About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 192 results decision clear search
How does knowledge infrastructure mobilization influence the safe operating space of regulated exploited ecosystems?
Jean-Denis Mathias | Published Tuesday, July 17, 2018Decision-makers often have to act before critical times to avoid the collapse of ecosystems using knowledge \textcolor{red}{that can be incomplete or biased}. Adaptive management may help managers tackle such issues. However, because the knowledge infrastructure required for adaptive management may be mobilized in several ways, we study the quality and the quantity of knowledge provided by this knowledge infrastructure. In order to analyze the influence of mobilized knowledge, we study how the following typology of knowledge and its use may impact the safe operating space of exploited ecosystems: 1) knowledge of the past based on a time series distorted by measurement errors; 2) knowledge of the current systems’ dynamics based on the representativeness of the decision-makers’ mental models of the exploited ecosystem; 3) knowledge of future events based on decision-makers’ likelihood estimates of extreme events based on modeling infrastructure (models and experts to interpret them) they have at their disposal. We consider different adaptive management strategies of a general regulated exploited ecosystem model and we characterize the robustness of these strategies to biased knowledge. Our results show that even with significant mobilized knowledge and optimal strategies, imperfect knowledge may still shrink the safe operating space of the system leading to the collapse of the system. However, and perhaps more interestingly, we also show that in some cases imperfect knowledge may unexpectedly increase the safe operating space by suggesting cautious strategies.
The code enables to calculate the safe operating spaces of different managers in the case of biased and unbiased knowledge.
An agent-based model to simulate the impact of developers’ capital possession on urban development
Agung Wahyudi | Published Saturday, June 23, 2018The model combines agent-based modelling and microeconomic approach to simulate the decision behaviour of land developers and how this impacts on the spatio-temporal processes of urban expansion.
Peer reviewed Strategy with Externalities
J M Applegate Glenn Hoetker | Published Thursday, December 21, 2017The SWE models firms search behaviour as the performance landscape shifts. The shift represents society’s pricing of negative externalities, and the performance landscape is an NK structure. The model is written in NetLogo.
Simulation of the Governance of Complex Systems
Fabian Adelt Johannes Weyer Robin D Fink Andreas Ihrig | Published Monday, December 18, 2017 | Last modified Friday, March 02, 2018Simulation-Framework to study the governance of complex, network-like sociotechnical systems by means of ABM. Agents’ behaviour is based on a sociological model of action. A set of basic governance mechanisms helps to conduct first experiments.
Peer reviewed Empathy & Power
J M Applegate Ned Wellman | Published Monday, November 13, 2017 | Last modified Thursday, December 21, 2017The purpose of this model is to explore the effects of different power structures on a cross-functional team’s prosocial decision making. Are certain power distributions more conducive to the team making prosocial decisions?
Demand Planning Model
Iris Lorscheid Jonas Hauke Matthias Meyer | Published Wednesday, October 04, 2017Demand planning requires processing of distributed information. In this process, individuals, their properties and interactions play a crucial role. This model is a computational testbed to investigate these aspects with respect to forecast accuracy.
Carington
William Kennedy Emily S Ihara Catherine J Tompkins Michael E Wolf-Branigin | Published Thursday, July 13, 2017The Carington model is designed to provide insights into the factors affecting informal health care for older adults. It encompasses older adults, caregivers, and factors affecting informal health care. The Carington model includes no submodels.
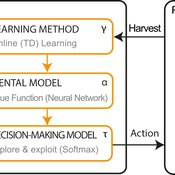
LBD Model: Learning-by-doing for sustainable management of renewable resources
Emilie Lindkvist Örjan Ekeberg Jon Norberg | Published Thursday, March 09, 2017This is a simulation model of an intelligent agent that has the objective to learn sustainable management of a renewable resource, such as a fish stock.
SMILI: Small-scale fisheries Institutions and Local Interactions
Emilie Lindkvist Maja Schlüter Xavier Basurto | Published Thursday, March 09, 2017The model represents an archetypical fishery in a co-evolutionary social-ecological environment, capturing different dimensions of trust between fishers and fish buyers for the establishment and persistence of self-governance arrangements.
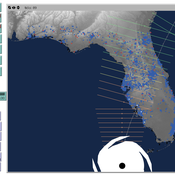
Peer reviewed CHIME ABM Hurricane Evacuation Model
Joshua Watts | Published Friday, March 03, 2017 | Last modified Wednesday, May 29, 2019The CHIME ABM explores information distribution networks and agents’ protective decision making in the context of hurricane landfall.
Displaying 10 of 192 results decision clear search