network model of the ancient Maya. Biophysical and anthropogenic processes interact to grow a complex social ecological system.
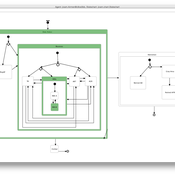
Life Cycle Cost of Military Manpower Model
Jonathan Ozik Todd Combs | Published Monday, January 05, 2015We demonstrate how Repast Simphony statecharts can efficiently encapsulate the deep classification hierarchy of the U.S. Air Force for manpower life cycle costing.
Displaying 10 of 334 results for "Chelsea E Hunter" clear search