About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 187 results for "Ed Manley" clear search
Individual bias and organizational objectivity
Bo Xu | Published Monday, April 15, 2013 | Last modified Monday, April 08, 2019This model introduces individual bias to the model of exploration and exploitation, simulates knowledge diffusion within organizations, aiming to investigate the effect of individual bias and other related factors on organizational objectivity.
How to not get stuck – an ant model showing how negative feedback due to crowding maintains flexibility in ant foraging
Tomer Czaczkes | Published Thursday, December 17, 2015Positive feedback can lead to “trapping” in local optima. Adding a simple negative feedback effect, based on ant behaviour, prevents this trapping
Effective population size and cultural evolution
Luke Premo | Published Tuesday, May 17, 2016This model illustrates how the effective population size and the rate of change in mean skill level of a cultural trait are affected by the presence of natural selection and/or the cultural transmission mechanism by which it is passed.
04 TpLab V2.08 – Teleological Pruning Laboratory
Garvin Boyle | Published Saturday, April 15, 2017Our societal belief systems are pruned by evolution, informing our unsustainable economies. This is one of a series of models exploring the dynamics of sustainable economics – PSoup, ModEco, EiLab, OamLab, MppLab, TpLab, CmLab.
CPNorm
Ruth Meyer | Published Sunday, June 04, 2017 | Last modified Tuesday, June 13, 2017CPNorm is a model of a community of harvesters using a common pool resource where adhering to the optimal extraction level has become a social norm. The model can be used to explore the robustness of norm-driven cooperation in the commons.
Netlogo Earned Value Management Model
Manuel Castañón-Puga Ricardo Fernando Rosales–Cisneros Julio César Acosta–Prado Alfredo Tirado–Ramos Camilo Khatchikian Elías Aburto–Camacllanqui | Published Thursday, November 24, 2022The model aims to illustrate how Earned Value Management (EVM) provides an approach to measure a project’s performance by comparing its actual progress against the planned one, allowing it to evaluate trends to formulate forecasts. The instance performs a project execution and calculates the EVM performance indexes according to a Performance Measurement Baseline (PMB), which integrates the description of the work to do (scope), the deadlines for its execution (schedule), and the calculation of its costs and the resources required for its implementation (cost).
Specifically, we are addressing the following questions: How does the risk of execution delay or advance impact cost and schedule performance? How do the players’ number or individual work capacity impact cost and schedule estimations to finish? Regardless of why workers cause delays or produce overruns in their assignments, does EVM assess delivery performance and help make objective decisions?
To consider our model realistic enough for its purpose, we use the following patterns: The model addresses classic problems of Project Management (PM). It plays the typical task board where workers are assigned to complete a task backlog in project performance. Workers could delay or advance in the task execution, and we calculate the performance using the PMI-recommended Earned Value.
02 OamLab V1.10 - Open Atwood Machine Laboratory
Garvin Boyle | Published Saturday, January 31, 2015 | Last modified Thursday, April 13, 2017Using chains of replicas of Atwood’s Machine, this model explores implications of the Maximum Power Principle. It is one of a series of models exploring the dynamics of sustainable economics – PSoup, ModEco, EiLab, OamLab, MppLab, TpLab, EiLab.
03 MppLab V1.09 – Maximum Power Principle Laboratory
Garvin Boyle | Published Saturday, April 15, 2017Using webs of replicas of Atwood’s Machine, we explore implications of the Maximum Power Principle. This is one of a series of models exploring the dynamics of sustainable economics – PSoup, ModEco, EiLab, OamLab, MppLab, TpLab, CmLab.
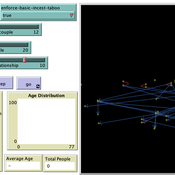
Peer reviewed Monogamous Reproduction in Small Populations and the Enforcement of the Incest Taboo
Ian Stuart | Published Wednesday, January 18, 2023This program was developed to simulate monogamous reproduction in small populations (and the enforcement of the incest taboo).
Every tick is a year. Adults can look for a mate and enter a relationship. Adult females in a Relationship (under the age of 52) have a chance to become pregnant. Everyone becomes not alive at 77 (at which point people are instead displayed as flowers).
User can select a starting-population. The starting population will be adults between the ages of 18 and 42.
…
A Bottom-Up Simulation on Competition and Displacement of Online Interpersonal Communication Platforms
great-sage-futao | Published Tuesday, December 31, 2019 | Last modified Tuesday, December 31, 2019This model aims to simulate Competition and Displacement of Online Interpersonal Communication Platforms process from a bottom-up angle. Individual interpersonal communication platform adoption and abandonment serve as the micro-foundation of the simulation model. The evolution mode of platform user online communication network determines how present platform users adjust their communication relationships as well as how new users join that network. This evolution mode together with innovations proposed by individual interpersonal communication platforms would also have impacts on the platform competition and displacement process and result by influencing individual platform adoption and abandonment behaviors. Three scenes were designed to simulate some common competition situations occurred in the past and current time, that two homogeneous interpersonal communication platforms competed with each other when this kind of platforms first came into the public eye, that a late entrant platform with a major innovation competed with the leading incumbent platform during the following days, as well as that both the leading incumbent and the late entrant continued to propose many small innovations to compete in recent days, respectively.
Initial parameters are as follows: n(Nmax in the paper), denotes the final node number of the online communication network node. mi (m in the paper), denotes the initial degree of those initial network nodes and new added nodes. pc(Pc in the paper), denotes the proportion of links to be removed and added in each epoch. pst(Pv in the paper), denotes the proportion of nodes with a viscosity to some platforms. comeintime(Ti in the paper), denotes the epoch when Platform 2 joins the market. pit(Pi in the paper), denotes the proportion of nodes adopting Platform 2 immediately at epoch comeintime(Ti). ct(Ct in the paper), denotes the Innovation Effective Period length. In Scene 2, There is only one major platform proposed by Platform 2, and ct describes that length. However, in Scene 3, Platform 2 and 1 will propose innovations alternately. And so, we set ct=10000 in simulation program, and every jtt epochs, we alter the innovation proposer from one platform to the other. Hence in this scene, jtt actually denotes the Innovation Effective Period length instead of ct.
Displaying 10 of 187 results for "Ed Manley" clear search