About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 818 results for "Blanca Gonzalez-Mon" clear search
Correlated random walk (Javascript)
Viktoriia Radchuk Uta Berger Thibault Fronville | Published Tuesday, May 09, 2023The first simple movement models used unbiased and uncorrelated random walks (RW). In such models of movement, the direction of the movement is totally independent of the previous movement direction. In other words, at each time step the direction, in which an individual is moving is completely random. This process is referred to as a Brownian motion.
On the other hand, in correlated random walks (CRW) the choice of the movement directions depends on the direction of the previous movement. At each time step, the movement direction has a tendency to point in the same direction as the previous one. This movement model fits well observational movement data for many animal species.
The presented agent based model simulated the movement of the agents as a correlated random walk (CRW). The turning angle at each time step follows the Von Mises distribution with a ϰ of 10. The closer ϰ gets to zero, the closer the Von Mises distribution becomes uniform. The larger ϰ gets, the more the Von Mises distribution approaches a normal distribution concentrated around the mean (0°).
In this script the turning angles (following the Von Mises distribution) are generated based on the the instructions from N. I. Fisher 2011.
This model is implemented in Javascript and can be used as a building block for more complex agent based models that would rely on describing the movement of individuals with CRW.
Correlated random walk
Thibault Fronville | Published Friday, April 01, 2022 | Last modified Monday, April 25, 2022The first simple movement models used unbiased and uncorrelated random walks (RW). In such models of movement, the direction of the movement is totally independent of the previous movement direction. In other words, at each time step the direction, in which an individual is moving is completely random. This process is referred to as a Brownian motion.
On the other hand, in correlated random walks (CRW) the choice of the movement directions depends on the direction of the previous movement. At each time step, the movement direction has a tendency to point in the same direction as the previous one. This movement model fits well observational movement data for many animal species.
The presented agent based model simulated the movement of the agents as a correlated random walk (CRW). The turning angle at each time step follows the Von Mises distribution with a ϰ of 10. The closer ϰ gets to zero, the closer the Von Mises distribution becomes uniform. The larger ϰ gets, the more the Von Mises distribution approaches a normal distribution concentrated around the mean (0°).
This model is implemented in python and can be used as a building block for more complex agent based models that would rely on describing the movement of individuals with CRW.
The Informational Dynamics of Regime Change
Dominik Klein Johannes Marx | Published Saturday, October 07, 2017 | Last modified Tuesday, January 14, 2020We model the epistemic dynamics preceding political uprising. Before deciding whether to start protests, agents need to estimate the amount of discontent with the regime. This model simulates the dynamics of group knowledge about general discontent.
Peer reviewed Egalitarian sharing
Marcos Pinheiro | Published Friday, January 27, 2023The model explores food distribution patterns that emerge in a small-scale non-agricultural group when individuals follow a set of spatially explicit sharing interaction rules derived from a theory on the evolution of the egalitarian social instinct.
Peer reviewed MOOvPOPsurveillance
Matthew Gompper Aniruddha Belsare Joshua J Millspaugh | Published Tuesday, April 04, 2017 | Last modified Tuesday, May 12, 2020MOOvPOPsurveillance was developed as a tool for wildlife agencies to guide collection and analysis of disease surveillance data that relies on non-probabilistic methods like harvest-based sampling.
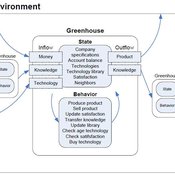
Universal Darwinism in Dutch Greenhouses
Julia Kasmire | Published Wednesday, May 09, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013An ABM, derived from a case study and a series of surveys with greenhouse growers in the Westland, Netherlands. Experiments using this model showshow that the greenhouse horticulture industry displays diversity, adaptive complexity and an uneven distribution, which all suggest that the industry is an evolving system.
Peer reviewed Axelrod_Cultural_Dissemination
Arezky Hernández | Published Wednesday, March 27, 2013 | Last modified Sunday, May 05, 2013The Axelrod’s model of cultural dissemination is an agent-model designed to investigate the dissemination of culture among interacting agents on a society.
Evolution of cooperation, punishment and retaliation
Marco Janssen | Published Friday, September 06, 2013Cultural group selection model of agents playing public good games and who are able to punish and punish back.
A model to explore the link between the gender-gap reversal in education and relative divorce risks
Jan Van Bavel Christine Schnor André Grow | Published Thursday, June 30, 2016 | Last modified Wednesday, September 13, 2017This model explores a social mechanism that links the reversal of the gender gap in education with changing patterns in relative divorce risks in 12 European countries.
Societal Simulator v203
Tim Gooding | Published Tuesday, October 01, 2013 | Last modified Friday, November 28, 2014Designed to capture the evolutionary forces of global society.
Displaying 10 of 818 results for "Blanca Gonzalez-Mon" clear search