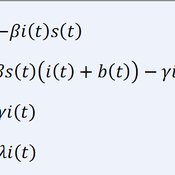About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 159 results for "L S Premo" clear search
Product Diffusion Model in an Advance Selling Strategy
Peng Shao | Published Tuesday, March 15, 2016 | Last modified Tuesday, March 15, 2016the model can be used to describe the product diffusion in an Advance Selling Strategy. this model takes into account the consumers product adoption, and describe consumer’s online behavior based on four states.
ReMoTe-S. Residential Mobility of Tenants in Switzerland: an agent-based model
Claudia Binder Anna Pagani Francesco Ballestrazzi Emanuele Massaro | Published Friday, April 01, 2022ReMoTe-S is an agent-based model of the residential mobility of Swiss tenants. Its goal is to foster a holistic understanding of the reciprocal influence between households and dwellings and thereby inform a sustainable management of the housing stock. The model is based on assumptions derived from empirical research conducted with three housing providers in Switzerland and can be used mainly for two purposes: (i) the exploration of what if scenarios that target a reduction of the housing footprint while accounting for households’ preferences and needs; (ii) knowledge production in the field of residential mobility and more specifically on the role of housing functions as orchestrators of the relocation process.
Central-place forager mobility and cultural diversity
Luke Premo | Published Wednesday, May 18, 2016This spatially explicit agent-based model addresses how effective foraging radius (r_e) affects the effective size–and thus the equilibrium cultural diversity–of a structured population composed of central-place foraging groups.
A simple Multi-Agent System of the Tragedy Of the Commons (MASTOC-s)
Julia Schindler | Published Friday, June 29, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is a simple model replicating Hardin’s Tragedy of the Commons using reactive agents that have psychological behavioral and social preferences.
Opportunity cost of walking away in the spatial iterated prisoner's dilemma
Luke Premo | Published Wednesday, April 03, 2019Previous work with the spatial iterated prisoner’s dilemma has shown that “walk away” cooperators are able to outcompete defectors as well as cooperators that do not respond to defection, but it remains to be seen just how robust the so-called walk away strategy is to ecologically important variables such as population density, error, and offspring dispersal. Our simulation experiments identify socio-ecological conditions in which natural selection favors strategies that emphasize forgiveness over flight in the spatial iterated prisoner’s dilemma. Our interesting results are best explained by considering how population density, error, and offspring dispersal affect the opportunity cost associated with walking away from an error-prone partner.
Time-averaging and the spatial scale of regional cultural differentiation in archaeological assemblages
Luke Premo | Published Sunday, July 08, 2018We employ this spatially explicit agent-based model to begin to examine how time-averaging can affect the spatial scale of cultural similarity in archaeological assemblage data. The model was built to address this question: to what extent does time-averaging affect the scale of local spatial association in the relative frequency of the most prevalent cultural variant in an archaeological landscape?
Cultural transmission in structured populations
Luke Premo | Published Wednesday, November 13, 2024This structured population model is built to address how migration (or intergroup cultural transmission), copying error, and time-averaging affect regional variation in a single selectively neutral discrete cultural trait under different mechanisms of cultural transmission. The model allows one to quantify cultural differentiation between groups within a structured population (at equilibrium) as well as between regional assemblages of time-averaged archaeological material at two different temporal scales (1,000 and 10,000 ticks). The archaeological assemblages begin to accumulate only after a “burn-in” period of 10,000 ticks. The model includes two different representations of copying error: the infinite variants model of copying error and the finite model of copying error. The model also allows the user to set the variant ceiling value for the trait in the case of the finite model of copying error.
PluchinoEtAl_ExtendedByAC
Andre Costopoulos | Published Tuesday, September 03, 2019 | Last modified Friday, January 31, 2020Extension of Pluchino et al.’s 2018 success vs talent model, to allow talented individuals to mitigate unlucky events.
Social Closure and the Evolution of Cooperation via Indirect Reciprocity
Károly Takács Simone Righi | Published Saturday, June 09, 2018 | Last modified Saturday, June 09, 2018Righi S., Takacs K., Social Closure and the Evolution of Cooperation via Indirect Reciprocity, Resubmitted after Revisions to Scientific Reports
Classical Swine Fever in wild boars
Volker Grimm Stephanie Kramer-Schadt Cédric Scherer Martin Lange Hans-Hermann Thulke | Published Friday, September 06, 2019The model is a combination of a spatially explicit, stochastic, agent-based model for wild boars (Sus scrofa L.) and an epidemiological model for the Classical Swine Fever (CSF) virus infecting the wild boars.
The original model (Kramer-Schadt et al. 2009) was used to assess intrinsic (system immanent host-pathogen interaction and host life-history) and extrinsic (spatial extent and density) factors contributing to the long-term persistence of the disease and has further been used to assess the effects of intrinsic dynamics (Lange et al. 2012a) and indirect transmission (Lange et al. 2016) on the disease course. In an applied context, the model was used to test the efficiency of spatiotemporal vaccination regimes (Lange et al. 2012b) as well as the risk of disease spread in the country of Denmark (Alban et al. 2005).
References: See ODD model description.
Displaying 10 of 159 results for "L S Premo" clear search