About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 677 results agent based clear search
Peer reviewed Agent-Based Ramsey growth model with endogenous technical progress (ABRam-T)
Sarah Wolf Aida Sarai Figueroa Alvarez Malika Tokpanova | Published Wednesday, February 14, 2024 | Last modified Monday, February 19, 2024The Agent-Based Ramsey growth model is designed to analyze and test a decentralized economy composed of utility maximizing agents, with a particular focus on understanding the growth dynamics of the system. We consider farms that adopt different investment strategies based on the information available to them. The model is built upon the well-known Ramsey growth model, with the introduction of endogenous technical progress through mechanisms of learning by doing and knowledge spillovers.
Agent-Based Modeling of C. Difficile Spread in Hospitals: Assessing Contribution of High-Touch vs. Low-Touch Surfaces and Inoculations’ Containment Impact
Sina Abdidizaji | Published Monday, January 22, 2024Clostridioides Difficile Infection (CDI) stands out as a critical healthcare-associated infection with global implications. Effectively understanding the mechanisms of infection dissemination within healthcare units and hospitals is imperative to implement targeted containment measures. In this study, we address the limitations of prior research by Sulyok et al., where they delineated two distinct categories of surfaces as high-touch and low-touch fomites, and subsequently evaluated the viral spread contribution of each surface utilizing mathematical modeling and Ordinary Differential Equations (ODE). Acknowledging the indispensable role of spatial features and heterogeneity in the modeling of hospital and healthcare settings, we employ agent-based modeling to capture new insights. By incorporating spatial considerations and heterogeneous patients, we explore the impact of high-touch and low-touch surfaces on contamination transmission between patients. Furthermore, the study encompasses a comprehensive assessment of various cleaning protocols, with differing intervals and detergent cleaning efficacies, in order to identify the most optimal cleaning strategy and the most important factor amidst the array of alternatives.
Peer reviewed Deforestation
MohammadAli Aghajani | Published Saturday, January 20, 2024 | Last modified Thursday, August 14, 2025Deforestation Simulation Model in NetLogo with GIS Layers
This model has developed in Netlogo software and utilizes
the GIS extension.
This NetLogo-based agent-based model (ABM) simulates deforestation dynamics using the GIS extension. It incorporates parameters like wood extraction, forest regeneration, agricultural expansion, and livestock impact. The model integrates spatial layers, including forest areas, agriculture zones, rural settlements, elevation, slope, and livestock distribution. Outputs include real-time graphical representations of forest loss, regeneration, and land-use changes. This model helps analyze deforestation patterns and conservation strategies using ABM and GIS.
Role of Diversity in Team Performance: the Case of Missing Expertise, an Agent Based Simulations
Tamás Kiss | Published Friday, December 29, 2023This ABM simulates problem solving agents as they work on a set of tasks. Each agent has a trait vector describing their skills. Two agents might form a collaboration if their traits are similar enough. Tasks are defined by a component vector. Agents work on tasks by decreasing tasks’ component vectors towards zero.
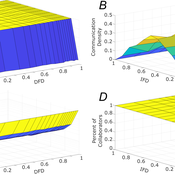
The simulation generates agents with given intrapersonal functional diversity (IFD), and dominant function diversity (DFD), and a set of random tasks and evaluates how agents’ traits influence their level of communication and the performance of a team of agents.
Modeling results highlight the importance of the distributions of agents’ properties forming a team, and suggests that for a thorough description of management teams, not only diversity measures based on individual agents, but an aggregate measure is also required.
…
Seascapes of the Unreal: Using Agent Based Modeling to Examine Traditional Coast Salish Maritime Mobility
Adam Rorabaugh | Published Friday, December 22, 2023Non-traditional tools and mediums can provide unique methodological and interpretive opportunities for archaeologists. In this case, the Unreal Engine (UE), which is typically used for games and media, has provided a powerful tool for non-programmers to engage with 3D visualization and programming as never before. UE has a low cost of entry for researchers as it is free to download and has user-friendly “blueprint” tools that are visual and easily extendable. Traditional maritime mobility in the Salish Sea is examined using an agent-based model developed in blueprints. Focusing on the sea canoe travel of the Straits Salish northwestern Washington State and southwest British Columbia. This simulation integrates GIS data to assess travel time between Coast Salish archaeological village locations and archaeologically represented resource gathering areas. Transportation speeds informed by ethnographic data were used to examine travel times for short forays and longer inter-village journeys. The results found that short forays tended to half day to full day trips when accounting for resource gathering activities. Similarly, many locations in the Salish Sea were accessible in long journeys within two to three days, assuming fair travel conditions. While overall transportation costs to reach sites may be low, models such as these highlight the variability in transport risk and cost. The integration of these types of tools, traditionally used for entertainment, can increase the accessibility of modeling approaches to researchers, be expanded to digital storytelling, including aiding in the teaching of traditional ecological knowledge and placenames, and can have wide applications beyond maritime archaeology.
This is v0.01 of a UE5.2.1 agent based model.
The Urban Drought Nexus Tool
Roger Cremades Muhamad Khairulbahri | Published Thursday, December 14, 2023The “Urban Drought Nexus Tool” is a system dynamics model, aiming to facilitate the co-development of climate services for cities under increasing droughts. The tool integrates multiple types of information and still can be applied to other case studies with minimal adjustments on the parameters of land use, water consumption and energy use in the water sector. The tool needs hydrological projections under climate scenarios to evaluate climatic futures, and requires the co-creation of socio-economic future scenarios with local stakeholders. Thus it is possible to provide specific information about droughts taking into account future water availability and future water consumption. Ultimately, such complex system as formed by the water-energy-land nexus can be reduced to single variables of interest, e.g. the number of events with no water available in the future and their length, so that the complexities are reduced and the results can be conveyed to society in an understandable way, including the communication of uncertainties. The tool and an explanatory guide in pdf format are included. Planned further developments include calibrating the system dynamics model with the social dynamics behind each flow with agent-based models.
Hollywood Underrepresentation Simulated Causes
Carmen Iasiello | Published Sunday, November 26, 2023Presented here is a socioeconomic agent-based model (ABM) to examine the Hollywood labor system as a network within a simulated movie labor market based on preferential attachment and compare the findings with 50 co-production ego networks during the 2015 movie year. Using the ABM, I test the role slight individual preference for racial and ethnic similarity within one’s own network at the microlevel and find that it is insufficient to explain the phenomena of racial and ethnic underrepresentation at the macrolevel. The ABM also includes the ability to test alternative explanations, such as overt opportunity loss as a possible explanation.
ABM Simulation of Transition from Late Longshan Cultures to Early Erlitou Culture
Carmen Iasiello | Published Sunday, November 26, 2023Within the archeological record for Bronze Age Chinese culture, there continues to be a gap in our understanding of the sudden rise of the Erlitou State from the previous late Longshan chiefdoms. In order to examine this period, I developed and used an agent-based model (ABM) to explore possible socio-politically relevant hypotheses for the gap between the demise of the late Longshan cultures and rise of the first state level society in East Asia. I tested land use strategy making and collective action in response to drought and flooding scenarios, the two plausible environmental hazards at that time. The model results show cases of emergent behavior where an increase in social complexity could have been experienced if a catastrophic event occurred while the population was sufficiently prepared for a different catastrophe, suggesting a plausible lead for future research into determining the life of the time period.
The ABM published here was originally developed in 2016 and its results published in the Proceedings of the 2017 Winter Simulation Conference.
DARTS: an agent-based model of the global food system for studying its resilience to shocks
Hubert Fonteijn | Published Wednesday, November 22, 2023DARTS simulates food systems in which agents produce, consume and trade food. Here, food is a summary item that roughly corresponds to commodity food types (e.g. rice). No other food types are taken into account. Each food system (World) consists of its own distribution of agents, regions and connections between agents. Agents differ in their ability to produce food, earn off-farm income and trade food. The agents aim to satisfy their food requirements (which are fixed and equal across agents) by either their own food production or by food purchases. Each simulation step represents one month, in which agents can produce (if they have productive capacity and it is a harvest month for their region), earn off-farm income, trade food (both buy and sell) and consume food. We evaluate the performance of the food system by averaging the agents’ food satisfaction, which is defined as the ratio of the food consumed by each agent at the end of each month divided by her food requirement. At each step, any of the abovementioned attributes related to the agents’ ability to satisfy their food requirement can (temporarily) be shocked. These shocks include reducing the amount of food they produce, removing their ability to trade locally or internationally and reducing their cash savings. Food satisfaction is quantified (both immediately after the shock and in the year following the shock) to evaluate food security of a particular food system, both at the level of agent types (e.g. the urban poor and the rural poor) and at the systems level. Thus, the effects of shocks on food security can be related to the food system’s structure.
Simulating Social Interaction in Times of COVID Restrictions
Oscar de Vries | Published Friday, November 17, 2023Social distancing is a strategy to mitigate the spread of contagious disease, but it bears negative impacts on people’s social well-being, resulting in non-compliance. This paper uses an integrated behavioral simulation model, called HUMAT, to identify a sweet spot
that balances strictness of and obedience to social distancing rules.
A novel agent-based model was developed that aims to explore social interaction while it is constrained by visitor limitations (due to Dutch COVID measures). Specifically, the model aims to capture the interaction between the need for social contact and the support for the visitors measure. The model was developed using the HUMAT integrated framework, which offered a psychological and sociological foundation for the behavior of the agents.
Displaying 10 of 677 results agent based clear search