About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 150 results environment clear search
Peer reviewed Agent-Based Insight into Eco-Choices: Simulating the Fast Fashion Shift
Daria Soboleva Angel Sánchez | Published Wednesday, August 07, 2024 | Last modified Wednesday, June 11, 2025The present model was created and used for the study titled ``Agent-Based Insight into Eco-Choices: Simulating the Fast Fashion Shift.” The model is implemented in the multi-agent programmable environment NetLogo 6.3.0. The model is designed to simulate the behavior and decision-making processes of individuals (agents) in a social network. It focuses on how agents interact with their peers, social media, and government campaigns, specifically regarding their likelihood to purchase fast fashion.
This paper presents an agent-based model to study the dynamics of city-state systems in a constrained environment with limited space and resources. The model comprises three types of agents: city-states, villages, and battalions, where city-states, the primary decision-makers, can build villages for food production and recruit battalions for defense and aggression. In this setting, simulation results, generated through a multi-parameter grid sampling, suggest that risk-seeking strategies are more effective in high-cost scenarios, provided that the production rate is sufficiently high. Also, the model highlights the role of output productivity in defining which strategic preferences are successful in a long-term scenario, with higher outputs supporting more aggressive expansion and military actions, while resource limitations compel more conservative strategies focused on survival and resource conservation. Finally, the results suggest the existence of a non-linear effect of diminishing returns in strategic investments on successful strategies, emphasizing the need for careful resource allocation in a competitive environment.
Agent-Based Model of Transhumant Decision-Making Processes in Senegal
Cheick Amed Diloma Gabriel TRAORE Etienne DELAY Alassane Bah Djibril Diop | Published Wednesday, July 03, 2024Sahelian transhumance is a type of socio-economic and environmental pastoral mobility. It involves the movement of herds from their terroir of origin (i.e., their original pastures) to one or more host terroirs, followed by a return to the terroir of origin. According to certain pastoralists, the mobility of herds is planned to prevent environmental degradation, given the continuous dependence of these herds on their environment. However, these herds emit Greenhouse Gases (GHGs) in the spaces they traverse. Given that GHGs contribute to global warming, our long-term objective is to quantify the GHGs emitted by Sahelian herds. The determination of these herds’ GHG emissions requires: (1) the artificial replication of the transhumance, and (2) precise knowledge of the space used during their transhumance.
This article presents the design of an artificial replication of the transhumance through an agent-based model named MSTRANS. MSTRANS determines the space used by transhumant herds, based on the decision-making process of Sahelian transhumants.
MSTRANS integrates a constrained multi-objective optimization problem and algorithms into an agent-based model. The constrained multi-objective optimization problem encapsulates the rationality and adaptability of pastoral strategies. Interactions between a transhumant and its socio-economic network are modeled using algorithms, diffusion processes, and within the multi-objective optimization problem. The dynamics of pastoral resources are formalized at various spatio-temporal scales using equations that are integrated into the algorithms.
The results of MSTRANS are validated using GPS data collected from transhumant herds in Senegal. MSTRANS results highlight the relevance of integrated models and constrained multi-objective optimization for modeling and monitoring the movements of transhumant herds in the Sahel. Now specialists in calculating greenhouse gas emissions have a reproducible and reusable tool for determining the space occupied by transhumant herds in a Sahelian country. In addition, decision-makers, pastoralists, veterinarians and traders have a reproducible and reusable tool to help them make environmental and socio-economic decisions.
Social Construction of Reality Agent-Based Model
Manuel Castañón-Puga E. Dante Suarez Loren Demerath | Published Saturday, June 29, 2024This model illustrates the processes underlying the social construction of reality through an agent-based genetic algorithm. By simulating the interactions of agents within a structured environment, we have demonstrated how shared information and popularity contribute to the formation of emergent social structures with diverse cultures. The model illustrates how agents balance environmentally valid information with socially reliable information. It also highlights how social interaction leads to the formation of stable, yet diverse, social groups.
Integrate land use policies into the agent-based model to simulate land use change
Jing Gao | Published Sunday, June 09, 2024This study employs a hierarchical cross-departmental ABM to explore the question: How and to what extent are the land use policies enforced when assessed against the real-world land use pattern? Specifically, two sub-questions are of interest: How can real-world policy interactions be abstracted into the behavior across hierarchical governmental departments in the model? How can the level of enforcement for each land use policy be quantified under these interactions? We build three hierarchical agents—the central level, the local level that incorporates three departments, and the village collective level—with simplified but plausible processes of land use change, with levels of enforcement of different land use policies as key parameters. We calibrate the model using a genetic algorithm to determine those parameters and answer our research question. We further applied the model to simulate potential land use changes and investigate the implications of different policy options. The results are expected to provide insights into the intricate relationships shaping land use processes, contributing to evidence-based decision-making in urban planning and sustainable land use management.
SeaROOTS ABM: Simulating Artificial Hominins Maritime Mobility at Inner Ionian, Greece
Angelos Chliaoutakis | Published Wednesday, May 29, 2024SeaROOTS ABM is a quite generic agent-based modeling system, for simulating and evaluating potential terrestrial and maritime mobility of artificial hominin groups, configured by available archaeological data and hypotheses. Necessary bathymetric, geomorphological and paleoenvironmental data are combined in order to reconstruct paleoshorelines for the study area and produce an archaeologically significant agent environment. Paleoclimatic and archaeological data are incorporated in the ABM in order to simulate maritime crossings and assess the emergent patterns of interaction between human agency and the sea.
SeaROOTS agent-based system includes completely autonomous, utility-based agents (Chliaoutakis & Chalkiadakis 2016), representing artificial hominin groups, with partial knowledge of their environment, for simulating their evolution and potential maritime mobility, utilizing alternative Least Cost Path analysis modeling techniques (Gustas & Supernant 2017, Gravel-Miguel & Wren 2021). Two groups of hominins, Neanderthals and Homo sapiens, are chosen in order to study the challenges and actions employed as a response to the fluctuating sea-levels, as well as probability scenarios with respect to sea-crossings via buoyant vessels (rafting) or the human body itself (swimming). SeaROOTS ABM aims to simulate various scenarios and investigate the degree climatic fluctuations influenced such activities and interactions in the Middle Paleolithic period.
The model focuses on simulating potential terrestrial and maritime routes, explore the interactions and relations between autonomous agents and their environment, as well as to test specific research questions; for example, when and under what conditions would Middle Paleolithic hominins be more likely to attempt a crossing and successfully reach the islands? By which agent type (Sapiens or Neanderthals) and how (e.g. swimming or by sea-vessels) could such short sea crossings be (mostly) attempted, and which (sea) routes were usually considered by the agents? When does a sea-crossing become a choice and when is it a result of forced migration, i.e. disaster- or conflict-induced displacement? Results show that the dynamic marine environment of the Inner Ionian, our case study in this work, played an important role in their decision-making process.
Peer reviewed The Megafauna Hunting Pressure Model
Isaac Ullah Miriam C. Kopels | Published Friday, February 16, 2024 | Last modified Friday, October 11, 2024The Megafaunal Hunting Pressure Model (MHPM) is an interactive, agent-based model designed to conduct experiments to test megaherbivore extinction hypotheses. The MHPM is a model of large-bodied ungulate population dynamics with human predation in a simplified, but dynamic grassland environment. The overall purpose of the model is to understand how environmental dynamics and human predation preferences interact with ungulate life history characteristics to affect ungulate population dynamics over time. The model considers patterns in environmental change, human hunting behavior, prey profitability, herd demography, herd movement, and animal life history as relevant to this main purpose. The model is constructed in the NetLogo modeling platform (Version 6.3.0; Wilensky, 1999).
Digital Mobility Model (DMM)
Na (Richard) Jiang Fiammetta Brandajs | Published Thursday, February 01, 2024 | Last modified Friday, February 02, 2024The purpose of the Digital Mobility Model (DMM) is to explore how a society’s adoption of digital technologies can impact people’s mobilities and immobilities within an urban environment. Thus, the model contains dynamic agents with different levels of digital technology skills, which can affect their ability to access urban services using digital systems (e.g., healthcare or municipal public administration with online appointment systems). In addition, the dynamic agents move within the model and interact with static agents (i.e., places) that represent locations with different levels of digitalization, such as restaurants with online reservation systems that can be considered as a place with a high level of digitalization. This indicates that places with a higher level of digitalization are more digitally accessible and easier to reach by individuals with higher levels of digital skills. The model simulates the interaction between dynamic agents and static agents (i.e., places), which captures how the gap between an individual’s digital skills and a place’s digitalization level can lead to the mobility or immobility of people to access different locations and services.
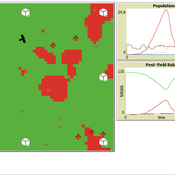
Peer reviewed Avian pest control: Yield outcome due to insectivorous birds, falconry, and integration of nest boxes.
David Jung | Published Monday, November 13, 2023 | Last modified Sunday, November 19, 2023The model aims to simulate predator-prey relationships in an agricultural setting. The focus lies on avian communities and their effect on different pest organisms (here: pest birds, rodents, and arthropod pests). Since most case studies focused on the impact on arthropod pests (AP) alone, this model attempts to include effects on yield outcome. By incorporating three treatments with different factor levels (insectivorous bird species, falconry, nest box density) an experimental setup is given that allows for further statistical analysis to identify an optimal combination of the treatments.
In light of a global decline of birds, insects, and many other groups of organisms, alternative practices of pest management are heavily needed to reduce the input of pesticides. Avian pest control therefore poses an opportunity to bridge the disconnect between humans and nature by realizing ecosystem services and emphasizing sustainable social ecological systems.
Peer reviewed Yards
srailsback Emily Minor Soraida Garcia Philip Johnson | Published Thursday, November 02, 2023This is a model of plant communities in urban and suburban residential neighborhoods. These plant communities are of interest because they provide many benefits to human residents and also provide habitat for wildlife such as birds and pollinators. The model was designed to explore the social factors that create spatial patterns in biodiversity in yards and gardens. In particular, the model was originally developed to determine whether mimicry behaviors–-or neighbors copying each other’s yard design–-could produce observed spatial patterns in vegetation. Plant nurseries and socio-economic constraints were also added to the model as other potential sources of spatial patterns in plant communities.
The idea for the model was inspired by empirical patterns of spatial autocorrelation that have been observed in yard vegetation in Chicago, Illinois (USA), and other cities, where yards that are closer together are more similar than yards that are farther apart. The idea is further supported by literature that shows that people want their yards to fit into their neighborhood. Currently, the yard attribute of interest is the number of plant species, or species richness. Residents compare the richness of their yards to the richness of their neighbors’ yards. If a resident’s yard is too different from their neighbors, the resident will be unhappy and change their yard to make it more similar.
The model outputs information about the diversity and identity of plant species in each yard. This can be analyzed to look for spatial autocorrelation patterns in yard diversity and to explore relationships between mimicry behaviors, yard diversity, and larger scale diversity.
Displaying 10 of 150 results environment clear search