About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 142 results human clear search
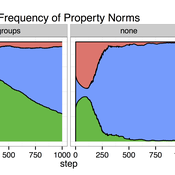
Cultural Group Selection of Sustainable Institutions
Timothy Waring Paul Smaldino Sandra H Goff | Published Wednesday, June 10, 2015 | Last modified Tuesday, August 04, 2015We develop a spatial, evolutionary model of the endogenous formation and dissolution of groups using a renewable common pool resource. We use this foundation to measure the evolutionary pressures at different organizational levels.
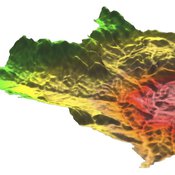
MedLanD Modeling Laboratory
C Michael Barton Sean Bergin Isaac Ullah Gary Mayer Hessam Sarjoughian Helena Mitasova | Published Friday, May 08, 2015 | Last modified Thursday, December 14, 2017The MML is a hybrid modeling environment that couples an agent-based model of small-holder agropastoral households and a cellular landscape evolution model that simulates changes in erosion/deposition, soils, and vegetation.
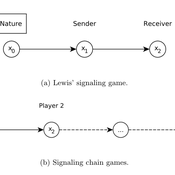
Lewis' Signaling Chains
Giorgio Gosti | Published Wednesday, January 14, 2015 | Last modified Friday, April 03, 2015Signaling chains are a special case of Lewis’ signaling games on networks. In a signaling chain, a sender tries to send a single unit of information to a receiver through a chain of players that do not share a common signaling system.
Exploring Creativity and Urban Development with Agent-Based Modeling
Ammar Malik Andrew Crooks Hilton Root Melanie Swartz | Published Thursday, October 30, 2014An agent-based model which explores Creativity and Urban Development
Formation of Lithic Assemblages v. 1
C Michael Barton Julien Riel-Salvatore | Published Thursday, September 04, 2014This model represents technological and ecological behaviors of mobile hunter-gatherers, in a variable environment, as they produce, use, and discard chipped stone artifacts. The results can be analyzed and compared with archaeological sites.
Land Use in the Chitwan Valley
Alex Zvoleff | Published Monday, June 02, 2014chitwanabm is a spatially explicit agent-based model of population and land use in the Chitwan Valley, Nepal, designed to explore feedbacks between population and environment, with a heavy focus on community context and individual-level variation.
The role of spatial foresight in models of hominin dispersal
Colin Wren | Published Monday, February 24, 2014 | Last modified Monday, July 14, 2014The natural selection of foresight, an accuracy at assess the environment, under degrees of environmental heterogeneity. The model is designed to connect local scale mobility, from foraging, with the global scale phenomenon of population dispersal.
PSMED - Patagonia Simple Model of Ethnic Differentiation
Xavier Vilà Joan A Barceló J A Cuesta Florencia Del Castillo Ricardo Del Olmo José M Galán Laura Mameli Francisco J Miguel David Poza José I Santos | Published Tuesday, December 10, 2013Patagonia PSMED is an agent-based model designed to study a simple case of Evolution of Ethnic Differentiation. It replicates how can hunter-gatherer societies evolve and built cultural identities as a consequence of the way they interacted.
On July 20th, James Holmes committed a mass shooting in a midnight showing of The Dark Knight Rises. The Aurora Colorado shooting was used as a test case to validate this framework for modeling mass shootings.
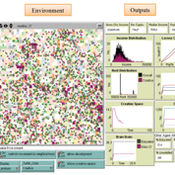
Societal Simulator v203
Tim Gooding | Published Tuesday, October 01, 2013 | Last modified Friday, November 28, 2014Designed to capture the evolutionary forces of global society.
Displaying 10 of 142 results human clear search