About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 21 results for "Hazel Parry" clear search
Co-evolution of mental models among socially learning agents
Garry Sotnik | Published Sunday, October 14, 2018The model simulates seven agents engaging in collective action and inter-network social learning. The objective of the model is to demonstrate how mental models of agents can co-evolve through a complex relationship among factors influencing decision-making, such as access to knowledge and personal- and group-level constraints.
Asymmetric two-sided matching
Naoki Shiba | Published Wednesday, January 09, 2013 | Last modified Tuesday, May 28, 2013This model is an extended version of the matching problem including the mate search problem, which is the generalization of a traditional optimization problem. The matching problem is extended to a form of asymmetric two-sided matching problem.
Neolithic Spread Model Version 1.0
Sean Bergin Salvador Pardo Gordo Joan Bernabeu Auban Michael Barton | Published Thursday, December 11, 2014 | Last modified Monday, December 31, 2018This model simulates different spread hypotheses proposed for the introduction of agriculture on the Iberian peninsula. We include three dispersal types: neighborhood, leapfrog, and ideal despotic distribution (IDD).
Modeling Asian-Papuan Admixture during the Neolithic Expansion across Island Southeast Asia
Murray Cox François Vallée | Published Friday, December 09, 2016This Repast Simphony model simulates genomic admixture during the farming expansion of human groups from mainland Asia into the Papuan dominated islands of Southeast Asia during the Neolithic period.
A Simulation of Entrepreneurial Spawning
Mark Bagley | Published Wednesday, June 08, 2016 | Last modified Friday, June 30, 2017Industrial clustering patterns are the result of an entrepreneurial process where spinoffs inherit the ideas and attributes of their parent firms. This computational model maps these patterns using abstract methodologies.
A modified model of breeding synchrony in colonial birds
James Millington | Published Tuesday, June 26, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This generic individual-based model of a bird colony shows how the influence neighbour’s stress levels synchronize the laying date of neighbours and also of large colonies. The model has been used to demonstrate how this form of simulation model can be recognised as being ‘event-driven’, retaining a history in the patterns produced via simulated events and interactions.
Vole-Mustelid model
Viktoriia Radchuk Harry Peter Andreassen Rolf Anker Ims | Published Monday, October 07, 2019The model reflects the predator-prey mustelid-vole population dynamics, typically observed in boreal systems. The goal of the model is to assess which intrinsic and extrinsic factors (or factor combinations) are needed for the generation of the cyclic pattern typically observed in natural vole populations. This goal is achieved by contrasting the alternative model versions by “switching off” some of the submodels in order to reflect the four combinations of the factors hypothesized to be driving vole cycles.
Peer reviewed Multilevel Group Selection I
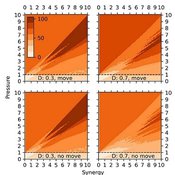
Wayne W. Wakeland Thaddeus Shannon Garry Sotnik | Published Tuesday, April 21, 2020 | Last modified Saturday, July 03, 2021New theoretical agent-based model of population-wide adoption of prosocial common-pool behavior with four parameters (initial percent of adopters, pressure to change behavior, synergy from behavior, and population density); dynamics in behavior, movement, freeriding, and group composition and size; and emergence of multilevel group selection. Theoretical analysis of model’s dynamics identified six regions in model’s parameter space, in which pressure-synergy combinations lead to different outcomes: extinction, persistence, and full adoption. Simulation results verified the theoretical analysis and demonstrated that increases in density reduce number of pressure-synergy combinations leading to population-wide adoption; initial percent of contributors affects underlying behavior and final outcomes, but not size of regions or transition zones between them; and random movement assists adoption of prosocial common-pool behavior.
SimAdapt
François Rebaudo | Published Wednesday, August 29, 2012 | Last modified Monday, October 13, 2014SimAdapt: An individual-based genetic model for simulating landscape management impacts on populations
Peer reviewed Co-adoption of low-carbon household energy technologies
Mart van der Kam Maria Lagomarsino Elie Azar Ulf Hahnel David Parra | Published Tuesday, August 29, 2023 | Last modified Friday, February 23, 2024The model simulates the diffusion of four low-carbon energy technologies among households: photovoltaic (PV) solar panels, electric vehicles (EVs), heat pumps, and home batteries. We model household decision making as the decision marking of one person, the agent. The agent decides whether to adopt these technologies. Hereby, the model can be used to study co-adoption behaviour, thereby going beyond traditional diffusion models that focus on the adop-tion of single technologies. The combination of these technologies is of particular interest be-cause (1) using the energy generated by PV solar panels for EVs and heat pumps can reduce emissions associated with transport and heating, respectively, and (2) EVs, heat pumps, and home batteries can help to integrate PV solar panels in local electricity grids by offering flexible demand (EVs and heat pumps) and energy storage (home batteries and EVs), thereby reducing grid impacts and associated upgrading costs.
The purpose of the model is to represent realistic adoption and co-adoption behaviour. This is achieved by grounding the decision model on the risks-as-feelings model (Loewenstein et al., 2001), theory from environmental and social psychology, and empirically informing agent be-haviour by survey-data among 1469 people in the Swiss region Romandie.
The model can be used to construct scenarios for the diffusion of the four low-carbon energy technologies depending on different contexts, and as a virtual experimentation environment for ex ante evaluation of policy interventions to stimulate adoption and co-adoption.
Displaying 10 of 21 results for "Hazel Parry" clear search