About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 134 results for "Abraham Mawere Ndlovu" clear search
Peer reviewed Modelling Agricultural Innovations as a Social-Ecological Phenomenon
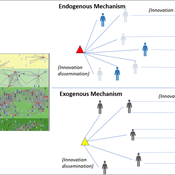
Maja Schlüter Udita Sanga | Published Thursday, November 17, 2022The goal of the AG-Innovation agent-based model is to explore and compare the effects of two alternative mechanisms of innovation development and diffusion (exogenous, linear and endogenous, non-linear) on emergent properties of food and income distribution and adoption rates of different innovations. The model also assesses the range of conditions under which these two alternative mechanisms would be effective in improving food security and income inequality outcomes. Our modelling questions were: i) How do cross-scalar social-ecological interactions within agricultural innovation systems affect system outcomes of food security and income inequality? ii) Do foreign aid-driven exogenous innovation perpetuate income inequality and food insecurity and if so, under which conditions? iii) Do community-driven endogenous innovations improve food security and income inequality and if so, under which conditions? The Ag-Innovation model is intended to serve as a thinking tool for for the development and testing of hypotheses, generating an understanding of the behavior of agricultural innovation systems, and identifying conditions under which alternated innovation mechanisms would improve food security and income inequality outcomes.
Agent-Based Model of Transhumant Decision-Making Processes in Senegal
Cheick Amed Diloma Gabriel TRAORE Etienne DELAY Alassane Bah Djibril Diop | Published Wednesday, July 03, 2024Sahelian transhumance is a type of socio-economic and environmental pastoral mobility. It involves the movement of herds from their terroir of origin (i.e., their original pastures) to one or more host terroirs, followed by a return to the terroir of origin. According to certain pastoralists, the mobility of herds is planned to prevent environmental degradation, given the continuous dependence of these herds on their environment. However, these herds emit Greenhouse Gases (GHGs) in the spaces they traverse. Given that GHGs contribute to global warming, our long-term objective is to quantify the GHGs emitted by Sahelian herds. The determination of these herds’ GHG emissions requires: (1) the artificial replication of the transhumance, and (2) precise knowledge of the space used during their transhumance.
This article presents the design of an artificial replication of the transhumance through an agent-based model named MSTRANS. MSTRANS determines the space used by transhumant herds, based on the decision-making process of Sahelian transhumants.
MSTRANS integrates a constrained multi-objective optimization problem and algorithms into an agent-based model. The constrained multi-objective optimization problem encapsulates the rationality and adaptability of pastoral strategies. Interactions between a transhumant and its socio-economic network are modeled using algorithms, diffusion processes, and within the multi-objective optimization problem. The dynamics of pastoral resources are formalized at various spatio-temporal scales using equations that are integrated into the algorithms.
The results of MSTRANS are validated using GPS data collected from transhumant herds in Senegal. MSTRANS results highlight the relevance of integrated models and constrained multi-objective optimization for modeling and monitoring the movements of transhumant herds in the Sahel. Now specialists in calculating greenhouse gas emissions have a reproducible and reusable tool for determining the space occupied by transhumant herds in a Sahelian country. In addition, decision-makers, pastoralists, veterinarians and traders have a reproducible and reusable tool to help them make environmental and socio-economic decisions.
Peer reviewed Torsten Hägerstrand’s Spatial Innovation Diffusion Model
Sean Bergin | Published Friday, September 14, 2012 | Last modified Saturday, April 27, 2013This model is a replication of Torsten Hägerstrand’s 1965 model–one of the earliest known calibrated and validated simulations with implicit “agent based” methodology.
Heterogeneity of preferences and the dynamics of voluntary contributions to public goods
Engi Amin Amal Soliman Mohamed Abouelela | Published Thursday, August 18, 2016 | Last modified Thursday, January 25, 2018This model simulates the heterogeneity of preferences in a PG game and how the interaction between them affects the dynamics of voluntary contributions. Model is based on the results of a human-based experiment.
DiDIY Factory
Ruth Meyer | Published Tuesday, February 20, 2018The DiDIY-Factory model is a model of an abstract factory. Its purpose is to investigate the impact Digital Do-It-Yourself (DiDIY) could have on the domain of work and organisation.
DiDIY can be defined as the set of all manufacturing activities (and mindsets) that are made possible by digital technologies. The availability and ease of use of digital technologies together with easily accessible shared knowledge may allow anyone to carry out activities that were previously only performed by experts and professionals. In the context of work and organisations, the DiDIY effect shakes organisational roles by such disintermediation of experts. It allows workers to overcome the traditionally strict organisational hierarchies by having direct access to relevant information, e.g. the status of machines via real-time information systems implemented in the factory.
A simulation model of this general scenario needs to represent a more or less abstract manufacturing firm with supervisors, workers, machines and tasks to be performed. Experiments with such a model can then be run to investigate the organisational structure –- changing from a strict hierarchy to a self-organised, seemingly anarchic organisation.
Roman Amphora reuse
Tom Brughmans | Published Wednesday, August 07, 2019 | Last modified Wednesday, March 15, 2023UPDATE in V1.1.0: missing input data files added; relative paths to input data files changed to “../data/FILENAME”
A model that allows for representing key theories of Roman amphora reuse, to explore the differences in the distribution of amphorae, re-used amphorae and their contents.
This model generates simulated distributions of prime-use amphorae, primeuse contents (e.g. olive oil) and reused amphorae. These simulated distributions will differ between experiments depending on the experiment’s variable settings representing the tested theory: variations in the probability of reuse, the supply volume, the probability of reuse at ports. What we are interested in teasing out is what the effect is of each theory on the simulated amphora distributions.
…
Peer reviewed Minding Norms in an Epidemic Does Matter
Klaus G. Troitzsch | Published Saturday, February 27, 2021 | Last modified Monday, September 13, 2021This paper tries to shed some light on the mutual influence of citizen behaviour and the spread of a virus in an epidemic. While the spread of a virus from infectious to susceptible persons and the outbreak of an infection leading to more or less severe illness and, finally, to recovery and immunity or death has been modelled with different kinds of models in the past, the influence of certain behaviours to keep the epidemic low and to follow recommendations of others to apply these behaviours has rarely been modelled. The model introduced here uses a theory of the effect of norm invocations among persons to find out the effect of spreading norms interacts with the progress of an epidemic. Results show that norm invocations matter. The model replicates the histories of the COVID-19 epidemic in various region, including “second waves” (but only until the end of 2021 as afterwards the official statistics ceased to be reliable as many infected persons did not report their positive test results after countermeasures were relieved), and shows that the calculation of the reproduction numbers from current reported infections usually overestimates the “real” but in practice unobservable reproduction number.
The Friendship Field
Eva Timmer Chrisja van de Kieft | Published Thursday, May 26, 2022 | Last modified Tuesday, August 30, 2022The Friendship Field model aims at modelling friendship formation based on three factors: Extraversion, Resemblance and Status, where social interaction is motivated by the Social Battery. Social Battery is one’s energy and motivation to engage in social contact. Since social contact is crucial for friendship formation, the model included Social Battery to affect social interactions. To our best knowledge, Social Battery is a yet unintroduced concept in research while it is a dynamic factor influencing the social interaction besides one’s characteristics. Extraverts’ Social Batteries charge while interacting and exhaust while being alone. Introverts’ Social Batteries charge while being alone and exhaust while interacting. The aim of the model is to illustrate the concept of Social Battery. Moreover, the Friendship Field shows patterns regarding Extraversion, Resemblance and Status including the mere-exposure effect and friendship by similarity. For the implementation of Status, Kemper’s status-power theory is used. The concept of Social Battery is also linked to Kemper’s theory on the organism as reference group. By running the model for a year (3 interactions moments per day), the friendship dynamics over time can be studied.
We presented the model at the Social Simulation Conference 2022.
Agent based modeling of the effects of carbon payments and forest owner cooperatives on carbon storage and revenue in Pacific Northwest forestlands.
Dan Brown Pranab Roy Chowdhury | Published Tuesday, May 09, 2023The Olympic Peninsula ABM works as a virtual laboratory to simulate the existing forestland management practices as followed by different forestland owner groups in the Olympic Peninsula, Washington, and explore how they could shape the future provisions of multifunctional ecosystem services such as Carbon storage and revenue generation under the business-as-usual scenario as well as by their adaptation to interventions. Forestlands are socio-ecological systems that interact with economic, socio-cultural, and policy systems. Two intervention scenarios were introduced in this model to simulate the adaptation of landowner behavior and test the efficacy of policy instruments in promoting sustainable forest practices and fostering Carbon storage and revenue generation. (1) A market-linked carbon offset scheme that pays the forestland owners a financial incentive in the form of a yearly carbon rent. (2) An institutional intervention policy that allows small forest owners (SFLO) to cooperate for increased market access and benefits under carbon rent scenario. The model incorporates the heterogeneous contexts within which the forestland owners operate and make their forest management decisions by parameterizing relevant agent attributes and contextualizing their unique decision-making processes.
Peer reviewed ABM for Social Cohesion and Wellbeing(ABMSCWB)
Taseer Salahuddin Hasan Vergil | Published Wednesday, June 25, 2025ABM model studying impact of social cohesion on wellbeing of a society. Ibn Khaldun’s cyclical theory of history is being used as the theoretical lens along with some other theories. Social cohesion is measured as TSC = (TVE + 2 * (TPI * TPL - TNI * TNL))/((TPI+TNI))
Where
TSC total-social-cohesion ; Variable for social cohesion
TPI total-positive-interactions ; Count of positive interactions
TNI total-negative-interactions ; Count of negative interactions
TPL total-positive-learning ; Count of positive learning outcomes
…
Displaying 10 of 134 results for "Abraham Mawere Ndlovu" clear search