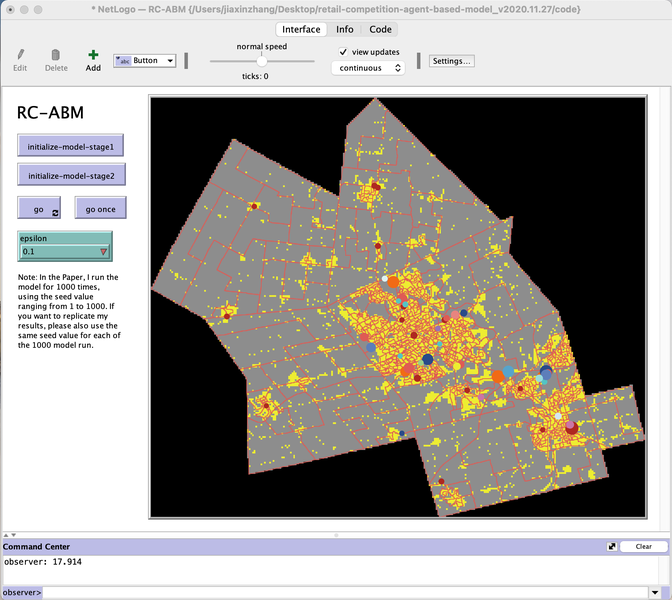
Retail Competition Agent-based Model (1.0.0)
The Retail Competition Agent-based Model (RC-ABM) is designed to simulate the retail competition system in the Region of Waterloo, Ontario, Canada, which which explicitly represents store competition behaviour. Through the RC-ABM, we aim to answer 4 research questions: 1) What is the level of correspondence between market share and revenue acquisition for an agent-based approach compared to a traditional location-allocation-based approach? 2) To what degree can the observed store spatial pattern be reproduced by competition? 3) To what degree are their path dependent patterns of retail success? 4) What is the relationship between retail survival and the endogenous geographic characteristics of stores and consumer expenditures?
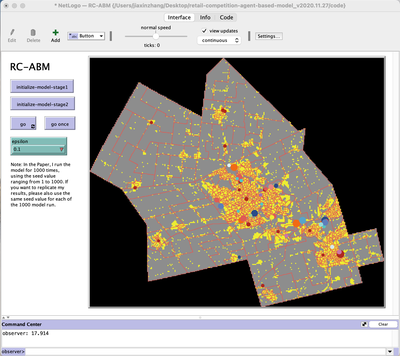
Release Notes
This model, entitled “Retail Competition Agent-based Model (RC-ABM),” is designed to simulate the home-improvement retail system in the Region of Waterloo, Ontario, Canada. By emphasizing the retail competition behaviours, the RC-ABM aims to answer four research questions: 1) What is the level of correspondence between market share and revenue acquisition for an agent-based approach compared to a traditional location-allocation-based approach? 2) To what degree can competition reproduce the observed store spatial pattern? 3) To what degree are their path-dependent patterns of retail success? 4) What is the relationship between retail survival and the endogenous geographic characteristics of stores and consumer expenditures? Inspired by ecological Niche theory and the idea of Many-Model thinking, we analogize the retail store agent as a species and consumer expenditures as environmental resources, whereby stores compete with each other for revenue derived from consumer expenditures. Moreover, the model’s landscape and most agent geographic characteristics are established based on the realistic GIS vector data. Note: This is the first version of RC-ABM.
Associated Publications
Zhang, J., 2021. Is competition sufficient to drive observed retail location and revenue patterns? An agent-based case study (Master’s thesis, University of Waterloo).
Retail Competition Agent-based Model 1.0.0
Submitted by
Jiaxin Zhang
Published Nov 10, 2021
Last modified Nov 10, 2021
The Retail Competition Agent-based Model (RC-ABM) is designed to simulate the retail competition system in the Region of Waterloo, Ontario, Canada, which which explicitly represents store competition behaviour. Through the RC-ABM, we aim to answer 4 research questions: 1) What is the level of correspondence between market share and revenue acquisition for an agent-based approach compared to a traditional location-allocation-based approach? 2) To what degree can the observed store spatial pattern be reproduced by competition? 3) To what degree are their path dependent patterns of retail success? 4) What is the relationship between retail survival and the endogenous geographic characteristics of stores and consumer expenditures?
Release Notes
This model, entitled “Retail Competition Agent-based Model (RC-ABM),” is designed to simulate the home-improvement retail system in the Region of Waterloo, Ontario, Canada. By emphasizing the retail competition behaviours, the RC-ABM aims to answer four research questions: 1) What is the level of correspondence between market share and revenue acquisition for an agent-based approach compared to a traditional location-allocation-based approach? 2) To what degree can competition reproduce the observed store spatial pattern? 3) To what degree are their path-dependent patterns of retail success? 4) What is the relationship between retail survival and the endogenous geographic characteristics of stores and consumer expenditures? Inspired by ecological Niche theory and the idea of Many-Model thinking, we analogize the retail store agent as a species and consumer expenditures as environmental resources, whereby stores compete with each other for revenue derived from consumer expenditures. Moreover, the model’s landscape and most agent geographic characteristics are established based on the realistic GIS vector data. Note: This is the first version of RC-ABM.