About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 184 results for "Nuno R Barros De Oliveira" clear search
Zombies
Jennifer Badham | Published Tuesday, June 08, 2021Zombies move toward humans and humans move (faster) away from zombies. They fight if they meet, and humans who lose become zombies.
LimnoSES - social-ecological lake management undergoing regime shifts
Romina Martin | Published Thursday, November 24, 2016 | Last modified Friday, January 18, 2019LimnoSES is a coupled system dynamics, agent-based model to simulate social-ecological feedbacks in shallow lake use and management.
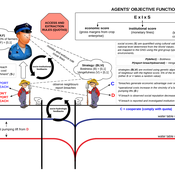
Individual bias and organizational objectivity
Bo Xu | Published Monday, April 15, 2013 | Last modified Monday, April 08, 2019This model introduces individual bias to the model of exploration and exploitation, simulates knowledge diffusion within organizations, aiming to investigate the effect of individual bias and other related factors on organizational objectivity.
Alpine land-use allocation model - ALUAM-AB
Simon Briner | Published Tuesday, January 31, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013A model for simulating farmers and foresters response on changing climate and changing socio-economic parameters. Modeled are changes in land-use as well as in ecosystem services provision.
The Groundwater Commons Game
Juan Castilla-Rho Rodrigo Rojas | Published Thursday, May 11, 2017 | Last modified Saturday, September 16, 2017The Groundwater Commons Game synthesises and extends existing work on human cooperation and collective action, to elucidate possible determinants and pathways to regulatory compliance in groundwater systems globally.
Modeling Personal Carbon Trading with ABM
Roman Seidl | Published Friday, December 07, 2018 | Last modified Thursday, July 29, 2021A simulated approach for Personal Carbon Trading, for figuring out what effects it might have if it will be implemented in the real world. We use an artificial population with some empirical data from international literature and basic assumptions about heterogeneous energy demand. The model is not to be used as simulating the actual behavior of real populations, but a toy model to test the effects of differences in various factors such as number of agents, energy price, price of allowances, etc. It is important to adapt the model for specific countries as carbon footprint and energy demand determines the relative success of PCT.
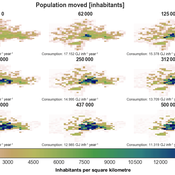
IUCM - The Integrated Urban Complexity Model
Roger Cremades Philipp S. Sommer | Published Thursday, December 14, 2023We present the Integrated Urban Complexity model (IUCm 1.0) that computes “climate-smart urban forms”, which are able to cut emissions related to energy consumption from urban mobility in half. Furthermore, we show the complex features that go beyond the normal debates about urban sprawl vs. compactness. Our results show how to reinforce fractal hierarchies and population density clusters within climate risk constraints to significantly decrease the energy consumption of urban mobility. The new model that we present aims to produce new advice about how cities can combat climate change. From a technical angle, this model is a geographical automaton, conceptually interfacing between cellular automata and spatial explicit optimisation to achieve normative sustainability goals related to low energy. See a complete user guide at https://iucm.readthedocs.io/en/latest/ .
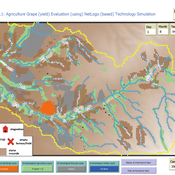
Peer reviewed Agriculture.Grape.yield.Evaluation.using.NetLogo.based.Technology.Simulation (AGENTS): A NetLogo agent-based model developed to assess viticulture efficiency in Byzantine Shivta.
Barak Garty Gil Gambash Guy BarOz Sharona T Levy | Published Friday, December 06, 2024AGENTS model is an agent-based computational framework designed to explore the socio-ecological and economic dynamics of agricultural production in the Byzantine Negev Highlands, with a focus on viticulture. It integrates historical, environmental, and social factors to simulate settlement sustainability, crop yields, and the impacts of varying climate conditions. The model is built in NetLogo and incorporates GIS-based topographical and hydrological data. Key features include the ability to assess climate impacts on crop profitability and settlement strategies, evaluate economic outputs of ancient vineyards, and simulate agent decision-making processes under diverse scenarios.
The AGENTS model is highly flexible, enabling users to simulate agricultural regimes with any two crops: one cash crop (a crop grown for profit, e.g., grapevines) and one staple crop (a crop grown for subsistence, e.g., wheat). While the default setup models viticulture and wheat cultivation in the Byzantine Negev Highlands, users can adapt the model to different environmental and socio-ecological contexts worldwide—both past and present.
Users can load external files to customize precipitation, evaporation, topography, and labor costs (measured as man-days per 0.1ha, converted to kg of wheat per model patch size area), and can also edit key parameters related to yield calculations. This includes modifying crop-specific yield formulas, soil and runoff indices, and any factors influencing crop performance. The model inherently simulates cash crops grown in floodplain regions and staple crops cultivated along riverbanks, providing a powerful tool to investigate societal resilience and responses to climate stressors across diverse environments.
…
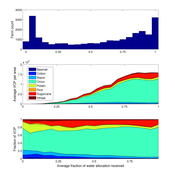
Irrigation Equity and Efficiency
Andrew Bell | Published Tuesday, August 30, 2016The purpose of this model is to examine equity and efficiency in crop production across a system of irrigated farms, as a function of maintenance costs, assessed water fees, and the capacity of farmers to trade water rights among themselves.
The relationship between product information quantity and diversity of consumer decisions
Marco Janssen Takao Sasaki David Vaughn Becker Rebecca Neel | Published Tuesday, October 27, 2015We developed an agent-based model to explore underlying mechanisms of behavioral clustering that we observed in human online shopping experiments.
Displaying 10 of 184 results for "Nuno R Barros De Oliveira" clear search