About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 1122 results for "A Flache" clear search
This is an agent-based model that simulates the structural evolution in food supply chain.
Endogenous Corruption as a Cellular Automaton
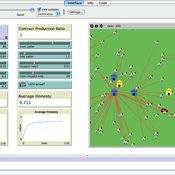
Warren Vierheller | Published Wednesday, June 27, 2018The model explores how corruption may spread endogenously within a closed society by depicting the behavior within a cellular automaton context (CA) between bureaucrats and citizens. Within the model, corruption is characterized as a behavior product dependent upon an individual’s personal disposition towards honesty, rational decisionmaking processes, and neighbors’ behavior.
HCAM: A Hybrid Climate Assessment Model
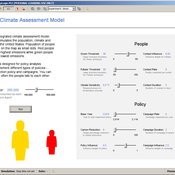
Peer-Olaf Siebers | Published Wednesday, November 06, 2019This model is part of a JASSS article that introduce a conceptual framework for developing hybrid (system dynamics and agent-based) integrated assessment models, which focus on examining the human impacts on climate change. This novel modelling approach allows to reuse existing rigid, but well-established integrated assessment models, and adds more flexibility by replacing aggregate stocks with a community of vibrant interacting entities. The model provides a proof-of-concept of the application of this conceptual framework in form of an illustrative example. taking the settings of the US. It is solely created for the purpose of demonstrating our hybrid modelling approach; we do not claim that it has predictive powers.
A Balance Model of Opinion Hyperpolarization
Simon Schweighofer Frank Schweitzer David Garcia Simon Schweighofer | Published Tuesday, December 17, 2019 | Last modified Tuesday, December 17, 2019Contains python3 code to replicate the opinion dynamics model from our (so far unpublished) JASSS sumbission “A Balance Model of Opinion Hyperpolarization”. The main function is run_model(), which returns a dictionary object containing various outcome metrics.
FlowLogo for a real case study
Vahid Aghaie | Published Monday, May 18, 2020Juan Castilla-Rho et al. (2015) developed a platform, named FLowLogo, which integrates a 2D, finite-difference solution of the governing equations of groundwater flow with agent-based simulation. We used this model for Rafsanjan Aquifer, which is located in an arid region in Iran. To use FLowLogo for a real case study, one needs to add GIS shapefiles of boundary conditions and modify the code written in NetLogo a little bit. The FlowLogo model used in our research is presented here.
FeedUS - A global food trade model
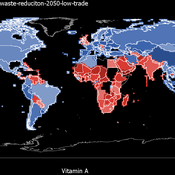
Jiaqi Ge | Published Thursday, February 25, 2021 | Last modified Friday, February 26, 2021The purpose of the model is to study the impact of global food trade on food and nutrition security in countries around the world. It will incorporate three main aspects of trade between countries, including a country’s wealth, geographic location, and its trade relationships with other countries (past and ongoing), and can be used to study food and nutrition security across countries in various scenarios, such as climate change, sustainable intensification, waste reduction and dietary change.
Forager mobility and interaction
L S Premo | Published Thursday, January 10, 2013 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is a relatively simple foraging-radius model, as described first by Robert Kelly, that allows one to quantify the effect of increased logistical mobility (as represented by increased effective foraging radius, r_e) on the likelihood that 2 randomly placed central place foragers will encounter one another within 5000 time steps.
Toward Market Structure as a Complex System: A Web Based Simulation Assignment Implemented in Netlogo
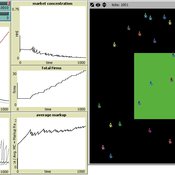
Timothy Kochanski | Published Monday, February 14, 2011 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This is the model for a paper that is based on a simulation model, programmed in Netlogo, that demonstrates changes in market structure that occur as marginal costs, demand, and barriers to entry change. Students predict and observe market structure changes in terms of number of firms, market concentration, market price and quantity, and average marginal costs, profits, and markups across the market as firms innovate. By adjusting the demand growth and barriers to entry, students can […]
Leviathan group model and its approximation
Thibaut Roubin Guillaume Deffuant | Published Tuesday, July 26, 2022The model is based on the influence function of the Leviathan model (Deffuant, Carletti, Huet 2013 and Huet and Deffuant 2017) with the addition of group idenetity. We aim at better explaining some patterns generated by this model, using a derived mathematical approximation of the evolution of the opinions averaged.
We consider agents having an opinion/esteem about each other and about themselves. During dyadic meetings, agents change their respective opinion about each other, and possibly about other agents they gossip about, with a noisy perception of the opinions of their interlocutor. Highly valued agents are more influential in such encounters. Moreover, each agent belongs to a single group and the opinions within the group are attracted to their average.
We show that a group hierarchy can emerges from this model, and that the inequality of reputations among groups have a negative effect on the opinions about the groups of low status. The mathematical analysis of the opinion dynamic shows that the lower the status of the group, the more detrimental the interactions with the agents of other groups are for the opinions about this group, especially when gossip is activated. However, the interactions between agents of the same group tend to have a positive effect on the opinions about this group.
Comparing agent-based models on experimental data of irrigation games
Marco Janssen Jacopo A. Baggio | Published Tuesday, July 02, 2013 | Last modified Wednesday, July 03, 2013Comparing 7 alternative models of human behavior and assess their performance on a high resolution dataset based on individual behavior performance in laboratory experiments.
Displaying 10 of 1122 results for "A Flache" clear search