An Agent-Based Model of Indirect Minority Influence on Social Change (1.0.0)
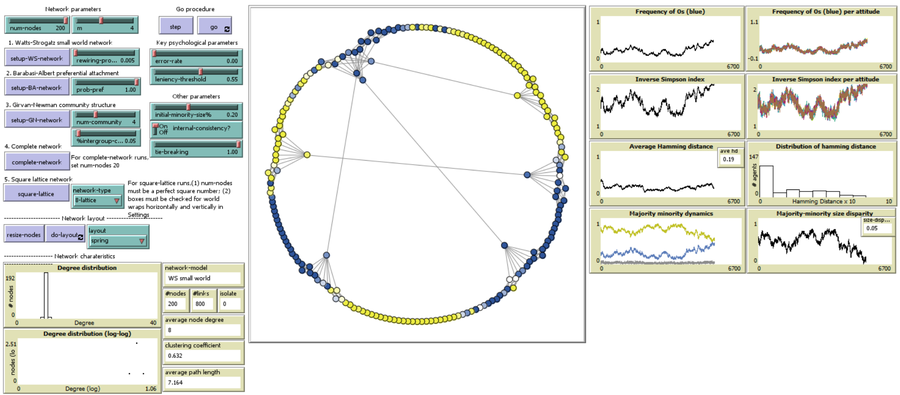
This model demonstrates how different psychological mechanisms and network structures generate various patterns of cultural dynamics including cultural diversity, polarization, and majority dominance, as explored by Jung, Bramson, Crano, Page, and Miller (2021). It focuses particularly on the psychological mechanisms of indirect minority influence, a concept introduced by Serge Moscovici (1976, 1980)’s genetic model of social influence, and validates how such influence can lead to social change.
Release Notes
Model for: Jung, J., Bramson, A., Crano, W. D., Page, S. E., & Miller, J. H. (2021). Cultural drift, indirect minority influence, network structure, and their impacts on cultural change and diversity. American Psychologist, 76, 1039–1053.
Associated Publications
Jung, J., Bramson, A., Crano, W. D., Page, S. E., & Miller, J. H. (2021). Cultural drift, indirect minority influence, network structure, and their impacts on cultural change and diversity. American Psychologist, 76(6), 1039–1053. https://doi.org/10.1037/amp0000844
An Agent-Based Model of Indirect Minority Influence on Social Change 1.0.0
Submitted by
Jiin Jung
Published Feb 05, 2025
Last modified Feb 05, 2025
This model demonstrates how different psychological mechanisms and network structures generate various patterns of cultural dynamics including cultural diversity, polarization, and majority dominance, as explored by Jung, Bramson, Crano, Page, and Miller (2021). It focuses particularly on the psychological mechanisms of indirect minority influence, a concept introduced by Serge Moscovici (1976, 1980)’s genetic model of social influence, and validates how such influence can lead to social change.
Release Notes
Model for: Jung, J., Bramson, A., Crano, W. D., Page, S. E., & Miller, J. H. (2021). Cultural drift, indirect minority influence, network structure, and their impacts on cultural change and diversity. American Psychologist, 76, 1039–1053.