About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 202 results ABM clear search
Game of Thrones model
Sean Bergin Claudine Gravel-Miguel | Published Sunday, January 03, 2021 | Last modified Sunday, January 03, 2021This model slowly evolves to become Westeros, with houses fighting for the thrones, and whitewalkers trying to kill all living things. You can download each version to see the evolution of the code, from the Wolf Sheep Predation model to the Game of Thrones model. If you are only interested in the end product, simply download the latest version.
For instructions on each step, see: https://claudinegravelmigu.wixsite.com/got-abm
Retail Competition Agent-based Model
Derek Robinson Jiaxin Zhang | Published Sunday, January 03, 2021 | Last modified Wednesday, November 10, 2021The Retail Competition Agent-based Model (RC-ABM) is designed to simulate the retail competition system in the Region of Waterloo, Ontario, Canada, which which explicitly represents store competition behaviour. Through the RC-ABM, we aim to answer 4 research questions: 1) What is the level of correspondence between market share and revenue acquisition for an agent-based approach compared to a traditional location-allocation-based approach? 2) To what degree can the observed store spatial pattern be reproduced by competition? 3) To what degree are their path dependent patterns of retail success? 4) What is the relationship between retail survival and the endogenous geographic characteristics of stores and consumer expenditures?
MCA-SdA (ABM of mining-community-aquifer interactions in Salar de Atacama, Chile)
Wenjuan Liu | Published Tuesday, December 01, 2020 | Last modified Thursday, November 04, 2021This model represnts an unique human-aquifer interactions model for the Li-extraction in Salar de Atacama, Chile. It describes the local actors’ experience of mining-induced changes in the socio-ecological system, especially on groundwater changes and social stressors. Social interactions are designed specifically according to a long-term local fieldwork by Babidge et al. (2019, 2020). The groundwater system builds on the FlowLogo model by Castilla-Rho et al. (2015), which was then parameterized and calibrated with local hydrogeological inputs in Salar de Atacama, Chile. The social system of the ABM is defined and customozied based on empirical studies to reflect three major stressors: drought stress, population stress, and mining stress. The model reports evolution of groundwater changes and associated social stress dynamics within the modeled time frame.
Peer reviewed Industrial Symbiosis Network implementation ABM
Igor Nikolic Kasper Pieter Hendrik Lange Gijsbert Korevaar Paulien Herder | Published Tuesday, December 01, 2020 | Last modified Wednesday, June 16, 2021The purpose of the model is to explore the influence of actor behaviour, combined with environment and business model design, on the survival rates of Industrial Symbiosis Networks (ISN), and the cash flows of the agents. We define an ISN to be robust, when it is able to run for 10 years, without falling apart due to leaving agents.
The model simulates the implementation of local waste exchange collaborations for compost production, through the ISN implementation stages of awareness, planning, negotiation, implementation, and evaluation.
One central firm plays the role of waste processor in a local composting initiative. This firm negotiates with other firms to become a supplier of their organic residual streams. The waste suppliers in the model can decide to join the initiative, or to have the waste brought to the external waste incinerator. The focal point of the model are the company-level interactions during the implementation or ending of synergies.
…
Peer reviewed AUTOMATION-INDUCED RESHORING: An Agent-based Model of the German Manufacturing Industry
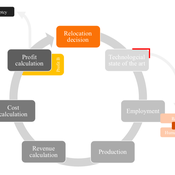
Laura Merz | Published Friday, November 20, 2020The agent-based perspective allows insights on how behaviour of firms, guided by simple economic rules on the micro-level, is dynamically influenced by a complex environment in regard to the assumed relocation, decision-making hypotheses. Testing various variables sensitive to initial conditions, increased environmental regulations targeting global trade and upward shifting wage levels in formerly offshore production locations have shown to be driving and inhibiting mechanisms of this socio-technical system. The dynamic demonstrates a shift from predominantly cited economic reasoning for relocation strategies towards sustainability aspects, pressingly changing these realities on an environmental and social dimension. The popular debate is driven by increased environmental awareness and the proclaimed fear of robots killing jobs. In view of reshoring shaping the political agenda, interest in the phenomenon has recently been fuelled by the rise of populism and protectionism.
Classrooms; teachers, students and learning
petertymms | Published Wednesday, October 07, 2020This a phenomenon-based model plan. Classroom in school are places when students are supposed to learn and the most often do. But things can go awry, the students can play up and that can result in an unruly class and learning can suffer. This model aims to look at how much students learn according to how good the teacher is a classroom control and how good he or she is at teaching per se.
Opinion dynamics and collective risk perception: An ABM model of institutional and media communication about disasters - Code and Datasets
danielevilone | Published Tuesday, October 06, 2020The O.R.E. (Opinions on Risky Events) model describes how a population of interacting individuals process information about a risk of natural catastrophe. The institutional information gives the official evaluation of the risk; the agents receive this communication, process it and also speak to each other processing further the information. The description of the algorithm (as it appears also in the paper) can be found in the attached file OREmodel_description.pdf.
The code (ORE_model.c), written in C, is commented. Also the datasets (inputFACEBOOK.txt and inputEMAILs.txt) of the real networks utilized with this model are available.
For any questions/requests, please write me at daniele.vilone@gmail.com
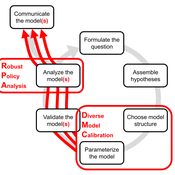
DMC-RPA: Diverse Model Calibration for Robust Policy Analysis (applied to an ABM of smallholder farmer resilience)
Tim Williams | Published Sunday, August 30, 2020This repository contains: (1) a model calibration procedure that identifies a set of diverse, plausible models; and (2) an ABM of smallholder agriculture, which is used as a case study application for the calibration method. By identifying a set of diverse models, the calibration method attends to the issue of “equifinality” prevalent in complex systems, which is a situation where multiple plausible process descriptions exist for a single outcome.
Peer reviewed DogPopDy: ABM for ABC planning
Aniruddha Belsare Abi Vanak | Published Saturday, August 01, 2020An agent-based model designed as a tool to assess and plan free-ranging dog population management programs that implement Animal Birth Control (ABC). The time, effort, financial resources and conditions needed to successfully control dog populations and achieve rabies control can be determined by performing virtual experiments using DogPopDy.
Peer reviewed Vigilant sharing in a small-scale society
Marcos Pinheiro | Published Wednesday, July 22, 2020 | Last modified Wednesday, July 29, 2020The model explores food distribution patterns that emerge in a small-scale non-agricultural group when sharing individuals engage in intentional consumption leveling with a given probability.
Displaying 10 of 202 results ABM clear search