About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 7 of 97 results for "Kam L Yeung" clear search
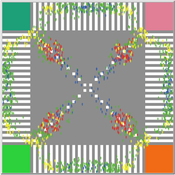
Pedestrian Scramble
Sho Takami Rami Lake Dara Vancea | Published Tuesday, November 30, 2021 | Last modified Tuesday, June 10, 2025This is a model intended to demonstrate the function of scramble crossings and a more efficient flow of pedestrian traffic with the presence of diagonal crosswalks.
JLootBox: An Agent-Based Model of Social Influence and Gambling in Online Video Games
Lila Zayed | Published Friday, May 06, 2022This model aims to explore how gambling-like behavior can emerge in loot box spending within gaming communities. A loot box is a purchasable mystery box that randomly awards the player a series of in-game items. Since the contents of the box are largely up to chance, many players can fall into a compulsion loop of purchasing, as the fear of missing out and belief in the gambler’s fallacy allow one to rationalize repeated purchases, especially when one compares their own luck to others. To simulate this behavior, this model generates players in different network structures to observe how factors such as network connectivity, a player’s internal decision making strategy, or even common manipulations games use these days may influence a player’s transactions.
Schelling Model of the City of Salzburg
Andreas Schlagbauer | Published Monday, December 05, 2022The purpose of the model is to better understand, how different factors for human residential choices affect the city’s segregation pattern. Therefore, a Schelling (1971) model was extended to include ethnicity, income, and affordability and applied to the city of Salzburg. So far, only a few studies have tried to explore the effect of multiple factors on the residential pattern (Sahasranaman & Jensen, 2016, 2018; Yin, 2009). Thereby, models using multiple factors can produce more realistic results (Benenson et al., 2002). This model and the corresponding thesis aim to fill that gap.
This model extends the original Artifical Anasazi (AA) model to include individual agents, who vary in age and sex, and are aggregated into households. This allows more realistic simulations of population dynamics within the Long House Valley of Arizona from AD 800 to 1350 than are possible in the original model. The parts of this model that are directly derived from the AA model are based on Janssen’s 1999 Netlogo implementation of the model; the code for all extensions and adaptations in the model described here (the Artificial Long House Valley (ALHV) model) have been written by the authors. The AA model included only ideal and homogeneous “individuals” who do not participate in the population processes (e.g., birth and death)–these processes were assumed to act on entire households only. The ALHV model incorporates actual individual agents and all demographic processes affect these individuals. Individuals are aggregated into households that participate in annual agricultural and demographic cycles. Thus, the ALHV model is a combination of individual processes (birth and death) and household-level processes (e.g., finding suitable agriculture plots).
As is the case for the AA model, the ALHV model makes use of detailed archaeological and paleoenvironmental data from the Long House Valley and the adjacent areas in Arizona. It also uses the same methods as the original model (from Janssen’s Netlogo implementation) to estimate annual maize productivity of various agricultural zones within the valley. These estimates are used to determine suitable locations for households and farms during each year of the simulation.
Peer reviewed E³-MAN. An Institutionally-guided multi-agent. Model for fair and efficient negotiation.
José luis bustelo | Published Monday, September 01, 2025Negotiation plays a fundamental role in shaping human societies, underpinning conflict resolution, institutional design, and economic coordination. This article introduces E³-MAN, a novel multi-agent model for negotiation that integrates individual utility maximization with fairness and institutional legitimacy. Unlike classical approaches grounded solely in game theory, our model incorporates Bayesian opponent modeling, transfer learning from past negotiation domains, and fallback institutional rules to resolve deadlocks. Agents interact in dynamic environments characterized by strategic heterogeneity and asymmetric information, negotiating over multidimensional issues under time constraints. Through extensive simulation experiments, we compare E³-MAN against the Nash bargaining solution and equal-split baselines using key performance metrics: utilitarian efficiency, Nash social welfare, Jain fairness index, Gini coefficient, and institutional compliance. Results show that E³-MAN achieves near-optimal efficiency while significantly improving distributive equity and agreement stability. A legal application simulating multilateral labor arbitration demonstrates that institutional default rules foster more balanced outcomes and increase negotiation success rates from 58% to 98%. By combining computational intelligence with normative constraints, this work contributes to the growing field of socially aware autonomous agents. It offers a virtual laboratory for exploring how simple institutional interventions can enhance justice, cooperation, and robustness in complex socio-legal systems.
MedLanD Modeling Laboratory
C Michael Barton Sean Bergin Isaac Ullah Gary Mayer Hessam Sarjoughian Helena Mitasova | Published Friday, May 08, 2015 | Last modified Thursday, December 14, 2017The MML is a hybrid modeling environment that couples an agent-based model of small-holder agropastoral households and a cellular landscape evolution model that simulates changes in erosion/deposition, soils, and vegetation.
Artificial Long House Valley-Black Mesa
Lisa Sattenspiel Amy Warren | Published Thursday, March 19, 2020This model is an extension of the Artificial Long House Valley (ALHV) model developed by the authors (Swedlund et al. 2016; Warren and Sattenspiel 2020). The ALHV model simulates the population dynamics of individuals within the Long House Valley of Arizona from AD 800 to 1350. Individuals are aggregated into households that participate in annual agricultural and demographic cycles. The present version of the model incorporates features of the ALHV model including realistic age-specific fertility and mortality and, in addition, it adds the Black Mesa environment and population, as well as additional methods to allow migration between the two regions.
As is the case for previous versions of the ALHV model as well as the Artificial Anasazi (AA) model from which the ALHV model was derived (Axtell et al. 2002; Janssen 2009), this version makes use of detailed archaeological and paleoenvironmental data from the Long House Valley and the adjacent areas in Arizona. It also uses the same methods as the original AA model to estimate annual maize productivity of various agricultural zones within the Long House Valley. A new environment and associated methods have been developed for Black Mesa. Productivity estimates from both regions are used to determine suitable locations for households and farms during each year of the simulation.
Displaying 7 of 97 results for "Kam L Yeung" clear search