About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 24 results for "Guillaume Arnoux Hébert" clear search
Hybrid traffic model
Patrick Taillandier Arnaud Banos Nathalie Corson | Published Thursday, March 16, 2017The model aims at simulating the car traffic. It allows to use either a macro or a micro sub-model for the simulation of the flow on the roads.
DARTS: modelling effects of shocks on global, regional, urban and rural food security
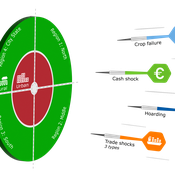
Geerten Hengeveld Hubert Fonteijn Pepijn van Oort | Published Tuesday, June 18, 2024Food trade networks represent a complex system where food is periodically produced in different regions of the world. Food is continuously stocked and traded. Food security in a globalised world is vulnerable to shocks. We present DARTS, a new agent based model that models monthly dynamics of food production, trade, stocking, consumption and food security for different interconnected world regions and a city state. Agents in different regions differ in their harvest seasons, wealth (rich and poor), degree of urbanisation and connection to domestic and global markets. DARTS was specifically designed to model direct and indirect effects of shocks in the food system. We introduce a new typology of 6 distinct shock types and analyse their impact on food security, modelling local and global effects and short term and longer term effects. An second important scientific novelty of the model is that DARTS can also model indirect effects of shocks (cascading in space and in time, lag effects due to trade and food stock buffering). A third important scientific novelty of the model is its’ capability of modelling food security at different scales, in which the rural/urban divide and differences in (intra-annually varying) production and trade connections play a key role. At the time of writing DARTS is yet insufficiently parameterised for accurate prediction for real world regions and cities. Simulations for a hypothetical in silico world with 3 regions and a city state show that DARTS can reproduce rich and complex dynamics with analogues in the real world. The scientific interest is more on deepening insight in process dynamics and chains of events that lead to ultimate shock effects on food security.
Evacuation of the city of Rouen using the GAMA advanced driving skill
Guillaume Czura Patrick Taillandier Pierrick Tranouez Eric Daudé | Published Thursday, April 25, 2019Model that illustrates the use of the GAMA advanced driving skill through a case study concerning the evacuation of the city of Rouen (France).
How does the world population adapt its policies on energy when it is confronted with a climate change? This model combines a climate-economy model with adaptive agents.
Alpine land-use allocation model - ALUAM-AB
Simon Briner | Published Tuesday, January 31, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013A model for simulating farmers and foresters response on changing climate and changing socio-economic parameters. Modeled are changes in land-use as well as in ecosystem services provision.
WeDiG Sim
Reza Shamsaee | Published Monday, May 14, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013WeDiG Sim- Weighted Directed Graph Simulator - is an open source application that serves to simulate complex systems. WeDiG Sim reflects the behaviors of those complex systems that put stress on scale-free, weightedness, and directedness. It has been implemented based on “WeDiG model” that is newly presented in this domain. The WeDiG model can be seen as a generalized version of “Barabási-Albert (BA) model”. WeDiG not only deals with weighed directed systems, but also it can handle the […]
Peer reviewed ArchMatNet: Archaeological Material Networks
Claudine Gravel-Miguel Robert Bischoff Cecilia Padilla-Iglesias | Published Monday, February 20, 2023The purpose of the model is to investigate how different factors affect the ability of researchers to reconstruct prehistoric social networks from artifact stylistic similarities, as well as the overall diversity of cultural traits observed in archaeological assemblages. Given that cultural transmission and evolution is affected by multiple interacting phenomena, our model allows to simultaneously explore six sets of factors that may condition how social networks relate to shared culture between individuals and groups:
- Factors relating to the structure of social groups
- Factors relating to the cultural traits in question
- Factors relating to individual learning strategies
- Factors relating to the environment
…
Space colonization
allagonne | Published Wednesday, January 05, 2022Agent-Based-Modeling - space colonization
ask me for the .nlogo model
WHAT IS IT?
The goal of this project is to simulate with NetLogo (v6.2) a space colonization of humans, starting from Earth, into the Milky Way.
HOW IT WORKS
…
(De-)Stabilising effect of diffusions
Julia Kasmire Bert Van Meeuwen Cornelis Eikelboom | Published Tuesday, August 11, 2015What is stable: the large but coordinated change during a diffusion or the small but constant and uncoordinated changes during a dynamic equilibrium? This agent-based model of a diffusion creates output that reveal insights for system stability.
Forager mobility and interaction
L S Premo | Published Thursday, January 10, 2013 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is a relatively simple foraging-radius model, as described first by Robert Kelly, that allows one to quantify the effect of increased logistical mobility (as represented by increased effective foraging radius, r_e) on the likelihood that 2 randomly placed central place foragers will encounter one another within 5000 time steps.
Displaying 10 of 24 results for "Guillaume Arnoux Hébert" clear search