About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 201 results for "Friederike Lenel" clear search
(De-)Stabilising effect of diffusions
Julia Kasmire Bert Van Meeuwen Cornelis Eikelboom | Published Tuesday, August 11, 2015What is stable: the large but coordinated change during a diffusion or the small but constant and uncoordinated changes during a dynamic equilibrium? This agent-based model of a diffusion creates output that reveal insights for system stability.
Central-place forager mobility and cultural diversity
Luke Premo | Published Wednesday, May 18, 2016This spatially explicit agent-based model addresses how effective foraging radius (r_e) affects the effective size–and thus the equilibrium cultural diversity–of a structured population composed of central-place foraging groups.
Peer reviewed Simulating the Economic Impact of Boko Haram on a Cameroonian Floodplain
Mark Moritz Nathaniel Henry Sarah Laborde | Published Saturday, October 22, 2016 | Last modified Wednesday, June 07, 2017This model examines the potential impact of market collapse on the economy and demography of fishing households in the Logone Floodplain, Cameroon.
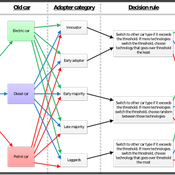
Peer reviewed Industrial Symbiosis Network implementation ABM
Igor Nikolic Kasper Pieter Hendrik Lange Gijsbert Korevaar Paulien Herder | Published Tuesday, December 01, 2020 | Last modified Wednesday, June 16, 2021The purpose of the model is to explore the influence of actor behaviour, combined with environment and business model design, on the survival rates of Industrial Symbiosis Networks (ISN), and the cash flows of the agents. We define an ISN to be robust, when it is able to run for 10 years, without falling apart due to leaving agents.
The model simulates the implementation of local waste exchange collaborations for compost production, through the ISN implementation stages of awareness, planning, negotiation, implementation, and evaluation.
One central firm plays the role of waste processor in a local composting initiative. This firm negotiates with other firms to become a supplier of their organic residual streams. The waste suppliers in the model can decide to join the initiative, or to have the waste brought to the external waste incinerator. The focal point of the model are the company-level interactions during the implementation or ending of synergies.
…
Social identity approach in a data-driven Axelrod model
alejandrodinkelberg | Published Thursday, July 28, 2022Simulations based on the Axelrod model and extensions to inspect the volatility of the features over time (AXELROD MODEL & Agreement threshold & two model variations based on the Social identity approach)
The Axelrod model is used to predict the number of changes per feature in comparison to the datasets and is used to compare different model variations and their performance.
Input: Real data
…
Agent-based tax evasion model for investigating impacts of public disclosure
Hiroyuki Sano | Published Thursday, March 14, 2024The model explores the impact of public disclosure on tax compliance among diverse agents, including individual taxpayers and a tax authority. It incorporates heterogeneous preferences and income endowments among taxpayers, captured through a utility function that considers psychic costs subtracted from expected pecuniary utility. These costs include moral, reciprocity, and stigma costs associated with norm violations, leading to variations in taxpayers’ risk attitudes and related parameters. The tax authority’s attributes, such as the frequency of random audits, penalty rate, and the choice between partial or full disclosure, remain fixed throughout the simulation. Income endowments and preference parameters are randomly assigned to taxpayers at the outset.
Taxpayers maximize their expected utility by reporting income, taking into account tax, penalty, and audit rates. They make annual decisions based on their own and their peers’ behaviors from the previous year. Taxpayers indirectly interact at the societal level through public disclosure conducted by the tax authority, exchanging tax information among peers. Each period in the simulation collects data on total reported income, average compliance rates per income group, distribution of compliance rates, counts of compliers, full evaders, partial evaders, and the numbers of taxpayers experiencing guilt and anger. The model evaluates whether public disclosure positively or negatively impacts compliance rates and quantifies this impact based on aggregated individual reporting behaviors.
Netlogo model ` Effect of Network Homophily and Partisanship on Social Media to “Oil Spill” Polarizations’
takuya nagura | Published Saturday, September 13, 2025This model was utilized for the simulation in the paper titled Effect of Network Homophily and Partisanship on Social Media to “Oil Spill” Polarizations. It allows you to examine whether oil spill polarization occurs through people’s communication under various conditions.
・Choose the network construction conditions you’d like to examine from the “rewire-style” chooser box.
・Select the desired strength of partisanship from the “partisanlevel” chooser box. You can also set the strength manually in the code tab.
・You can set the number of dynamic topics using the “number-of-topics” slider.
・Use the “divers-of-opinion” slider to set the number of preference types for each dynamic topic.
…
TechNet_04: Cultural Transmission in a Spatially-Situated Network
Andrew White | Published Monday, October 08, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013The TechNet_04 is an abstract model that embeds a simple cultural tranmission process in an environment where interaction is structured by spatially-situated networks.
Relative Agreement Model and Network Structure
Spiro Maroulis David Adelberg | Published Friday, January 29, 2016This adaptation of the Relative Agreement model of opinion dynamics (Deffuant et al. 2002) extends the Meadows and Cliff (2012) implementation of this model in a manner that explores the effect of the network structure among the agents.
Impact of topography and climate change on Magdalenian social networks
Claudine Gravel-Miguel | Published Monday, September 11, 2017The model presented here was created as part of my dissertation. It aims to study the impacts of topography and climate change on prehistoric networks, with a focus on the Magdalenian, which is dated to between 20 and 14,000 years ago.
Displaying 10 of 201 results for "Friederike Lenel" clear search