About the CoMSES Model Library more info
Our mission is to help computational modelers develop, document, and share their computational models in accordance with community standards and good open science and software engineering practices. Model authors can publish their model source code in the Computational Model Library with narrative documentation as well as metadata that supports open science and emerging norms that facilitate software citation, computational reproducibility / frictionless reuse, and interoperability. Model authors can also request private peer review of their computational models. Models that pass peer review receive a DOI once published.
All users of models published in the library must cite model authors when they use and benefit from their code.
Please check out our model publishing tutorial and feel free to contact us if you have any questions or concerns about publishing your model(s) in the Computational Model Library.
We also maintain a curated database of over 7500 publications of agent-based and individual based models with detailed metadata on availability of code and bibliometric information on the landscape of ABM/IBM publications that we welcome you to explore.
Displaying 10 of 114 results interaction clear search
Exploring the aftermath of transition failures: An agent-based model
Gangmin Park Junmin Lee Jisoo Lee Keungoui Kim | Published Friday, March 06, 2026This computational model is an agent-based model (ABM) developed to investigate how repeated failures of emerging niches accumulate and influence the trajectory of socio-technical transitions. Built in AnyLogic 8.7.11, the model simulates the dynamic interactions between a dominant regime and sequential niche entrants within a two-dimensional practice space. It models alignment, movement, and competition based on technological maturity and market penetration. The model utilizes a reinforcing feedback structure linking consumer support, output, resource accumulation, and capacity development (Physical and Institutional Capacity). A complete model specification following the ODD+D (Overview, Design concepts, Details, and Decision) protocol is included in the documentation.
Selective Depolarization by Endogenous Migration in Attraction-Repulsion Opinion Dynamics (NetLogo)
poyeker | Published Tuesday, February 17, 2026This model implements a coupled opinion-mobility agent-based framework in NetLogo, extending Attraction-Repulsion Model (ARM) dynamics with endogenous migration in continuous 2D space.
Each agent has an opinion s in [0,1] and a spatial position (x,y). Agents interact locally within an interaction radius, with exposure-controlled interaction probability. Opinion updates follow ARM rules: attraction for small opinion distance and repulsion for large distance (tolerance threshold T). After social interaction, agents move according to a social-force mechanism that balances attraction to similar neighbors and avoidance of dissimilar neighbors, controlled by orientation bias (approaching goods vs leaving bads). The model also includes an optional exposure-mobility coupling setting.
Main outputs include polarization (P), spatial assortativity (Moran’s I), mixed-neighbor fraction (f_mix), and good-component count (N_g). The model is designed to study phase behavior of polarization and segregation under mobility and tolerance heterogeneity.
…
Netlogo model ` Effect of Network Homophily and Partisanship on Social Media to “Oil Spill” Polarizations’
takuya nagura | Published Saturday, September 13, 2025This model was utilized for the simulation in the paper titled Effect of Network Homophily and Partisanship on Social Media to “Oil Spill” Polarizations. It allows you to examine whether oil spill polarization occurs through people’s communication under various conditions.
・Choose the network construction conditions you’d like to examine from the “rewire-style” chooser box.
・Select the desired strength of partisanship from the “partisanlevel” chooser box. You can also set the strength manually in the code tab.
・You can set the number of dynamic topics using the “number-of-topics” slider.
・Use the “divers-of-opinion” slider to set the number of preference types for each dynamic topic.
…
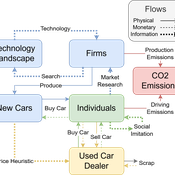
Driving in the wrong direction? A co-evolutionary model of electric vehicle adoption and innovation
Daniel Torren-Peraire | Published Friday, July 11, 2025Car-centric societies face substantial challenges in moving towards sustainable
mobility systems, with internal combustion engine vehicles remaining a major
source of emissions. Electric vehicles play a critical role in addressing this challenge, yet their diffusion depends on the interaction of consumer behaviour, firm
innovation, and policy incentives. This paper develops an agent-based model to
examine these dynamics, calibrated on the data for the state of California over
2001-2023. In the model, heterogeneous car users influenced by their social peers
…
Peer reviewed ABM for Social Cohesion and Wellbeing(ABMSCWB)
Taseer Salahuddin Hasan Vergil | Published Wednesday, June 25, 2025ABM model studying impact of social cohesion on wellbeing of a society. Ibn Khaldun’s cyclical theory of history is being used as the theoretical lens along with some other theories. Social cohesion is measured as TSC = (TVE + 2 * (TPI * TPL - TNI * TNL))/((TPI+TNI))
Where
TSC total-social-cohesion ; Variable for social cohesion
TPI total-positive-interactions ; Count of positive interactions
TNI total-negative-interactions ; Count of negative interactions
TPL total-positive-learning ; Count of positive learning outcomes
…
FilterBubbles_in_Carley1991
Benoît Desmarchelier | Published Wednesday, May 21, 2025The model is an extension of: Carley K. (1991) “A theory of group stability”, American Sociological Review, vol. 56, pp. 331-354.
The original model from Carley (1991) works as follows:
- Agents know or ignore a series of knowledge facts;
- At each time step, each agent i choose a partner j to interact with at random, with a probability of choice proportional to the degree of knowledge facts they have in common.
- Agents interact synchronously. As such, interaction happens only if the partnert j is not already busy interacting with someone else.
…
Peer reviewed Environmental stochasticity, resource heterogeneity, and the evolution of cooperation
Michaela Starkey Colin Lynch Terry Hunt Carl Lipo | Published Friday, March 14, 2025 | Last modified Wednesday, July 30, 2025The emergence of cooperation in human societies is often linked to environmental constraints, yet the specific conditions that promote cooperative behavior remain an open question. This study examines how resource unpredictability and spatial dispersion influence the evolution of cooperation using an agent-based model (ABM). Our simulations test the effects of rainfall variability and resource distribution on the survival of cooperative and non-cooperative strategies. The results show that cooperation is most likely to emerge when resources are patchy, widely spaced, and rainfall is unpredictable. In these environments, non-cooperators rapidly deplete local resources and face high mortality when forced to migrate between distant patches. In contrast, cooperators—who store and share resources—can better endure extended droughts and irregular resource availability. While rainfall stochasticity alone does not directly select for cooperation, its interaction with resource patchiness and spatial constraints creates conditions where cooperative strategies provide a survival advantage. These findings offer broader insights into how environmental uncertainty shapes social organization in resource-limited settings. By integrating ecological constraints into computational modeling, this study contributes to a deeper understanding of the conditions that drive cooperation across diverse human and animal systems.
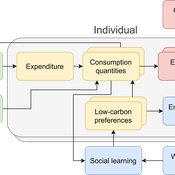
The cultural multiplier of climate policy
Daniel Torren-Peraire | Published Thursday, October 31, 2024For deep decarbonisation, the design of climate policy needs to account for consumption choices being influenced not only by pricing but also by social learning. This involves changes that pertain to the whole spectrum of consumption, possibly involving shifts in lifestyles. In this regard, it is crucial to consider not just short-term social learning processes but also slower, longer-term, cultural change. Against this background, we analyse the interaction between climate policy and cultural change, focusing on carbon taxation. We extend the notion of “social multiplier” of environmental policy derived in an earlier study to the context of multiple consumer needs while allowing for behavioural spillovers between these, giving rise to a “cultural multiplier”. We develop a model to assess how this cultural multiplier contributes to the effectiveness of carbon taxation. Our results show that the cultural multiplier stimulates greater low-carbon consumption compared to fixed preferences. The model results are of particular relevance for policy acceptance due to the cultural multiplier being most effective at low-carbon tax values, relative to a counter-case of short-term social interactions. Notably, at high carbon tax levels, the distinction between social and cultural multiplier effects diminishes, as the strong price signal drives even resistant individuals toward low-carbon consumption. By varying socio-economic conditions, such as substitutability between low- and high-carbon goods, social network structure, proximity of like-minded individuals and the richness of consumption lifestyles, the model provides insight into how cultural change can be leveraged to induce maximum effectiveness of climate policy.
Social Construction of Reality Agent-Based Model
Manuel Castañón-Puga E. Dante Suarez Loren Demerath | Published Saturday, June 29, 2024This model illustrates the processes underlying the social construction of reality through an agent-based genetic algorithm. By simulating the interactions of agents within a structured environment, we have demonstrated how shared information and popularity contribute to the formation of emergent social structures with diverse cultures. The model illustrates how agents balance environmentally valid information with socially reliable information. It also highlights how social interaction leads to the formation of stable, yet diverse, social groups.
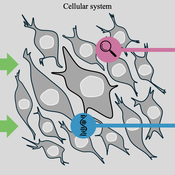
GenoScope
Kristin Crouse | Published Wednesday, May 29, 2024 | Last modified Wednesday, April 09, 2025GenoScope is a modular agent-based model designed to simulate how cells respond to environmental stressors or other treatment conditions across species. Genes, treatment conditions, and cell physiology outcomes are represented as interacting agents that influence each other’s behavior over time. Rather than imposing fixed interaction rules, GenoScope initializes with randomized regulatory logic and calibrates rule sets based on empirical data. Calibration is grounded in a common-garden experiment involving 16 mammalian species—including humans, dolphins, bats, and camels—exposed to varying levels of temperature, glucose, and oxygen. This comparative approach enables the identification of mechanisms by which animal cells achieve robustness under extreme environmental conditions.
Displaying 10 of 114 results interaction clear search